NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 4 – In the Earliest Cities (Social Science), contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 4. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand From In the Earliest Cities Class 6 History, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science helps to check the concept you have learned from detailed classroom sessions and the application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 6 |
| Subject | History (Social Science) |
| Chapter | Chapter 4 – In the Earliest Cities |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 4 – In the Earliest Cities
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 4 – In the Earliest Cities – NCERT Exercises
Question 1:-
How do archaeologists know that cloth was used in the Harappan civilisation?
Answer 1:-
- Archaeologists are certain that cloth was used in the Harappan civilisation as they have found evidences of actual pieces of cloth which were found attached to the lid of a silver vase and certain copper objects at Mohenjodaro,
- The archaeologists have also come across spindle whorls, which were made up of terracotta and faience and were used to spin thread.
Question 2:-
Match the columns:

Answer 2:-

Question 3:-
Why were metals, writing, the wheel, and the plough important for the Harappans?
Answer 3:-
Metals held importance for the Harappans as they were used for various purposes. Copper and bronze were used to make tools, weapons, ornaments and vessels. Gold and silver were used to make ornaments and vessels.
Writing was important for facilitating communication, maintenance of records and was used in preparation of seals.
These seals were in turn used for long-distance trade and as a mark of authority.
The wheel was important as it was used in carts which were engaged in ferrying people and goods. It was also used in pottery.
The wheels in the Harappan civilization were not spiked wheels. It can be ascertained from terracotta models of bullock carts.
The plough was important as it was used for tilling purposes i.e. to dig the earth for turning the soil and planting seeds. Evidence of ploughing can be seen from Kalibangan.
Question 4:-
Make a list of all the terracotta toys shown in the lesson. Which do you think children would have enjoyed playing with the most?
Answer 4:-
The terracotta toys shown in the lesson are:
- Toy carts
- Toy ploughs
- Various animal figures
In my opinion, children would have enjoyed playing with toy carts the most as it could be dragged and moved to the amusement of children.
Question 5:-
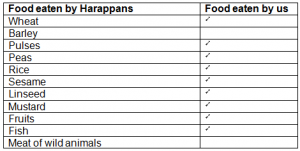
Make a list of what the Harappans ate, and put a tick mark against the things you eat today.
Answer 5:-
Question 6:-
Do you think that the life of farmers and herders who supplied food to the Harappan cities was different from that of the farmers and herders you read about in chapter 3? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer 6:-
The life of farmers and herders who supplied food to the Harappan cities was certainly different from that of the older farmers and herders (read about in the previous chapter).
Archaeologists suggest the Harappan farmers used some form of irrigation and did not rely on rainfall unlike the early farmers who had no access to any form of irrigation facilities.
Also, the earlier farmers did not access to wooden tools like the plough in order to undertake tilling of their land, like the farmers of Harappan civilization did.
The harappan farmers also had access to well-built granaries for their storage purposes, while the early farmers used clay pots and baskets for the same.
It is also important to understand that farmers in Harappa were not merely subsistence farmers like the earlier farmers
Question 7:-
Describe three important buildings in your city or village. Are they located in a special part of the settlement (e.g. the centre)? What are the activities that take place in these buildings?
Answer 7:-
Three important buildings in my city include:
- The Akshardham temple – place of worship – located on the outskirts of the city.
- The Cannaught Place series of buildings – place of trade and commerce – located in the centre of the city.
- Agrasen ki Baoli – place of tourism – located in the centre of the city.
Question 8:-
Are there any old buildings in your locality? Find out how old they are and who looks after them.
Answer 8:-
Near my locality, lies the ‘Purana Qila’ of Delhi which was built in 16th century CE. It is looked after by the ASI (Archaeological survey of India).
Topics Covered in Chapter 4 – In the Earliest Cities Class 6 History (Social Science)
- The story of Harappa
- What was special about these cities?
- Houses, drains and streets
- Life in the city
- New crafts in the city
- In search of raw materials
- Food for people in the cities
- A closer look — Harappan towns in Gujarat
- The mystery of the end
Important Terms Relevant for NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 4 – In the Earliest Cities :
City: A city refers to an organized place of inhabitation where people settle and buildings and bodies of institutional importance tend to emerge.
Citadel: The smaller but higher part lying in the west division of a city (which was divided into parts) has been referred to as citadel.
Ruler: Ruler refers to the person holding the supreme position of power managing all the affairs of a city.
Scribe: Scribes were people who knew how to write and helped prepare the seals. They wrote on others materials too which now cease to survive.
Crafts Person: Crafts person refer to skilled people who make things by hand (e.g. ornaments, pottery etc.)
Metal: A metal is a solid, hard and malleable material used in crafts in order to make vessels, ornaments, tools etc.
Seal: A seal refers to a piece of stamp attached as a guarantee of authenticity.
Specialist: A specialist is a person who is trained to do only one kind of work.
Raw Material: Raw materials are substances that are either found naturally (such as wood or metal ores) or produced by farmers or herders.
Plough: Plough refers to a tool used in digging of earth for turning the soil and planting seeds in farming.
Irrigation: Irrigation refers to the process of supplying water to the farmland and farmland crops.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History (Social Science)
- What, Where, How and When
- On the Trail of the Earliest People
- From Gathering to Growing Food
- In the Earliest Cities
- What Books and Burials Tell us
- Kingdoms, Kings and an Early Republic
- New Questions and Ideas
- Ashoka, The Emperor who Gave up War
- Vital Villages, Thriving Towns
- Traders, Kings and Pilgrims
- New Empires and Kingdoms
- Buildings, Paintings and Books