NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 1 What, Where, How, and When? (Social Science), contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 1. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand What, Where, How and When? Class 6 History, has been explained in a simple and easy-to-understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science helps to check the concept you have learned from detailed classroom sessions and the application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 6 |
| Subject | History (Social Science) |
| Chapter | Chapter 1 What, Where, How, and When? |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 1 – What, Where, How and When?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 1 – What, Where, How and When – NCERT Exercises
Question 1:-
Match the following:
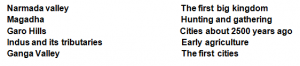
Answer 1: –

Question 2:-
List one major difference between manuscripts and inscriptions.
Answer 2:-
Manuscripts are historical records written by hand on soft surfaces such as palm leaves or on a ‘birch’, a specially prepared bark of a tree grown in the Himalayas. For example: The Vedas were manuscripts
Inscriptions, on the other hand, are historical records written on relatively harder surfaces such as metals or stones. For example, the edicts of Ashoka.
Question 3:-
Return to Rasheeda’s question. Can you think of some answers to it?
Answer 3:-
Rasheeda’s question focused on how one could know of the extreme past and what had happened so many years ago.
The answers to this could be that one gets to know of the events of the past through historical sources like the manuscripts, inscriptions and other historical writings or by studying physical evidences such as the tools and weapons of the past.
Question 4:-
Make a list of all the objects that archaeologists may find. Which of these could be made of stone?
Answer 4:-
The objects which archaeologists may find include:
- Tools
- Weapons
- Currency coins
- Ornaments
- Pots
- Pans
- Objects of clay
- Objects of bone (skulls)
- Sculptures
to name a few.
Out of these, the ones which could be made out of stone include:
- Tools
- Weapons
- Ornaments
- Sculptures
Question 5:-
Why do you think ordinary men and women did not generally keep records of what they did?
Answer 5:-
- In my opinion, ordinary men and women did not generally keep records of what they did as it was not easy to do so in the past.
- The royalty managed to hold records which were often carved on stones, but it was difficult for the ordinary men and women who couldn’t carry out carving on stones.
- They also weren’t usually involved in performing notable tasks like the royalty who recorded instances like battle victories.
- Also, most of these ordinary people were not literate enough to read and write in order to record their doings.
Question 6:-
Describe at least two ways in which you think the lives of kings would have been different from those of farmers?
Answer 6:-
The lives of kings were certainly different from that of the farmers:
- While the kings had the luxury to reside in forts and castles, the farmers had no such access to extravagant living and lived in smaller residences like huts and small homes.
- While the king’s primary responsibility was protection of all its subjects and kingdom, the farmer had the main responsibility of producing food grains.
Question 7:-
Find the word crafts persons on page 1. List at least five different crafts that you know about today. Are the crafts persons – (a) men (b) women (c) both men and women?
Answer 7:-
The word ‘crafts persons’ can be found in the second paragraph of the first page of the chapter in the fifth line, under the heading ‘What can we know about the past?’.
Different crafts practiced today include:
- Pottery – practiced by both men and women.
- Music – practiced by both men and women.
- Herding – practiced by both men and women.
- Tailoring – practiced by both men and women.
- Carpentry – practiced by men.
Question 8:-
What were the subjects on which books were written in the past? Which of these would you like to read?
Answer 8:-
Subjects on which books were written in the past included:
- Religion and Philosophy
- Science and medicine
- Travelogues
- Kingship
- Polity
- Poetry and Drama
The books on religion and philosophy would be interesting to read since they still hold somewhat relevance in today’s society.
Topics Covered in Chapter 1 – What, Where, How and When Class 6 History (Social Science)
- Finding out what happened
- What can we know about the past?
- Where did people live?
- Names of the land
- Finding out about the past
- One past or many?
- What do dates mean?
Important Terms Relevant for NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 1 – What, Where, How and When?:
Travelling: Travelling is the process of movement from one place to another, typically involving considerable distance.
Manuscript: Manuscripts refer to historical records written in Sanskrit, Prakrit and Tamil by hand long ago on soft surfaces like palm leaves or birches. It derives from the Latin word ‘manu’ meaning ‘hand’. They dealt with all kinds of subjects ranging from medicine and science, religious beliefs and practices, epics, poetries, plays and accounts of lives of royalty.
Inscription: Inscriptions refer to historical writings on relatively hard surfaces like metal and stone and the subjects included recording of activities done by men and women including the royalty (kings and queens), victorious battle records and orders of the monarch for people to see, read and obey.
Archaeology: Archaeology refers to the study of human history via excavation and analysis of historical artefacts and other historical physical remains. Those who study these are termed as ‘archaeologists’.
Historian: A historian is a scholar of history who is involved with studying the subject and producing scholarly synthesis of the same.
Source: Source refers to the place of origin or extraction.
Decipherment: Decipherment refers to the process of decoding the meaning of written texts, especially anciently written and obscure texts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History (Social Science)
- What, Where, How and When
- On the Trail of the Earliest People
- From Gathering to Growing Food
- In the Earliest Cities
- What Books and Burials Tell us
- Kingdoms, Kings and an Early Republic
- New Questions and Ideas
- Ashoka, The Emperor who Gave up War
- Vital Villages, Thriving Towns
- Traders, Kings and Pilgrims
- New Empires and Kingdoms
- Buildings, Paintings and Books