NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues, contains solutions to various questions in Exercises for Chapter 6. Tissues Class 9 NCERT Solutions have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 help to check the concept you have learned from detailed classroom sessions and the application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 9 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 6 – Tissues |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues Questions Question Answers
1. What is a tissue?
Answer.
A tissue is a group of similar or dissimilar cells combined together to perform a common function and have a common origin.
2. What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
Answer.
In multicellular organisms, different types of tissues perform different functions. So, tissues in multicellular organisms possess a definite division of labour.
Tissues class 9 Question Answers Page 74
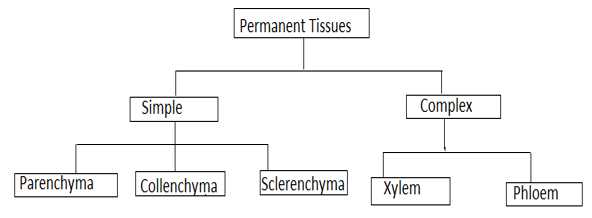
1. Name types of simple tissues.
Answer.
Three types of simple tissues are:
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
2. Where is apical meristem found?
Answer.
Apical meristem is found in the shoot apex and root apex.
3. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer.
Sclerenchymatous tissue
4. What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer.
The four constituents of phloem are:
- Sieve Tube
- Companion cell
- Phloem parenchyma
- Phloem fibres
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissue Question Answer Intext Questions: Page 78
1. Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer.
Muscular tissue
2. What does a neuron look like?
Answer.
A neuron consists of a cell body and various structures emerging from it. These structures include a long axon and fibrous short dendrites.
3. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer.
Features of cardiac muscles are:
- These are involuntary
- The cells are cylindrical, branched and uninucleated.
- Cardiac muscles show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout the life.
4. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer.
Areolar tissue are connective tissues that support internal organs and help in the repair of the tissue when required.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues – NCERT Exercises : Page 79
1. Define the term “tissue”.
Answer.
A tissue is a group of similar or dissimilar cells that perform a common function and have a common origin.
2. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer.
Xylem tissue is made up of 4 types of elements:
- Tracheids
- Vessels
- Xylem parenchyma
- Xylem fibres
3. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer.
| Simple Tissue | Complex Tissue |
| They are made up of one type of cells | They are made up of multiple types of cells |
| They are mostly similar in structure and perform a common function. | Different type of cells perform different functions. |
| Ex Prenchyma, Collenchyma | Ex. Xylem, Phloem |
4. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Answer.
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| Cell wall is primary | Cell wall is primary | Cell wall is secondary |
| Cell wall is thin made up of cellulose | Cell wall has localized thickening of cellulose. | Cell wall is uniformly thick and has thickening of lignin. |
5. What are the functions of stomata?
Answer.
The important functions of cellulose are:
- Exchange of gases with the atmosphere.
- Loss of water in the form of vapours (transpiration)
6. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Answer.
7. What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Answer.
Cardiac muscles contract and relax rhythmically throughout the life.
8. Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and location in the body.
Answer.
| Striated muscle | Unstriated muscle | Cardiac muscle |
| The cells are long, cylindrical, unbranched and multinucleate.
Striated muscles are present in our limbs and join the bones. |
The cells of unstriated muscles are long, pointed at ends and uninucleate.
These muscles are present in our alimentary canal, blood vessels, iris of eye, ureters and bronchi. |
The cells of cardiac muscle are cylindrical, branched and uninucleate.
Cardiac muscles are present in our heart. |
9. Draw a labelled diagram of neuron.
Answer
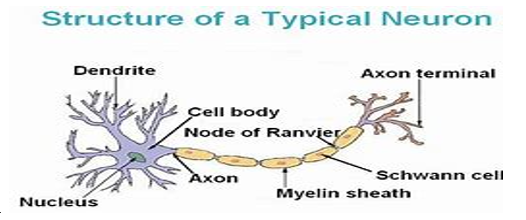
10. Name the following:
(1) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(2) Tissue that connect muscle to bone in humans.
(3) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(4) Tissue that store fat in our body.
(5) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(6) Tissue present in the brain.
Answer.
- Squamous epithelium
- Tendon
- Phloem
- Adipose tissue
- Blood
- Nervous tissue
11. Identify the type of tissue in the following: Skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer.
Skin- Epithelial tissue
Bark of tree- Cork
Bone- Connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubules- Cuboidal epithelium
Vascular bundle- Xylem and Phloem
12. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer.
Parenchyma is present in the cortex and pith of stem and roots. It is also present in mesophyll of leaves.
13. What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Answer.
Role of epidermis in plants is-
- It provides protection to internal organs
- It becomes thick and prevents loss of water in dry habitats
- Leaf epidermis has stomata and helps in gaseous exchange.
14. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer.
Cork cells are dead and do not have any inter-cellular spaces. The cell walls are coated with suberin. Due to these properties, cork acts as a protective tissue.
15. Complete the table:
Topics Covered in Tissues Class 9 Science
- Are Plants and Animals Made of Same Types of Tissues?
- Plant Tissues
- MERISTEMATIC TISSUE
- PERMANENT TISSUE
- Animal Tissues
- EPITHELIAL TISSUE
- CONNECTIVE TISSUE
- MUSCULAR TISSUE
- NERVOUS TISSUE