NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 5 – Judiciary (Social Science), contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 5. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Chapter 5 Judiciary Class 8 Civics, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 |
| Subject | Civics (Social Science) |
| Chapter | Chapter 5 – Judiciary |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 5 – Judiciary
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 5 – Judiciary – NCERT Exercises
Question 1:-
You read that one of the main functions of the judiciary is ‘upholding the law and Enforcing Fundamental Rights’. Why do you think an independent judiciary is necessary to carry out this important function?
Answer 1:-
As the upholder of the law and our Fundamental Rights, it is necessary for the judiciary to function as an independent body. It is crucial that the government or the legislature do not interfere in the work of the judiciary and do not influence its decisions. This independence allows courts to ensure that there is no misuse of power by the legislature or the executive as according to the principle of separation of powers and that justice is prevailed.
Question 2:-
Re-read the list of Fundamental Rights provided in Chapter 1. How do you think the Right to Constitutional Remedies connects to the idea of judicial review?
Answer 2:
The Right to Constitutional Remedies allows citizens to move to the courts if they feel that any of their Fundamental Rights have been violated by the State. Judicial Review is the power of the judiciary to check whether a decision is in synchronization with the principles of the Constitution or not. If a person believes that he/she has not been given justice because of a decision of the State, he/she can approach the courts. Now, the courts decide if the decision actually violates the Constitution. Thus, the Right to Constitutional Remedies under article 32 of the Indian Constitution is connected to the review power of the judiciary and can be rightly said as the heart and soul of the constitution
Question 3:-
In the following illustration, fill in each tier with the judgments given by the various courts in the Sudha Goel case. Check your responses with others in class.
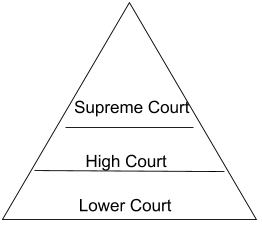
Answer 3:-
Lower Court – It convicted Sudha’s husband, his mother and his brother-in-law and sentenced them to death.
High Court – It concluded that Sudha died due to an accidental fire caused by the kerosene stove and her husband, his mother and his brother-in-law were declared not guilty.
Supreme Court – It found the husband and the mother-in-law guilty and they were sentenced to life imprisonment. The brother-in-law was acquitted due to lack of evidence against him.
Question 4:-
Keeping the Sudha Goel case in mind, tick the sentences that are true and correct the ones that are false.
(a) The accused took the case to the High Court because they were unhappy with the decision of the Trial Court.
(b) They went to the High Court after the Supreme Court had given its decision.
(c) If they do not like the Supreme Court verdict, the accused can go back again to the Trial Court.
Answer 4:-
(a) True.
(b) False. They went to the High Court after the Trial Court had given its decision.
(c) False. The decision of the Supreme Court is binding on all lower courts.
Question 5:-
Why do you think the introduction of Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in the 1980s is a significant step in ensuring access to justice for all?
Answer:-
Apparently, according to the rules and laws laid down by the constitution, all citizens of India can have access over the courts of the country. However in reality, the legal procedures are often very long drawn, expensive and require a lot of paperwork, making it difficult for the poor to actually approach the courts. To correct this situation, the Supreme Court in 1980’s devised a mechanism of Public Interest Litigation. It allowed any individual or organization to file a PIL or Public interest litigation on behalf of the aggrieved. It simplified the legal process and amplified access to justice. Even a letter or a telegram addressed to the courts could be treated as a PIL. It helped in rescuing bonded labourers, fight for the rights of the victims of Bhopal gas tragedy, in securing the release of prisoners in Bihar etc.
Thus, the introduction of PIL was significant in ensuring access to justice for all.
Question 6:-
Re-read excerpts from the judgment on the Olga Tellis vs Bombay Municipal Corporation case. Now write in your own words what the judges meant when they said that the Right to Livelihood was part of the Right to Life.
Answer 6:-
In the judgment on the Olga Tellis vs Bombay Municipal Corporation case, the judges recognized the Right to Livelihood as a part of the Right to Life. According to them life did not merely mean living life like an animal but he has more rights under article 21 of the Indian constitution.. No person can live a gracious life without the means of living. To deny a person the means of securing the necessities of life like food, shelter, clothing etc. would be equal to denying him life.
In the case mentioned above, the judges ruled that eviction of the petitioners from the slums would deprive them of their livelihood and would thus be deprivation of life under article 21 of the Indian constitution.
Question 7:-
Write a story around the theme, ‘Justice delayed is justice denied’.
Answer 7:-
This is a creative answer and students can modify it accordingly.
Justice is one such right of any citizen which he or she should receive at the earliest and without any further hazards. But often it is not the case and people have to wait for decades to receive the justice they are entitled to.
This is a story about a 13-year-old girl who was often harassed, and threatened by her physical education teacher to get herself engage in sexual activities with him.So after a long and tedious period of being victimized by this teacher she decides to let her parents know about it. Even though she was scared but gathered all her strength to tell the truth to her parents. But things dint go as she expected, as when her parents complained to the school authorities about the same the teacher was given a warning and left. And so out of rage, one day he started blackmailing her to fail her in her final exams if she did to abide herself to his wishes. She was scared and helpless and accepted the domination. And soon after she attempted suicide. Even though after her suicide inquiry began and after a long period of 10 years the charges against him were proved but surely justice was denied to this little girl as due to the delay she could not be saved. We can clearly say from this story that justice delayed is justice denied as had it been earlier that strict actions were taken against this teacher an innocent life could have been saved.
Question 8:-
Make sentences with each of the glossary words given on the next page.
Acquit, To Appeal, Compensation, Eviction, Violation.
Answer 8:-
- Acquit: Sanjay was acquitted by the high court because charges against him could not be proven.
- To Appeal: He went to the High Court to appeal against the rash decision of the District Court.
- Compensation: The government paid Rs.10,000 as compensation to the victim’s family.
- Eviction: The tenant was given an eviction notice because he did not pay his rent for the past 3 months.
- Violation: Her parents did not let her attend school which was a violation of her right to education..
Topics Covered in Judiciary Chapter 5 Civics (Social Science)
- What is the Role of the Judiciary?
- What is an Independent Judiciary?
- What is the Structure of Courts in India?
- What are the Different Branches of the Legal System?
- Does Everyone Have Access to the Courts?
Important Terms Relevant for NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 5 – Judiciary :
Acquit: When the court declares a person not guilty for a crime for which he/she was tried.
To Appeal: To approach a higher court to reconsider a judgment given by the lower court.
Compensation: The relief provided to someone to undo the wrong done to them or to make amends for an injury, loss or suffering.
Eviction: Displacing someone from a property with the help of a legal notice.
Violation: In this chapter, it refers to the infringement of one’s rights.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics
- Chapter 1 – The Indian Constitution
- Chapter 2 – Understanding Secularism
- Chapter 3 – Why do we need a Parliament?
- Chapter 4 – Understanding Laws
- Chapter 5 – Judiciary
- Chapter 6 – Understanding our Criminal Justice System
- Chapter 7 – Understanding Marginalisation
- Chapter 8 – Confronting Marginalisation
- Chapter 9 – Public Facilities
- Chapter 10 – Law and Social Justice