NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Control and Coordination, contains solutions to various questions in Exercises for Chapter 7. Control and Coordination Class 10 NCERT Solutions have been explained in a simple and easy-to-understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 help to check the concept you have learned from detailed classroom sessions and the application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 7 – Control and Coordination |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Control and Coordination
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Intext Questions
1. What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Answer:
| Reflex Actions | Walking |
|---|---|
| Involuntary action in response to stimuli. | Walking is a voluntary action that occurs under the control of the cerebellum of the brain. |
| Unconcious action mostly coordinated by the spinal cord | Controlled by brain and done on need. |
2. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer:
At the synapse, the electrical signals from the neuron are converted into chemical signals also called neurotransmitters and are passed to the next neuron where they convert back into electrical form.
3. Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer:
Cerebellum, a part of the hind brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body.
4. How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Answer:
The aromatic gas molecules are detected by the olfactory cells present in our nose. These olfactory receptors send a suitable electrical signal to the forebrain. These signals are interpreted and recognised by the brain as the smell of an agarbatti.
5. What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer:
The body senses a stimuli and as a result, a reflex action is generated by the spinal cord. The information about this action and its stimulus is also sent to the brain. The brain stores this information for future use and to recognise the stimuli that can be dangerous in order to avoid them in future.
Intext Questions – Page 122
1. What are plant hormones?
Answer:
Plant hormones are the organic substances that a plant needs to coordinate growth, develop and for giving appropriate responses to the environment. They are made at one location and are usually transported to the required locations. Some examples of plant hormones are cytokines, abscisic acid,etc.
2. How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Answer:
The differences between movement of leaves of a sensitive plant and movement of shoot towards light are:
| Movement of Sensitive Plant | Movement of shoot towards light |
|---|---|
| It occurs because of a sudden loss of water because of a stimulus by touch. | It occurs because of stimulus towards light and unequal growth of shoot. |
| It is a nastic movement. | It is a tropic movement. |
| Occurs instantly | It is a slow process. |
| It is not a growth movement, just a response to stimuli. | It is a growth movement. |
3. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer:
Auxins and Gibberlins are the plant hormones that promote growth. Auxins are found on tip of shoot and roots and help in elongation of shoot cells and also regulates growth. Gibberlins are responsible for stem elongation and germination of plants.
4. How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer:
The auxins promote the growth of a tendril around the support by growing the opposite side of the tip. The tips of the tendril have auxins. Auxins being sensitive towards touch, do not show as much growth on the side of the plant which is in contact with the support. The other side grows faster and the tendril bends towards the support. Then the process is repeated on this side, making the plant grow slowly around it.
5. Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer:
We can follow the below mentioned steps to demonstrate hydrotropism:
- Take a seedling in a vessel containing sand or soil.
- In the same vessel, add a porous pot and fill it with water.
- Let the seedling grow for a few days.
After a few days, we observe that the roots of the plant have grown towards the source of water and are curved and bent. This proves that roots are attracted towards water and are hydrotropic in nature.
We can observe the required setup in the given diagram.
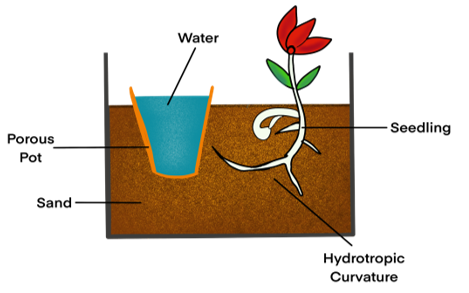
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Intext Questions – Page 125
1. How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer:
Chemical messengers known as hormones are responsible for the chemical coordination in animals. They are produced by the organs of the endocrine system, also known as glands. Each gland produces a specific hormone for a specific function. They contribute in growth, development and in general well being of animals. In humans, pituitary gland is the master gland that controls the functioning of almost all other glands.
2. Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer:
Iodine is important for the release of thyroxine. Thyroxine is a hormone produced in thyroid gland. It is important for a good metabolism and proper growth of the body. Deficiency of iodine can also cause a deficiency disease called goitre.
3. How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Answer:
Adrenaline is a hormone which is secreted when someone is frightened, excited or disturbed. It increases the breathing rate, makes the heart beat faster requiring extra oxygen, raise the blood pressure and allows extra glucose to enter the blood stream. These changes make our body ready for any emergency situation or any fight or flight situation.
4. Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer:
Insulin is a hormone that keeps blood sugar in check by converting extra glucose into glycogen. In diabetes, the production of insulin is either low or stops. Excess blood sugar can cause a number of problems and adversely affect many vital organs. To maintain the glucose level, injections of insulin are given to compensate it’s low production in the body.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – NCERT Exercise – Page 126
1. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin
Answer:
(d ) Cytokinin
2. The gap between two neurons is called a
(a) dendrite
(b) synapse
(c) axon
(d) impulse
Answer:
(b) synapse
3. The brain is responsible for
(a) thinking
(b) regulating the heart beat
(c) balancing the body
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
4. What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer:
The main receptors in our body are present on our sense organs such as eyes, nose, skin, etc. The function of these receptors is to collect information from our environment in the form of stimuli and send proper signals to the brain. The brain directs required actions based on these stimuli.
In situations where receptors do not work properly, brain is not able to detect and give proper response to a stimuli and no action is taken. This can lead to dangerous situations sometimes.
5. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Answer:
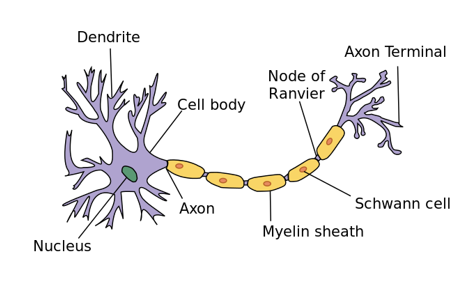
Neurons are long cells which are responsible for carrying signals from organs to the brain and from brain to the required organs. It has three major parts, dendrites, axon, and the cell body.
Dendrites are tendril like structures that detect information coming from sense organs or other neurons and send it to the cell body. Cell body is the place where the nucleus of the cell is present and it is also responsible for the growth and maintenance of the cell. The axons carry the signal and transfer it to the next cell.
Myelin sheath is a protective film wrapped around the axon. Two dendrites exchange information through synapse.
6. How does phototropism occur in plants?
Answer:
The directional movement or orientation of plant in response to light is called as phototropism. The plants cells that are away from light, in the dark have a chemical or hormone called auxin. Due to presence of auxin in higher quantity on the darker side, the growth of the cells present there is more rapid resulting in larger leaves and shoot. This results in the bending of the plant towards the light.
7. Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Answer:
The signals coming from brain as well as the ones going to the brain will get disrupted in case of spinal cord injury since, all the signals pass through spinal cord.
In such case, the reflex actions will be also affected as they originate from spinal cord itself.
8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Answer:
Chemical coordination occurs in plants through chemicals known as hormones. They are organic substances that a plant needs to coordinate growth, develop and for giving appropriate responses to the environment. They are made at one location and are usually transported to the required locations.
There are mainly two types of hormones, growth promoters like auxin and cytokinin or growth inhibitors like abscisic acid.
9. What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Answer:
A number of functions and movements go on in our body simultaneously. Some of these movements are voluntary and some are involuntary and continuous.
For an organism to survive and work properly, these actions must be properly controlled coordinated. For example, in humans, there are various types of movements like beating of heart, movement of food, voluntary motions like walking and talking and hormonal movements like secretion of hormones from their respective glands. If any of these movements get out of control or are not coordinated properly, they may lead to unhealthy and fatal conditions.
Similarly, such coordination can also be seen in other organisms such as plants. They require the correct amount of hormones for growth and photosynthesis. These hormones are controlled and thus enable a plant to thrive and grow in a healthy tree.
10. How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Answer:
| Involuntary Actions | Reflex Action |
|---|---|
| They occur automatically without any consciousness of an organism. | They occur as a result of certain stimuli or cues. |
| Are controlled by the mid-brain or medulla oblongata and are relative. | Are controlled by the spinal cord and are instantaneous as a response to certain stimuli. |
| Only involves smooth muscles. | Can occur in both glands and muscles. |
| Example: Beating of heart. | Example: Running away on seeing an insect. |
11. Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Answer:
| Nervous Mechanism | Hormonal Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Result of communication between the nervous system and the brain. | Made of an endocrine system that secretes hormones in the blood. |
| Electrical signals, not specific to their action. | Chemical with specific action |
| Short Response time | Long response time and slow response |
| The rapid flow of information | The flow of information is slow and timely as per requirement |
12. What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
Answer:
| Movement in sensitive plant | Movement in our legs |
|---|---|
| Involuntary action | Voluntary action. |
| No special tissues. | Dedicated nervous system |
| No Special movement | Have special muscles to aid in movement. |
Topics Covered in Control and Coordination Class 10 Science
- Animals-Nervous System
- What happens in Reflex Actions?
- Human Brain
- How are these Tissues protected?
- How does the Nervous Tissue cause Action?
- Coordination in Plants
- Immediate Response to Stimulus
- Movement Due to Growth
- Hormones in Animals
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Metals and Non metals
- Carbon and its Compounds
- Periodic Classification of Elements
- Life Processes
- Control and Coordination
- How Do Organisms Reproduce?
- Heredity and Evolution
- Light – Reflection and Refraction
- The Human Eye And Colorful World
- Electricity
- Magnetic Effects Of Electric Current
- Sources of Energy
- Our Environment
- Sustainable Management Of Natural Resources