NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 9 – Soil, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 9. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 9 – Soil, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 7 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 9 – Soil |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 9 – Soil
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 9- Soil– Solutions to Question 1 to Question 3
Tick the most suitable answer in questions 1 and 2.
Question 1:-
In addition to the rock particles, the soil contains
(i) air and water
(ii) water and plants
(iii) minerals, organic matter, air and water
(iv) water, air and plants
Answer 1:-
iii. Minerals, organic matter, air and water
This option completely describes the composition of soil. All the other options are incomplete.
Question 2:-
The water holding capacity is the highest in
(i) sandy soil
(ii) clayey soil
(iii) loamy soil
(iv) mixture of sand and loam
Answer 2:-
(ii)Clayey soil
Clayey soil has more number of fine particles than large particles therefore its water retaining capacity is more.
Question 3:-
Match the items in Column I with those in Column II:
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| A Home for living organisms | Large Particles |
| Upper Layer of the Soil | All kinds of Soil |
| Sandy Soil | Dark In Colour |
| Middle layer of the soil | Small particles and packed tight |
| Clayey Soil | Lesser amount of humus |
Answer 3:-
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| A Home for living organisms | All kinds of Soil |
| Upper Layer of the Soil | Dark in Colour |
| Sandy Soil | Large particles |
| Middle layer of the soil | Lesser amount of humus |
| Clayey Soil | Small particles and packed tight |
Question 4:-
Explain how soil is formed.
Answer 4:-
Soil is formed by the process of weathering. Weathering involves breaking down ofrocks by the forces of wind, water and climate. The rock, from which soil is produced determines its type.
Question 5:-
How is clayey soil useful for crops?
Answer 5:-
Clayey soil is composed of fine particles which are responsible for its good waterretention ability. It is also rich in humus and organic matter. Crop such as paddy are grown in clayey soil because they require a lot of water and clayey soil can hold large amount of water. Cereals such as wheat and gram also grow in clayey soil because they require good amount of humus and organic content.
Question 6:-
List the differences between clayey soil and sandy soil.
Answer 6:-
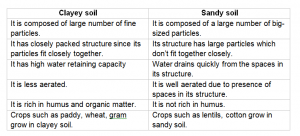
Question 7:-
Sketch the cross section of soil and label the various layers.
Answer 7:-
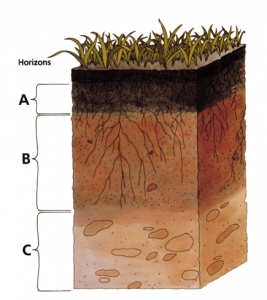
Question 8:-
Razia conducted an experiment in the field related to the rate of percolation.She observed that it took 40 min for 200 mL of water to percolate through the soil sample. Calculate the rate of percolation.
Answer 8:-
Given:Time taken by water to percolate= 40 min
Quantity of water taken= 200 mL
Formula:
Percolation rate= amount of water taken(mL)/ percolation time (min)
Calculation: Percolation rate= 200/40 = 5 mL/min
Question 9:-
Explain how soil pollution and soil erosion could be prevented.
Answer 9:-
Soil erosion can be prevented by planting trees. Soil erosion is the process in which the top layer of soil is removed by wind or water. The roots of plants and trees hold the soil and prevent it from being washed away by wind or water.
Soil pollution can be prevented by reducing the use of polythene. Soil pollution can lead to infertile soil and planting more and more trees will help it retain its fertility.
Question 10:-
Solve the following crossword puzzle with the clues given:
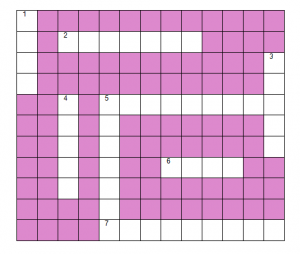 Across:
Across:
2. Plantation prevents it.
5. Use should be banned to avoid soil pollution.
6. Type of soil used for making pottery.
7. Living organism in the soil.
Down:
1. In desert soil erosion occurs through.
3. Clay and loam are suitable for cereals like.
4. This type of soil can hold very little water.
5. Collective name for layers of soil.
Answer 10 :-
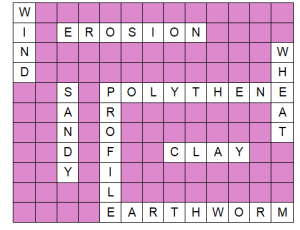
Topics Covered in Chapter 9 Soil Class 7 Science :-
- Soil teeming with life
- Soil profile
- Soil types
- Properties of soil
- Moisture in soil
- Absorption of water by soil
- Soil and crops
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Soil:-
Clayey: Clayey soil is a type of soil which is composed of a greater number of fine particles than large particles.
Humus: Humus is the dead material present in soil that decays and provides nutrients to the soil.
Loamy: Loamy soil is a type of soil in which the amount of fine and large particles is about the same.
Percolation: The process in which water flows down into soil by passing through its various layers is called percolation.
Moisture: Traces of water in the form of vapour or condensed form in small quantities is called moisture.
Sandy: Sandy soil is a type of soil which contains a greater number of large particles than fine particles.
Water retention: The process by which soil holds water that runs through its different layers and mixes in groundwater is called water retention.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science
- Nutrition in Plants
- Nutrition in Animals
- Fiber To Fabric
- Heat
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Physical And Chemical Changes
- Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Soil
- Respiration in Organisms
- Transportation in Animals And Plants
- Reproduction in Plants
- Motion And Time
- Electric Current And Its Effects