NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 – Transportation in Animals And Plants, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 11. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals And Plants Class 7, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 7 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 11 – Transportation in Animals And Plants |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 – Transportation in Animals And Plants
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11- Transportation in Animals And Plants– Solutions to Question 1 and Question 2
Question 1:-
Match structures given in Column I with functions given in Column II.
| Column 1 | Column2 |
|---|---|
| (i) Stomata | (a) Absorption of Water |
| (ii) Xylem | (b) Transpiration |
| ( iii) Root Hairs | (c) Transport of Food |
| (iv) Phloem | (d) Synthesis of Carbohydrates |
Answer 1:-
| Column 1 | Column2 |
|---|---|
| (i) Stomata | (b) Transpiration |
| (ii) Xylem | (d) Transport of Water |
| ( iii) Root Hairs | (a) Absorption of Water |
| (iv) Phloem | (c) Transport of Food |
Question 2:-
Fill in the blanks.
(i) The blood from the heart is transported to all parts of the body by the _____.
(ii) Haemoglobin is present in _______cells.
(iii) Arteries and veins are joined by a network of _________.
(iv) The rhythmic expansion and contraction of the heart is called ______.
(v) The main excretory product in human beings is_______.
(vi) Sweat contains water and _____.
(vii)Kidneys eliminate the waste materials in the liquid form called______.
(viii)Water reaches great heights in the trees because of suction pull caused by _____.
Answer 2:-
(i) The blood from the heart is transported to all parts of the body by the arteries.
(ii) Haemoglobin is present in red blood
(iii) Arteries and veins are joined by a network of capillaries.
(iv) The rhythmic expansion and contraction of the heart is called heartbeat.
(v) The main excretory product in human beings is urea.
(vi) Sweat contains water and salt.
(vii)Kidneys eliminate the waste materials in the liquid form called urine.
(viii)Water reaches great heights in the trees because of suction pull caused by transpiration.
Question 3:-
Choose the correct option:
(a)In plants, water is transported through:
(i) Xylem
(ii) Phloem
(iii) Stomata
(iv) Root hair
(b)Water absorption through roots can be increased by keeping the plants:
(i) In the shade
(ii) In dim light
(iii) Under the fan
(iv) Covered with a polythene bag
Answer 3:-
(a) (i) Xylem
(b) (iii) Under the fan
Question 4:-
Why is transport of materials necessary in a plant or in an animal? Explain.
Answer 4:-
The transport of materials is necessary in a plant or in an animal because minerals, nutrients, water, oxygen etc. important materials can only be transferred to the cells of the body by transportation system of an organism. The transport of these materials to cells is important because cells are the smallest functioning unit of the body and the synthesis performed by cells using these will result in proper functioning of organs.
Question 5:-
What will happen if there are no platelets in the blood?
Answer 5:-
Platelets are disc-shaped component of blood that help in the clotting of blood in times of injury. If platelets were removed from our blood stream then there would have been no such agent to check the flow of blood and humans would lose a lot of blood even in small injury which could make human body weak.
Question 6:-
What are stomata? Give two functions of stomata.
Answer 6:-
Stomata are the tiny openings present on the surface of leaves. Their two main functions are –
1. Stomata help in gaseous exchange between plants and atmosphere.
2. Plants lose some water through stomata. This process is called transpiration and it is necessary for transportation of minerals, nutrients, water to even the topmost part of a plant.
Question 7:-
Does transpiration serve any useful function in the plants? Explain.
Answer 7:-
Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water by evaporation from the stomata present on the surface of its leaves. This process creates a suction pull and due to this water and other minerals are pulled up to the top a plant and transported effectively to every part.
Question 8:-
What are the components of blood?
Answer 8:-
The main components of blood are –
1. Plasma: It is the fluid that forms a major part of blood. All other blood components remain suspended in plasma.
2. Red blood cells: These are a type of blood cells that are responsible for the transport of oxygenated blood throughout the body. It also contains haemoglobin that binds red blood cells with oxygen and provides blood its red colour.
3. White blood cells: These are a type of blood cells that are responsible for protecting the body against germs and harmful foreign particles that enter the bloodstream.
4. Platelets: This component of blood is responsible for the clotting of blood at times of injury to minimise blood loss from body.
Question 9:-
Why is blood needed by all the parts of a body?
Answer 9:-
Blood is needed by all parts of body because –
1. Blood supplies them with oxygen and nutrients for their proper functioning.
2. Blood carries CO2 back to the lungs for its removal through exhalation.
3. It carries digested food to all the organs and provides them with energy.
4. Blood also helps fight the infections and harmful agents that enter the body.
Question 10:-
What makes the blood look red?
Answer 10:-
Blood looks red due to the presence of a red coloured pigment present in red blood cells called haemoglobin. Haemoglobin helps in binding oxygen to red blood cells and ensures effective transport of oxygen to every tissue of body.
Question 11:-
Describe the function of the heart.
Answer 11:-
Heart is an important organ of transportation system whose main function is to pump blood throughout the body. The size of heart is fist-sized and it has 4 chambers separated by wall of muscle to avoid mixing of oxygenated blood with deoxygenated blood. The 4 chambers of heart are- right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle. The function of hearts begins in right ventricle from where deoxygenated blood is pumped to lungs which is carried by pulmonary artery and oxygenated blood is brought back to the left atrium by pulmonary vein. The blood is pushed to left ventricle from where it is pumped into the main artery aorta and after circulating throughout the body the deoxygenated blood is brought to right atrium by vena cava which is pushed into the right ventricle and the cycle continues.
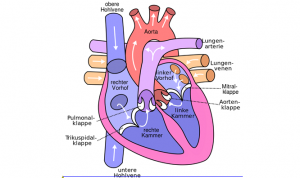 Question 12:-
Question 12:-
Why is it necessary to excrete waste products?
Answer 12:-
All the organs of body, during their functioning produce waste products which sometimes may be toxic and harmful to the human body. For example- urea, a major component of waste released by human body is capable to cause harm to bones and joints if allowed to enter bloodstream. Such waste products need to be removed from the body as soon as possible. The excretory system is responsible for the removal toxic and harmful waste generated in the human body.
Question 13:-
Draw a diagram of the human excretory system and label the various parts.
Answer 13:-
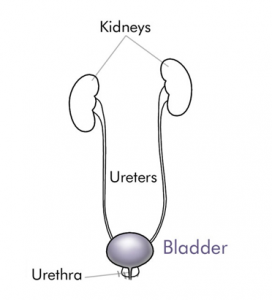
Topics Covered in Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals And Plants Class 7 Science :-
- Circulatory system
- Excretion in animals
- Transport of substances in plants
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals And Plants : –
Ammonia: Animals like fish release the waste from their bodies in the form of water-soluble substance called ammonia.
Artery: Artery is a type of blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to other parts of the body.
Blood: Blood is a fluid which flows in our body through a system of blood vessels and transports digested food, oxygen, waste from their source to destination.
Blood vessels: Blood vessels are thin tube-like structure that form an interconnected network in our body. Blood flows in our body through blood vessels.
Capillary: Capillaries are the finest among blood vessels.Their main function is to transport oxygenated blood from arteries to various tissues of the body and deoxygenated blood from tissues to the veins.
Circulatory system: Circulatory system comprises of arteries, veins, capillaries and heart. It is responsible for transportation of oxygenated blood from lungs to various parts of body and collect deoxygenated blood from various parts of the body to the lungs for removal of CO2.
Dialysis: When a person’s kidney stops functioning, waste products start to collect in the body which need to be removed. To do so, an artificial kidney-like instrument is used. This process is called dialysis
Excretion: The process by which waste products are removed from the human body is called excretion.
Excretory system: The biological system that is responsible for removing waste and unwanted material from the human body is called excretory system.
Haemoglobin: Haemoglobin is the pigment that provides blood its red colour. Its function is to bind RBCs with oxygen to ensure transport of oxygen to all cells of the body
Heart beat: The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the muscles that make up the wall of chambers of heart produces a beat like sound. This is called heartbeat.
Kidneys: Kidneys are the pair of organs that are responsible for removal waste materials from the human body.
Phloem: Phloem is a tissue present in plants whose main function is to transport food prepared by leaves to all parts of plants.
Plasma: The main component of blood in which all types of blood cells are suspended is called plasma.
Platelets: The component of blood responsible for clotting of blood in case of injuries is called platelets. Platelets are disc-shaped in structure.
Pulse: The rhythmic throbbing felt in certain parts of body such as wrist, neck, chest etc. is called pulse. This is caused by the impulse felt by the blood flowing through the arteries.
Red blood cell: These are a type of cells present in the blood which are responsible for the transport of oxygen throughout the body. Red blood cells contain haemoglobin which binds oxygen to blood and provides blood its red colour.
Root hair: The small hair-like fine projections present on the surface of roots of plants are called root hairs. These are responsible for absorption of water and nutrients from soil.
Stethoscope: It is an instrument that is used by doctors to hear heartbeats of patients to get an idea about their health condition.
Sweat: The excretion of excess salts, urea and water from the body takes place in the form of moisture. This moisture is called sweat and is released from the pores present on the skin.
Tissue: The group of cells that perform a specific function in an organism is called tissue. For example- xylem and phloem are plant tissues.
Urea: Urea is the major component of excretory products released by humans.
Ureter: Ureter is a tube-like structure that transports urine from kidneys to urinary bladder.
Urethra: It is the muscular tube that is present at the end of urinary bladder through which urine is released from the body.
Uric acid: Uric acid is the excretory product produced by land organisms such as lizards, birds, snakes which is in semi-solid form.
Urinary bladder: It is a part of excretory system and its main function is to store the urine until it is released from the human body.
Vein: It is a type of blood vessel that carries blood rich in carbon dioxide back to the heart.
White blood cell: White blood cells are a type of cells present in blood whose main function is to protect the body against germs and harmful foreign particles.
Xylem: It is a type of tissue whose main function is to transport water and nutrients to all parts of plant.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science
- Nutrition in Plants
- Nutrition in Animals
- Fiber To Fabric
- Heat
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Physical And Chemical Changes
- Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Soil
- Respiration in Organisms
- Transportation in Animals And Plants
- Reproduction in Plants
- Motion And Time
- Electric Current And Its Effects