NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 14 – Electric Current And Its Effects, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 14. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 14 – Electric Current And Its Effects Class 7 Science, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. We are providing NCERT Solutions for Class 7 all subjects which can be accessed by clicking here.
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 14 – Electric Current And Its Effects
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 14 – Electric Current And Its Effects – NCERT Exercises
Question 1:-
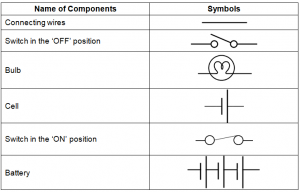
Draw in your notebook the symbols to represent the following components of electrical circuits: connecting wires, switch in the ‘OFF’ position, bulb, cell, switch in the ‘ON’ position, and battery.
Answer 1:-
Question 2:-
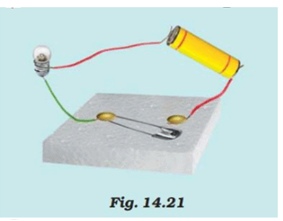
Draw the circuit diagram to represent the circuit shown in Fig.14.21.
Answer 2:-
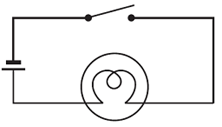
Question 3:-
Fig.14.22 shows four cells fixed on a board. Draw lines to indicate how you will connect their terminals with wires to make a battery of four cells
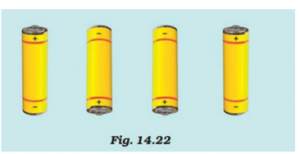
Answer 3:-
To make a battery the positive terminal of one cell needs to be connected to the negative terminal of other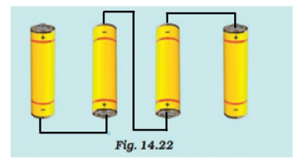
Question 4:-
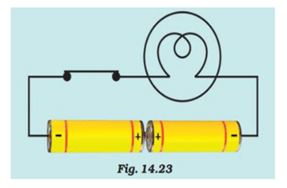
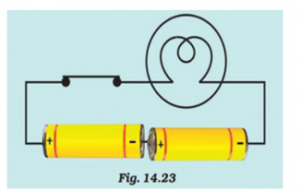
The bulb in the circuit shown in Fig.14.23 does not glow. Can you identify the problem? Make necessary changes in the circuit to make the bulb glow.
Answer 4:-
In the given circuit, the two cells are not connected correctly with each other. The positive terminal of one cell needs to be connected to negative terminal of another cell.
Question 5:-
Name any two effects of electric current
Answer 5:-
Two effects of electric current are –
1. Electricity produces heat: When current passes through a wire, it produces heat. This is called heating effect of electric current. For example – electric iron has a coil wound around its base and when current is passed through it, the coil heats up and we are able to iron the clothes
2. Electricity produces magnetism: When electricity is passed through a wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. This is called magnetic effect of current. For example – electric bell, electric fan function on magnetic effect of current
Question 6:-
When the current is switched on through a wire, a compass needle kept nearby gets deflected from its north-south position. Explain.
Answer 6:-
When the current is switched on through a wire, a magnetic field is produced around the wire. When a compass is brought near it, it experiences a magnetic force because the compass itself contains a magnet. Due to repulsion or attraction experienced by the poles of compass, it deflects.
Question 7:-
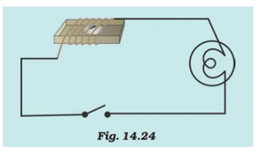
Will the compass needle show deflection when the switch in the circuit shown by Fig.14.24 is closed?
Answer 7:-
No, the compass needle will not show any deflection when the switch is closed because there is no source or battery attached in this circuit. In the absence of source, electric current will not flow in the circuit and therefore, no magnetism will be produced.
Question 8:-
Fill in the blanks:
(a)Longer line in the symbol for a cell represents its ________ terminal.
(b)The combination of two or more cells is called a _____ .
(c)When current is switched ‘on’ in a room heater, it ________ .
(d)The safety device based on the heating effect of electric current iscalled a __________ .
Answer 8:-
(a)Longer line in the symbol for a cell represents its positive
(b)The combination of two or more cells is called a
(c)When current is switched ‘on’ in a room heater, itemits heat.
(d)The safety device based on the heating effect of electric current is called a
Question 9:-
Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(a)To make a battery of two cells, the negative terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the other cell. (T/F)
(b)When the electric current through the fuse exceeds a certain limit, the fuse wire melts and breaks. (T/F)
(c)An electromagnet does not attract a piece of iron. (T/F)
(d)An electric bell has an electromagnet. (T/F)
Answer 9:-
(a)F
(b)T
(c)F
(d)T
Question 10:-
Do you think an electromagnet can be used for separating plastic bags from a garbage heap? Explain.
Answer 10:-
No, an electromagnet cannot be used to separate plastic bags from garbage heap. An electromagnet is a piece of metal that has magnetism because of electric current passing through the wire wound around it. It behavesexactly the same way as a magnet and only attracts iron, cobalt and nickel objects. Plastic bags cannot beattracted by it and so, we cannot separate them from the garbage heap.
Question 11:-
An electrician is carrying out some repairs in your house. He wants to replace a fuse by a piece of wire. Would you agree? Give reasons for your response.
Answer 11:-
A fuse is a safety device that consists of a specific type of wire that melts onheating when excessive current is passed and protects the appliances. If the electrician uses a standard fuse wire that melts on passing a certain amount of current, only then I will agree for replacing it. In case he uses an ordinary wire, which does not melt, then I will not agree because it can lead to short circuit of appliances causing a huge loss.
Question 12:-
Zubeda made an electric circuit using a cell holder shown in Fig. 14.4, a switch and a bulb. When she put the switch in the ‘ON’ position, the bulb did not glow. Help Zubeda in identifying the possible defects in the circuit.
Answer 12:-
The possible defects in the circuit could be –
- The bulb may be fused or defective
- The arrangement of cells in the holder may not be correct
- The cells may have been used up and left with no energy
- The switch may be defective
- Connection made may be loose
Question 13:-
In the circuit shown in Fig. 14.25
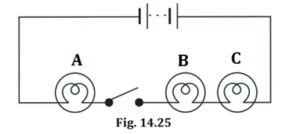
(i) Would any of the bulb glow when the switch is in the ‘OFF’ position?
(ii) What will be the order in which the bulbs A, B and C will glow when the switch is moved to the ‘ON’ position?
Answer 13:-
(i) No, none of the bulbs will glow because the circuit is incomplete. The path for the flow of current is incomplete.
(ii) All the bulbs will glow together. The circuit will be complete and there will be no delay in the movement of current through the circuit.
Topics Covered in Chapter 14 Electric Current And Its Effects Class 7 Science :-
- Symbols of electric components
- Heating effect of electric current
- Magnetic effect of electric current
- Electromagnet
- Electric bell
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 14 – Electric Current And Its Effects : –
Battery: The combination of two or more cells is called a battery.
Circuit diagram: The representation of an electrical circuit using symbols is called a circuit diagram. It is easy to use and draw and therefore is the more common way of representing circuits.
Electric components: The various devices and parts used in making an electric circuit are called electric components.
Electric bell:It is an instrument that works on magnetic effect of current. It consists of an electromagnet, an iron strip with a hammer attached at its end and a contact screw. When the current passes through the coil the iron strip is attracted towards it and the bell gongs and this process is repeated again and again.
Electromagnet: It is an instrument that is made by wrapping a coil of wire around a metal object and connecting it to a battery. It behaves exactly the same way as a magnet.
Fuse: It is a safety device installed in houses to protect the appliances from short-circuit. A fuse is made up of a wire that melts upon heating when excessive current passes through it thereby saving the appliances.
Heating effect of current: When current passes through a wire, it heats up the wire. This is called heating effect of current.
Magnetic effect of current: When current passes through a wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. This is called magnetic effect of current.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science
- Nutrition in Plants
- Nutrition in Animals
- Fiber To Fabric
- Heat
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Physical And Chemical Changes
- Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Soil
- Respiration in Organisms
- Transportation in Animals And Plants
- Reproduction in Plants
- Motion And Time
- Electric Current And Its Effects