NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 – Nutrition in Plants, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 1. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 – Nutrition in Plants, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 7 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 1 – Nutrition in Plants |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 – Nutrition in Plants
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 – Nutrition in Plants – NCERT Exercises
1. Why do organisms take food?
Answer 1-
Organisms require nutrients for the growth and development of the body. Since food provides these nutrients, thus organisms take in food by different means to sustain their lives healthily. The energy to carry out different life processes and functions comes from these nutrients. It regulates the metabolism of the body.
2. Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph.
Answer 2-
| Parasite | Saprotroph |
| 1. They are eukaryotic organisms (have a true nucleus) | 1. They may be eukaryotic or prokaryotic. |
| 2. They feed upon a living organism by living inside the body of the host and using it as a source of nutrition. | 2. They feed on dead and decaying matter by decomposing it (breaking down into simpler compounds). |
| 3. They may or may not cause harm to the host. | 3. They don’t cause harm, in lieu, they help clean the environment. |
| 4. They have intercellular digestion. | 4. They have intracellular digestion. |
| 5. Example- tapeworms, fleas etc. | 5. Example- Fungi, bacteria etc. |
3. How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Answer 3-
Presence of starch can be tested in following steps:-
(i) Boil the leaf in alcohol in a beaker. The beaker should be heated in a water bath (alcohol is inflammable)
(ii) Take out the leaf and put on some iodine solution drops.
(iii) If the leaf turns blue black, there is starch present in the leaf and if the leaf doesn’t turn blue black, there’s no starch present.
(iv) Boiling in alcohol would have extracted chlorophyll, so the leaf will not remain green in colour.
4. Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants.
Answer 4-
The process by which green plants synthesise their food is called photosynthesis. Only plants which have the presence of a green pigment called chlorophyll can perform photosynthesis. The raw materials required are water and carbon dioxide. The plants acquire minerals along with the water from the soil through roots and the process is called osmosis. Carbon dioxide is taken through stomata present in leaves and oxygen is given out through the stomata. Chlorophyll is responsible for the absorption of sunlight. The equation is as follows:-
Carbon dioxide + water ——-> Glucose + oxygen
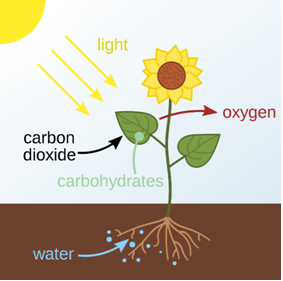
5. Show with the help of a sketch that plants are the ultimate source of food.
Answer 4-
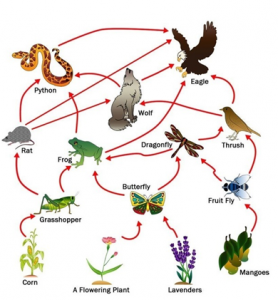
In the above figure, we can see that all the food chains start with the producers — green plants. This implies that they are the primary source of energy on earth. Only they can convert solar energy into chemical energy by the means of photosynthesis.
For eg. Grasshopper eats grass, rat eats grasshopper, python eats rat, and eagle eats snake. This is an example of a simple food chain with 4 trophic levels. Here, green grass is the main and primary source of nutrients and food in the chain.
6. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Green plants are called _________________ since they synthesise their own food.
(b) The food synthesised by plants is stored as _________________.
(c) In photosynthesis solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called ___________.
(d) During photosynthesis plants take in ___________ and release __________ gas.
Answer 6-
(a) Green plants are called autotrophs since they synthesise their own food.
(b) The food synthesised by plants is stored as starch.
(c) In photosynthesis solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called chlorophyll.
(d) During photosynthesis plants take incarbon dioxide and release oxygen gas.
7. Name the following:
(i) A parasitic plant with yellow, slender and branched stem.
(ii) A plant that is partially autotrophic.
(iii) The pores through which leaves exchange gases.
Answer 7-
i) Cuscuta
ii) Pitcher plant
iii) Stomata
Tick the correct answer:
(a) Cuscuta is an example of:
(i) autotroph (ii) parasite (iii) saprotroph (iv) host
(b) The plant which traps and feeds on insects is:
(i) Cuscuta (ii) china rose (iv) pitcher plant (iv) rose
Answer 8-
(a) (ii) Parasite
(b)(iv) Pitcher plant
9. Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| Chlorophyll | Rhizobium |
| Nitrogen | Heterotrophs |
| Cuscuta | Pitcher plant |
| Animals | Leaf |
| Insects | Parasite |
Answer 11-
| Column I | Column II |
| Chlorophyll | Leaf |
| Nitrogen | Rhizobium |
| Cuscuta | Parasite |
| Animals | Heterotrophs |
| Insects | Pitcher plant |
10. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(i) Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis.
(ii) Plants which synthesise their food are called saprotrophs.
(iii) The product of photosynthesis is not a protein.
(iv) Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
Answer 10-
(i) False
(ii) False
(iii) True
(iv) True
11. Choose the correct option from the following:
Which part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
(i) Root hair (ii) Stomata (iii) Leaf veins (iv) Petals
Answer 11-
(ii) Stomata
12. Choose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their:
(i) roots (ii) stem (iii) flowers (iv) leaves
Answer 12-
(iv) Leaves
13. Why do farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large greenhouses? What are the advantages to the farmers?
Answer 13-
Greenhouse provides greenhouse effect because of which the crops get more sunlight and higher temperatures subsequently.Moreover, it acts as a protection of crops from the abnormalities of nature i.e. winds with high velocity, heavy rainfall, storms etc. It even protects the crops from the insects , birds and rats. It gives higher crop yields. They can avoid using a large amount of chemical pesticides ,insecticides and fertilisers.
Topics Covered in Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science :-
- Mode of Nutrition in Plants
- Photosynthesis – Food Making Process in Plants
- Other modes of Nutrition in Plants
- Saprotrophs
- How Nutrients are replenished in the Soil.
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants: –
Autotrophic– Autotrophic means self – nutrition. It is a process in which organism itself produces its food with the help of simple inorganic materials like water, carbon dioxide and sunlight.
Chlorophyll– It is a green pigment responsible for the green colour of the plant. It absorbs light due to which photosynthesis is possible.
Heterotrophs- Heterotrophs are organisms which are unable to produce their food by themselves. They make their food by taking nutrition from animal or plant. Example- Humans, algae.
Host-Host is an organism that harbours another organism inside or near their body and through which a parasite obtains its nutrition and/or shelter. For example- Nematodes.
Insectivorous–They are plants or animals that eat insects. Example – Frogs, bats, Venus flytrap.
Nutrient– These are molecular substances which provide energy to organisms. Some major nutrients are – Carbohydrates, proteins, water, fat(lipid), vitamins and minerals.
Nutrition-The process of taking food by an organism and using it for growth and repair of living cells is called nutrition
Parasite– A plant or an animal which feeds on a host and takes its nourishment is called a parasite. Example- Protozoa, tapeworm, dodders.
Photosynthesis– A process that uses sunlight to turn carbon dioxide(CO2 ) into sugars that the plant cell can use as energy is called photosynthesis. In this process, oxygen is released by plants. Example- Plants and algae use this process to make their food.
Saprotroph – Saprotrophs are the organism who feeds upon the non-living organic matter. Example- Fungi decomposes complex organic molecule.
Stomata– Stomata is a pore present on the epidermis of leaves. It is mostly found on a leaf’s lower surfaces and is capable of opening and closing according to environmental conditions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science
- Nutrition in Plants
- Nutrition in Animals
- Fiber To Fabric
- Heat
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Physical And Chemical Changes
- Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Soil
- Respiration in Organisms
- Transportation in Animals And Plants
- Reproduction in Plants
- Motion And Time
- Electric Current And Its Effects