NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 – Reproduction in Plants, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 12. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants Class 7, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 7 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 12 – Reproduction in Plants |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 – Reproduction in Plants
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 – Reproduction in Plants– Solutions to Question 1 and Question 2
Question 1:-
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called_____________.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called_____________.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as ____________.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as _____________.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of _____________,_____________ and _____________.
Answer 1:-
(a)Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called vegetative propagation.
(b)A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called unisexual.
(c)The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as pollination.
(d)The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as fertilisation.
(e)Seed dispersal takes place by means of wind, water and animals.
Question 2:-
Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Answer 2:-
There are 4 different methods of asexual reproduction –
1. Vegetative propagation: In this method, new plants are generated from vegetative parts of a plant such as roots, stem, bud, leaves. For example – new rose plants can be obtained from planting the stem of existing rose plant, potato can be grown from the eyes of potato, Bryophyllum leaf has buds in the margin of leaves and each bud is capable of forming a new plant.
2. Budding: Microscopic organism such as yeast reproduces by budding. It involves formation of a small bulb-like projection on the body of yeast which detaches from it upon growing. This projection further grows to produce new organism.
3. Fragmentation: Spirogyra is an organism that multiplies through fragmentation. This involves breaking up of the body of organism into fragments and each fragment grows to become a new organism.
4. Spore formation: Spores are generated by organisms such as fungi in large quantities. They are light in weight and are covered by a protective covering. When the conditions are favourable, they burst out of their cover and spread in various places giving rise to more fungi.
Question 3:-
Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Answer 3:-
Sexual reproduction is one of the modes of reproduction which involves the formation of seeds. In sexual reproduction both male and female reproductive parts are required. In plants, these organs are present in the flower. It is the most common method of reproduction in organisms and produces identical organisms.
Question 4:-
State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Answer 4:-
| It Involves the formation of seeds | It does not involve seed formation |
| It requires both parents | It can take place through only one parent |
| It produces identical organisms | It does not produce an identical organism |
| Flowers are the main reproductive part of plans | It does not require any specific part of reproduction |
| Example: All Flowering plants | Example: Yeast, spirogyra, potato, Ginger etc. |
Question 5:-
Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Answer 5:-
Male reproductive part-
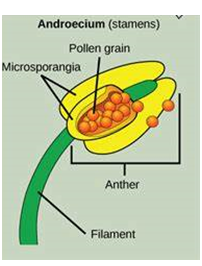
Female reproductive part-
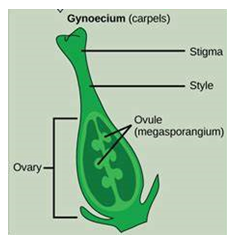
Question 6:-
Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination
Answer 6:-
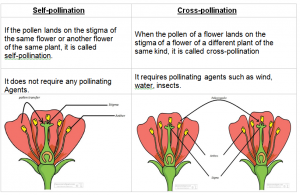
Question 7:-
How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers?
Answer 7:-
The process of fertilisation takes place in the following ways –
- The male reproductive parts of a plant located as pollen on anthers are pollinated to transfer them to the female reproductive part of flower. This is done by insects, wind, water which visit the flower and take away pollen to finally transfer them onto stigma of same or other flowers.
- The next step involves fusion of gametes. Upon landing onto the stigma, the male gamete germinates and grows a pollen tube through style to reach the ovum. Through this tube it travels all the way down to the ovary and the gametes fuse together to form zygote. This is called fertilisation.
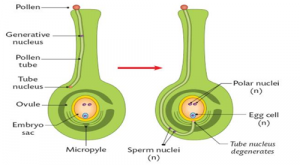
Question 8:-
Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Answer 8:-
Seeds are dispersed in the following ways –
1. By wind: Seeds which are light in weight or have developed wings, easily get flown away by the wind and are dispersed to new locations for germination. For example – Drumstick, Maple, Sunflower, Aak etc.
2. By water: Those seeds that have a spongy or fibrous coating on them develop floating ability and are easily dispersed by water. For example – Coconut
3. By animals: Some seeds use animals as their dispersing medium. Such seeds usually have spines or hooks to get attached with the body of animals. They are then dispersed to various places. For example – Xanthium, Urena.
Question 9:-
Match items in Column I with those in Column II:
| (a) Bud | (i) Maple |
| (b) Eyes | (ii) Spirogyra |
| (c) Fragmentation | (iii) Yeast |
| (d) Wings | (iv) Bread Mould |
| (e) Spores | (v) Rose |
Answer 9:-
| (a) Bud | (i) Yeast |
| (b) Eyes | (ii) Potato |
| (c) Fragmentation | (iii) Spirogyra |
| (d) Wings | (iv) Maple |
| (e) Spores | (v) Bread mould |
Question 10:-
Tick the correct answer:
(a)The reproductive part of a plant is the –
(i) Leaf
(ii) Stem
(iii) Root
(iv) Flower
(b)The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called –
(i) Fertilization
(ii) Pollination
(iii) Reproduction
(iv) Seed formation
(c)Mature ovary forms the –
(i) Seed
(ii) Stamen
(iii) Pistil
(iv) Fruit
(d)A spore producing organism is –
(i) Rose
(ii) Bread mould
(iii) Potato
(iv) Ginger
(e)Bryophyllum can reproduce by its –
(i) Stem
(ii) Leaves
(iii) Roots
(iv) Flower
Answer 10:-
(a) (iv) Flower
(b) (i) Fertilization
(c) (iv) Fruit
(d) (ii) Bread mould
(e) (ii) Leaves
Topics Covered in Chapter 12 – Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Science :-
- Modes of reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
- Fruits and Seed formation
- Seed Dispersal
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 – Reproduction in Plants : –
Asexual reproduction: It is a method of reproduction that involves only one parent and no formation of seeds takes place. Examples – Budding, Fragmentation, Vegetative propagation etc.
Budding: It is a method of asexual reproduction. Budding is usually observed in yeast and it involves formation of bulb-like projection on the body of organism that detaches from it and grows into an individual organism of same type.
Embryo:It is the developed zygote, which is formed during fertilisation.
Fertilisation: The fusion of male and female gametes results in the formation of zygote. This process is called fertilisation.
Fragmentation: It is a method of asexual reproduction. It involves breaking of the body of organisms into small fragments each of which develops into a new individual organism of the same kind.
Gametes: The male and female reproductive parts contain gametes which fuse together to form zygote.
Hypha: The body of a fungus has a hairy coating and each of this hair is called hypha.
Ovule: The female gamete in flowers is present inside ovule of flower. Ovule is the part further develops into seed.
Pollen grain: Pollen grains are present on the anthers of stamen. These are the part of flower that contain male gametes and need to be transferred to the stigma of carpel/pistil of flower.
Pollen tube: When the pollen lands on stigma of flower, it germinates and a tube is developed between stigma and ovary that provides a route to the male gamete to reach female gamete and fertilise.
Pollination: The process of transfer of pollen grains to the stigma of same flower or another flower of same kind by agents such as wind, water and insects is called pollination.
Seed dispersal: The process by which seeds of plant are carried away by wind, water or animals to save them from competing with other plants is called seed dispersal.
Sexual reproduction: The mode of reproduction which involves formation of seeds and requires both male and female gamete is called sexual reproduction. For example – all flowering plants reproduce sexually.
Spore: It is a tiny reproductive unit that is produced in large quantities by organisms such as fungus. It helps in reproduction by spreading out in large numbers and developing into new organisms.
Sporangium: The structure that holds spores until the conditions become favourable for it to burst and spread is called sporangium.
Vegetative propagation: It is a mode of asexual reproduction in which new plants are grown from the vegetative parts of plants such as leaves in bryophyllum, stem cuttings in rose, eyes in potato etc.
Zygote: The fusion of male and female gametes produces zygote that develops into seed.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science
- Nutrition in Plants
- Nutrition in Animals
- Fiber To Fabric
- Heat
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Physical And Chemical Changes
- Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Soil
- Respiration in Organisms
- Transportation in Animals And Plants
- Reproduction in Plants
- Motion And Time
- Electric Current And Its Effects