NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 – Getting to Know Plants, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 7. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 – Getting to Know Plants, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 6 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 7 – Getting to Know Plants |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 – Getting to Know Plants
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 – Getting to Know Plants – NCERT Exercises
Question 1:-
Correct the following statements and rewrite them in your notebook.
(a) Stem absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Leaves hold the plant upright.
(c) Roots conduct water to the leaves.
(d) The number of petals and stamens in a flower is always equal.
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are also joined together.
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is joined to the petal.
Answer 1: –
(a) Root absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Stems hold the plant upright.
(c) Stems conduct water to the leaves.
(d) The number of petals and stamens in a flower may or may not be always equal.
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are separate.
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil may or may not be joined to the petal.
Question 2:-
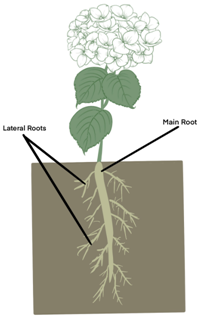
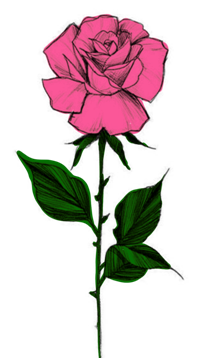
Draw (a) a leaf, (b) a taproot and (c) a flower, you have studied for Table 7.3.
Answer 2:-
(a) a leaf
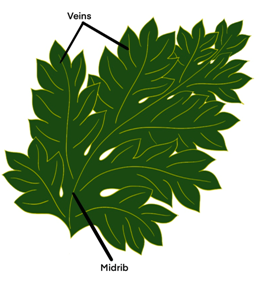
(b) a taproot
(c) a flower
Question 3:-
Can you find a plant in your house or in your neighborhood, which has a long but weak stem? Write its name. In which category will you place it?
Answer 3:-
Yes, climbers and creepers have long but weak stems. Money plant is one such plant. It is a climber and requires support of another tree or object to climb.
Question 4:-
What is the function of a stem?
Answer 4: –
Stems play an important role in the development of a plant. They hold the plant upright, they conduct water and minerals from root to the leaves, and they carry food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Question 5:-
Which of the following leaves have reticulate venation?
Wheat, tulsi, maize, grass, coriander (dhania), China rose
Answer 5: –
Leaves having net-like venation are said to have reticulate venation. Tulsi, Coriander and China rose have reticulate venation.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 – Getting to Know Plants
Question 6:-
If a plant has fibrous root, what type of venation do its leaves have?
Answer 6: –
Plants with fibrous roots have parallel venation.
Question 7:-
If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kind of roots will it have?
Answer 7: –
If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, it will have taproot.
Question 8:-
Is it possible for you to find out whether a plant has taproot or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper?
Answer 8:-
Yes, it is possible to find whether a plant has taproot or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf. Leaves with reticulate venation have taproot and leaves with parallel venation have fibrous roots.
Question 9:-
What are the parts of a flower.
Answer 9: –
Parts of a flower are:
1. Sepals: Small leaf-like structures surrounding the petals.
2. Petals: The colorful, leafy parts, surrounding the reproductive parts of the flower
3. Stamens: Stamens produce pollens in flower. They consist of anther and filament.
4. Pistil: Pistil is the female reproductive part of a flower. It is the innermost part of the flower and comprises of Stigma, Style and Ovary.
Question 10:-
From the following plants, which of them have flowers?
Grass, maize, wheat, chilli, tomato, tulsi, peepal, shisham, banyan, mango, jamun, guava, pomegranate, papaya, banana, lemon, sugarcane, potato, groundnut.
Answer 10: –
Plants containing flowers are:
Chilli, Tomato, Tulsi, Mango, Pomegranate, Jamun, Guava, Papaya, Banana, Lemon.
Question 11:-
Name the part of plant which produces food. Name the process.
Answer 11: –
Leaves produce food in plants by the process of Photosynthesis.
Question 12:-
In which part of a flower, you will find the ovary?
Answer 12: –
Ovary is a part of pistil. It is the lowest and swollen part of the pistil.
Question 13:-
Name two plants in which one has joined sepals and the other has separate sepals.
Answer 13: –
Plants that have joined sepals are Hibiscus and Cotton.
Plants that have separate sepals are Jasmine and Lotus.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 – Getting to Know Plants – Video Explanation
When we go out, we see a variety of plants around us. Some are small and some very big.
Let us get to know the different parts of any plant. This will help us understand the differences between plants of different kinds.
Topics Covered in Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants:-
- HERBS, SHRUBS AND TREES
- STEM
- LEAF
- ROOT
- FLOWER
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 – Getting to Know Plants:-
Climbers: Plants with weak and thin stems that take support from other trees or tall objects and climb upand grow vertically are called climbers. Some examples of climbers are money plant, grapevine, pea, etc.
Conduct: The process through which water and minerals are carried to different parts of a plant is called conduction.
Creepers: Creepers have a weak stem and cannot stand upright. Because of this, they spread or creep on the ground giving them the name. Strawberry and watermelon are creepers.
Fibrous roots: Fibrous roots are formed by thin, thread like similar structures. These roots do not have a main root. Some plants that have fibrous roots are grass,onion, wheat, etc.
Herbs: Herbs are small plants with tender stems. They usually have few branches and contain a lot of nutritional benefits. Herbs such as tomato, ginger, radish, and wheat are used frequently in our day to day lives.
Lamina: The broad and flat part of the leaf that contains chloroplasts is called lamina.
Lateral roots: The smaller parts of the tap root that branch out from the main root are called lateral roots. They anchor the plant to the soil and help in water and nutrient intake.
Midrib: Midrib is the primary vein of a leaf. It is a thick line running along the lamina of a leaf.
Ovule: Small bead like structures found inside the ovary are called ovules. They are responsible for reproduction in plants.
Parallel Venation: When the veins on the lamina of a leaf are arranged parallel to each other, it is known as parallel venation. Parallel venation can be observed in banana leaves.
Petal: The colorful, leafy parts, surrounding the reproductive parts of the flower are called petals. For Example, Petals of the rose flower come in various colors like red, yellow, and pink.
Petiole: The part of a leaf through which it is connected to the stem is known as a petiole.
Photosynthesis: The process by which plants produce food with help of sunlight, water, Carbon Dioxide, and chlorophyll, is called photosynthesis. They release oxygen as a by-product of this action.
Pistil: Pistil is the female reproductive part of a flower. It is the innermost part of the flower and comprises of Stigma, Style and Ovary.
Reticulate venation: The net like vein pattern found in some leaves is called reticulate venation. Leaves of maple tree have reticulate venation.
Sepal: Small leaf-like structures that protect the flower in bud and support petals are known as Sepals.
Shrubs: Medium sized plants with hard but flexible stems are called shrubs. Shrubs develop branches near the base of the stem. Some common shrubs are Roses, Tulsi and lemons.
Stamen: Stamens produce pollens in flower. They consist of anther and filament. The anther contains the pollen grains. Different flowers have different kind of stamens.
Taproot: In taproot system, a main root is branched into various latent roots. Mango tree, carrots, etc. have taproots.
Transpiration: Plants release water from the leaves in the form of vapour by the process of transpiration.
Trees: Plants that are very tall and have hard and thick stem with branches in the upper parts of the stem are called trees. Example: Mango tree and Guava tree.
Veins: The lines on leaves that are responsible for transporting water and minerals to the leaves are known as veins. There are two types of venations, reticulate and parallel.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science
- Food : Where does it come from
- Components of food
- Fibre to Fabric
- Sorting Material into Groups
- Separation of Substances
- Changes Around us
- Getting to Know Plants
- Body Movements
- Living Organism – Characteristics and Habitats
- Motion and Measurement of Distance
- Light, Shadows and Reflections
- Electricity and Circuits
- Fun with Magnets
- Water
- Air Around us
- Garbage in, Garbage out