NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7-Conservation of Plants and Animals, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 7. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 7-Conservation of Plants and Animals, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 7 – Conservation of Plants and Animals |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 – Conservation of Plants and Animals
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 – Conservation of Plants and Animals – NCERT Exercises
Question 1
Fill in the blanks:
(a) A place where animals are protected in their natural habitat is called ________.
(b) Species found only in a particular area is known as _________.
(c) Migratory birds fly to far-away places because of ________ changes.
Answer 1.
(a) A place where animals are protected in their natural habitat is called wildlife sanctuary.
(b) Species found only in a particular area is known as Endemic species.
(c) Migratory birds fly to far-away places because of climatic changes.
Question 2
Differentiate between the following:
(a) Wildlife sanctuary and biosphere reserve
(b) Zoo and wildlife sanctuary
(c) Endangered and extinct species
(d) Flora and fauna
Answer 2.
(a)
| Wildlife Sanctuary | Biosphere Reserve |
|---|---|
| An area that is conserved for the protection of wild animals and their natural habit. | An ecosystem to protect the biodiversity and culture of the plants and animals living there. |
| There are 543 wildlife sanctuaries in India | There are only 11 Biosphere reserves in India. |
(b)
| Zoo | Wildlife Sanctuary |
|---|---|
| In Zoos, the animals can be bought, sold, or traded. | Sanctuary does not buy, sell or trade animals. |
| Animals live in an artificial man created an environment in Zoos | Animals live in a natural habitat in a sanctuary. |
| Animals are kept in Zoos for public view, entertainment and preserved in small areas. | Animals here are protected and conserved over large areas. |
(c)
| Endangered Species | Extinct Species |
|---|---|
| These are the species whose numbers are drastically reducing and are on the verge of extinction. | These are the species that no longer exist and have already become extinct. |
| For Example: orangutans, tigers, sea turtles, etc. | For Example: Dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, etc. |
(d)
| Flora | Fauna |
|---|---|
| They represent all plant life on the earth | They represent all the animals living on the earth |
| They represent all plant life on the earth | They represent all the animals living on the earth |
| They lack mobility | They are capable of moving |
| For Example Sunflowers, palm trees, etc. | For Example Tigers, Cows, etc. |
Question 3
Discuss the effects of deforestation on the following:
(a) Wild animals
(b) Environment
(c) Villages (Rural areas)
(d) Cities (Urban areas)
(e) Earth
(f) The next generation
Answer 3.
(a)Due to deforestation, the natural habitat of many animals gets destroyed and they are left without any place to live and breed promoting their extinction.
(b)Deforestation leads to global warming because the carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere is absorbed by the plants which are now destroyed causing the global temperatures to increase.
(c)Villages in rural areas get affected a lot. Due to deforestation, the animals lose their place to breed and live so roam around freely causing dangers to the farmers. Also, the forests are sources for wood, resources, fruits and means to prevent soil erosion, floods etc to the farmers.
(d)The cities are dependant upon the rural regions and villages to supply them with the livestock and resources they need. Also, deforestation causes a change in climate and temperatures which affect the citizens and their lives.
(e)Deforestation has resulted in changes in climate across the earth, global warming, converted fertile regions into deserts and disturbed the biosphere.
(f)Deforestation has resulted in global warming, increase in temperature of the earth, loss of flora and fauna, extinction of various species, climate changes and increased pollution levels adding problems for the next generation.
Question 4
What will happen if:
(a) we go on cutting trees.
(b) the habitat of an animal is disturbed.
(c) the top layer of soil is exposed.
Answer 4.
(a)If we go on cutting trees, then there will be loss of shelter for animals and birds, loss of fruits, wood and other resources, loss of fertility of soil increasing soil erosion and chances of flood, reduction in underground water level and global warming.
(b)If we disturb the habitat of animals, then we will be making survival difficult for them as they will lose their places to live and breed and hence it will ultimately lead to their extinction.
(c)If we expose the top layer of the soil, then the lower, rocky and hard layers of the soil which are unfertile will cause loss of plant life and desertification. Further the depth of the rivers will decrease and chances of flood, droughts will increase many-folds.
Question 5
Answer in brief:
(a) Why should we conserve biodiversity?
(b) Protected forests are also not completely safe for wild animals. Why?
(c) Some tribals depend on the jungle. How?
(d) What are the causes and consequences of deforestation?
(e) What is Red Data Book?
(f) What do you understand by the term migration?
Answer 5.
(a)Biodiversity is the realm of all the living things present in the world. We should preserve it and prevent it from becoming extinct.
(b)Protected forests are also not completely safe for the wild animals because the poachers have the access into these forests and they are killing animals according to their will. This happens due to leniency in the implementation of laws of trespassing and poaching.
(c)Some tribals depend on the jungle because it is their source of livelihood. They dwell in the jungle and the forests provide wood, fruits and shelter for them. So, they area dependent on them for their survival.
(d)Due to the increase in the industrialization and urbanisation, more and more forest and reserved areas are being deforested and cleared to provide living facilities to people and to keep up with the present population demands. The consequences of it include loss in soil fertility, extinction of animals and birds, reduction in water levels and increase in natural calamities like floods etc.
(e)The Red Data Book is the book which is the source of information of all the endangered species of plants and animals on the planet.
(f)Migration refers to the movement of the whole population of the animals from one place to another due to the seasonal and climatic changes.
Question 6
In order to meet the ever-increasing demand in factories and for shelter, trees are being continually cut. Is it justified to cut trees for such projects?
Discuss and prepare a brief report.
Answer 6.
In order to meet the ever-increasing demand in factories and for shelter, the cutting of trees is not justified. Cutting of trees should only be done when reforestation is done for every region deforested to maintain the ecosystem balance. Cutting down of trees results in various tribulations such as floods, soil erosion, loss of shelter for animals and birds, extinction of species and loss of natural resources. Thus, it is not advisable to cut down trees only for human benefit. If necessary, reforestation and other measures should be taken to diminish the repercussions.
Question 7
How can you contribute to the maintenance of green wealth of your locality?
Make a list of actions to be taken by you.
Answer 7.
Conservation and maintenance of green wealth of our locality is a concern for each and every citizen. We can take the following measures for contributing :
- Spread awareness among the residents of the locality regarding the consequences of deforestation and saving trees.
- We should take care of the existing plants in our neighbourhood.
- We should promote the growth of at least one new plant by every resident in the locality.
- We should degrade the cutting down of trees and provide the trees with proper nourishment.
Question 8
Explain how deforestation leads to reduced rainfall.
Answer 8.
Deforestation means the cutting down of the trees. As a result of this, there is a reduction in the absorption levels of carbon dioxide needed for photosynthesis by the plants and this increases the carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere causing global warming. This results in the disturbance in the water cycle due to interference in the natural recycling of the moisture from the soil. Thus, there is a reduction in the rainfall.
Question 9
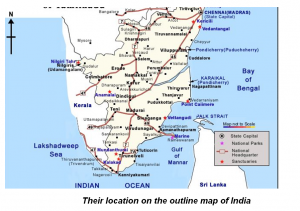
Find out the information about the national parks in your state. Identify
and show their location on the outline map of India.
Answer 9.
List of National Parks found in some of the states of India are as follows:
- Andhra Pradesh: Papikonda National Park, Rajiv Gandhi National Park.
- Assam: Kaziranga National Park, Manas National Park.
- Gujarat: Gir Forest National Park.
- Himachal Pradesh: Great Himalayan National Park.
- Kerala: Periyar National Park.
- West Bengal: Sundarbans National Park
- Satara, Sangli, Kolhapur: Chandoli National Park
Question 10
Why should paper be saved? Prepare a list of ways by which you can save paper.
Answer 10.
Paper should be saved because it is used in our day to day activities. Indiscriminate cutting down of trees leads to loss of mankind as well. It takes more than a dozen full grown trees to produce one tonne of paper therefore they should be conserved.
A list of ways by which we can save paper is:
- We should encourage the purchase of recycled products
- We should not waste paper by littering it here and there
- We should collect used paper and recycle it
- We should spread awareness about paper conservation
- We should stop making use of paper bags from stores.Instead, we should carry our own bags
Question 11
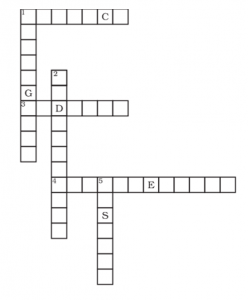
Complete the word puzzle:
Down
1. Species on the verge of extinction.
2. A book carrying information about endangered species.
5. Consequence of deforestation.
Across
1. Species which have vanished.
3. Species found only in a particular habitat.
4. Variety of plants, animals and microorganisms found in an area.
Answers:
1.EXTINCT
2.RED DATA BOOK
3.ENDEMIC
4.BIODIVERSITY
5.DESERTS
Topics Covered in Chapter Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8 Science :-
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Consequences of Deforestation
- Conservation of Forest and Wildlife
- Biosphere Reserve
- Flora and Fauna
- Endemic Species
- Wildlife Sanctuary
- National Park
- Red Data Book
- Migration
- Recycling of Paper
- Reforestation
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7-Conservation of Plants and Animals:-
Deforestation: It refers to the process of the permanent removal or clearance of the forests from a region to use it for other purposes.
Desertification: Due to deforestation on a large scale, the upper fertile and rich layer of the soil gets replaced by the lower unfertile layers. As a result, the fertile region of the land gets converted into deserts due to lack of humus.
Infiltration rate: The movement of the water from the soil surface into the ground.
Biosphere: The living zone of the earth. It is the part of the earth where all the living organisms exist and evolve.
Sanctuary: It is a protected area where the animals and birds are kept so they can be protected from any kind of danger or disturbance to their habitat.
National Park:It is a park which is used for conservation purposes and where the animals and their habitats, plants and other natural/semi-natural life can exist and freely use the natural resources.
Biosphere Reserve: It is an ecosystem responsible for the evolution and protection of plants and animals with unusual scientific and natural importance. It promotes biodiversity.
Flora: All plant life present in a particular region of time or geological period.
Fauna: All animal life present in a particular region, habitat or period of time.
Species: It refers to the set of organisms that have similar characteristics and are capable of exchanging genes and interbreeding.
Endemic Species: These are the species of plants and animals which are found especially in a particular area or region of land.
Wildlife sanctuary: These are the protected and reserved areas for the wild plant and animal life adequate for floral, faunal and geographical significance.
Project Tiger: A tiger conservation national programme launched in April 1973 by the government of India at the Jim Corbett National Park to preserve and save the population of tigers.
Endangered Animals: Animals whose numbers are degrading to a drastically low level such that they are on the verge of extinction.
Ecosystem: A community of living and interacting organisms of a region along with the non-living components of the region such as the climate, soil, air, water etc.
Red Data Book: A source book which keeps the information about all the endangered plants and animals.
Migration: The complete movement of the animal population from one place to another in response to the regional changes in temperature, seasons etc.
Reforestation: The process of replanting and rejuvenating the forest areas that have been destroyed or the benefits of mankind.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
- Crop Production and Management
- Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
- Coal and Petroleum
- Combustion and Flame
- Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Cell Structure and Functions
- Reproduction in Animals
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Force and Pressure
- Friction
- Sound
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Some Natural Phenomena
- Light
- Stars and The Solar System
- Pollution of Air and Water