NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 – Combustion and Flame, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 6. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 6 – Combustion and Flame, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 6 – Combustion and Flame |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 – Combustion And Flame
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 – Combustion and Flame – NCERT Exercises
Question 1
List the conditions under which combustion can take place.
Answer 1.
The conditions under which combustion can take place are-
- Air (or the presence of oxygen in air)
- Fuel
- A minimum ignition temperature
Question 2
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes_______ of air.
(b) A liquid fuel, used in homes is ________.
(c) Fuel must be heated to its ______ _______ before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by _______.
Answer 2.
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes pollution of air.
(b) A liquid fuel, used in homes is Liquefied petroleum Gas(LPG).
(c) Fuel must be heated to its Ignition temperature before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by water.
Question 3
Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Answer 3.
Fuels such as petroleum and coal on combustion produce a large amount of harmful gases such as sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. These sources can increase global warming causing greenhouse effect and also respiratory problems. CNG on the other hand is a much cleaner fuel and produces harmful gases at a much smaller quantity. Hence it has helped to reduce pollution.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 – Combustion and Flame – Video Explanation
Question 4
Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
Answer 4.
| LPG | Wood |
|---|---|
| It has a higher calorific value | It has a lower calorific value |
| It does not cause any pollution on burning as it’s smokeless | It causes more pollution on burning as it produces a lot of smoke. |
| It has a lower ignition temperature | It has a higher ignition temperature |
| It is easier to transport in cylinders and pipes | It is difficult to transport and occupies a lot of space |
Question 5
Give reasons:
(a) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not.
Answer 5.
(a)Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment because water, being a good conductor of electricity will conduct electricity across and may cause damage to the person trying to douse the fire.
(b)LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood because it has a lower ignition temperature so it burns easily and also is a smokeless fuel, thereby checking pollution
(c)Paper catches fire easily because of its low ignition temperature. When it is wrapped around an aluminium pipe then heat is conductor across paper to aluminium so the paper does not reach its ignition temperature easily.
Question 6
Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
Answer 6 –
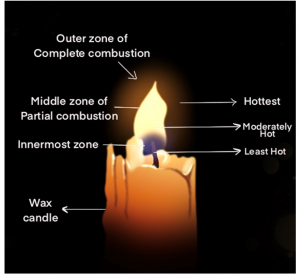
Question 7
Name the unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed.
Answer 7.
Calorific value of a fuel is expressed in Kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg)
Question 8
Explain how Carbon dioxide is able to control fires.
Answer 8.
Carbon dioxide acts as a fire- extinguisher. It forms a kind of blanket around the flame and takes away the oxygen component of the air, thus dousing off the fire. It is released at a high pressure and also reduces the temperature of the fuel supporting the fire.
Question 9
It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain.
Answer 9.
It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves because the green leaves have a lot of moisture in them thus they have a higher ignition temperature compared to the dry leaves which have a lower ignition temperature due to very little or no moisture.
Question 10
Which zone of a flame does a goldsmith use for melting gold and silver and why?
Answer 10.
A goldsmith always uses the outermost or the non-luminous portion of the flame for melting gold and silver because it is that portion of the flame which is the hottest and has the highest temperature. So, for melting gold and silver which have high melting points, a goldsmith uses these portions of the flame.
Question 11
In an experiment 4.5 kg of a fuel was completely burnt. The heat produced
was measured to be 180,000 kJ. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel.
Answer 11.
Calorific value is defined as the heat produced/ released on completely burning 1Kg of fuel. So,
Total mass of the fuel = 4.5Kg
Total Heat produced on burning = 180,000 kJ
Therefore, heat produced in burning 1Kg of fuel = 180,000 kJ/4.5 Kg = 40,000 kJ/Kg
Thus, calorific value of the fuel is 40,000 kJ/Kg.
Question 12
Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
Answer 12.
Combustion is defined as a chemical process which involves the reaction between an oxidant and fuel producing heat and light. In rusting, no heat and light are produced during the process, thus it cannot be called combustion.
Question 13
Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time?
Answer 13.
Water stored in Ramesh’s beaker will get heated in a shorter time because the outermost portion of a flame is the hottest portion of the flame.
Topics Covered in Chapter Chapter 6 – Combustion And Flame Class 8 Science :-
- What is Combustion?
- How do We Control Fire?
- Types of Combustion
- Flame
- Structure of a Flame
- What is a Fuel?
- Fuel Efficiency
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 – Combustion And Flame :-
Combustion: It is a process in which a substance chemically reacts with oxygen resulting in the generation of heat and light in the form of a flame.
Ignition temperature: It is the lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire.
Inflammable substances: The substances which catch fire very easily due to having a low ignition temperature are known as inflammable.
Rapid combustion: It is a form of combustion in which large amounts of heat and light energy are released and occurs rapidly.
Spontaneous combustion: It is type of combustion in which self-ignition takes place and the substance unexpectedly bursts into flames without any apparent cause or source of heat.
Explosion: It is also a result of combustion in which a rapid energy release and volume increase occurs resulting in release of gases, light and a loud sound.
Calorific value: The amount of heat energy released when 1Kg of a substance is completely burned/combusted. It’s unit is kilo joule per kg.
Global warming: The increase in the average temperature of the earth due to the greenhouse effect of the pollutants and other gases is known as global warming.
Acid rain: A form of rain/ precipitation in which acid falls in the form of rain. It has a lower pH than usual due to the presence of sulphuric and nitric acid oxides.
Deforestation: It is the permanent removal and clearance of a land from forests which is then later used by man for non- forest uses such as industrialisation etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
- Crop Production and Management
- Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
- Coal and Petroleum
- Combustion and Flame
- Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Cell Structure and Functions
- Reproduction in Animals
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Force and Pressure
- Friction
- Sound
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Some Natural Phenomena
- Light
- Stars and The Solar System
- Pollution of Air and Water