NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 – Materials : Metals and Non-Metals, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 4. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 4 – Materials : Metals and Non-Metals, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 4 – Materials : Metals and Non-Metals |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 – Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 – Materials: Metals and Non-Metals– Solutions to Question 1 to Question 4
Question 1
Which of the following can be beaten into thin sheets?
(a) Zinc (b) Phosphorus (c) Sulphur (d) Oxygen
Answer 1.
(a)Zinc
Question 2
Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) All metals are ductile.
(b) All non-metals are ductile.
(c) Generally, metals are ductile.
(d) Some non-metals are ductile.
Answer 2.
(c) Generally, metals are ductile.
Question 3
Fill in the blanks:(a) Phosphorus is very _________ non-metal.
(b) Metals are _______conductors of heat and __________.
(c) Iron is _________ reactive than copper.
(d) Metals react with acids to produce _________ gas.
Answer 3. (a) Phosphorus is very reactive non-metal.
(b) Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
(c) Iron is more reactive than copper.
(d) Metals react with acids to produce hydrogen gas.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 – Materials : Metals and Non-Metals – Video Explanation
Question 4
Mark ‘T’ is the statement is true and ‘F’ if the statement is false.
(a)Generally, non-metals react with acids.
(b) Sodium is a very reactive metal.
(c) Copper displaces zinc from zinc sulphate solution.
(d) Coal can be drawn into wires.
Answer 4.
(a)F
(b)T
(c)F
(d)F
Question 5
Some properties are listed in the following Table. Distinguish between metals and non-metals on the basis of these properties.
| Properties | Metals | Non-Metal |
|---|---|---|
|
Answer 5
| Properties | Metals | Non-Metal |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Appearance | Lustrous | Non-Lustrous |
| 2. Hardness | Hard except for sodium and potassium | Generally soft except diamond |
| 3. Malleability | Generally Malleable | Non-malleable |
| 4. Ductility | Generally ductile | Non-ductile |
| 5. Heat Conduction | Good Conductors | Poor Conductors |
| 6. Conduction of Electricity | Good Conductors | Poor Conductors |
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 – Materials:Metals and Non-Metals – NCERT Exercises
Question 6
Give reasons for the following:
(a) Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items.
(b) Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances.
(c) Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
(d) Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene.
Answer 6.
(a)Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items because Aluminium is one of the least reactive metals and it does not react with the food items and therefore does not alter the taste. Furthermore, Aluminium being a metal is highly malleable and can be easily beaten into sheets to wrap the food.
(b)Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances because metals are good conductors of electricity and therefore they get heated easily when current passes through the metallic substance.
(c)Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution because according to the rule, metals occurring below another metal in the metal activity series cannot displace the one above it. Zinc lies above Copper in the metal activity series. Therefore, Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
(d)Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene because both sodium and potassium are highly reactive metals and readily react with air if kept in the open. The reaction is violent, very reactive and the metals catch fire easily. As a result, they are stored in kerosene in order to prevent any damage from happening.
Question 7
Can you store lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil? Explain.
Answer 7.
No, we cannot store lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil because lemon contains around 5-8 % citric acid content and aluminium is a metal. If stored in Aluminium container, it would react with the acid liberating hydrogen gas and ultimately result in the spoilage of pickle.
Question 8
In the following Table some substances are given in Column I. In Column II some uses are given. Match the items in column I with those in Column II
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| (i) Gold | (a) Thermometers |
| (ii) Iron | (b) Electric Wire |
| (iii) Aluminium | (c) Wrapping Food |
| (iv) Carbon | (d) Jewellery |
| (iii) Copper | (e) Machinery |
| (iii) Mercury | (f) Fuel |
Answer 8.
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| (i) Gold | (d) Jewellery |
| (ii) Iron | (e) Machinery |
| (iii) Aluminium | (c) Wrapping Food |
| (iv) Carbon | (f) Fuel |
| (iii) Copper | (b) Electric Wire |
| (iii) Mercury | (a) Thermometers |
Question 9
What happens when
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate?
(b) Iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution? Write word equations of the reactions involved
Answer 9.
(a)When dilute sulphuric acid poured on a copper plate then no reaction takes place.
(b)When iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution then iron being more reactive than copper displaces copper from the copper sulphate solution resulting
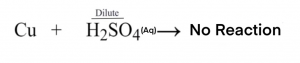
in the formation of iron sulphate and copper gets deposited on iron after being displaced.

Question 10
Saloni took a piece of burning charcoal and collected the gas evolved in a test tube.
(a) How will she find the nature of the gas?
(b) Write down word equations of all the reactions taking place in this process.
Answer 10.
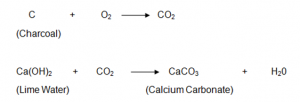
A burning piece of charcoal releases Carbon dioxide gas. In order to find out the nature of the gas, Saloni can do the lime-water test, litmus-paper test, or burning splint test:-
Carbon dioxide when passed through lime water, turns lime water milky due to the formation of Calcium carbonate. Carbon dioxide is a non supporter of combustion and therefore burning splint blows out. Further, carbon dioxide turns moist blue litmus paper red showing that it is acidic in nature.
The reactions involved is shown below:
Question 11
One day Reeta went to a jeweller’s shop with her mother. Her mother gave old gold jewellery to the goldsmith to polish. Next day when they brought the jewellery back, they found that there was a slight loss in its weight. Can you suggest a reason for the loss in weight?
Answer 11.
Premium metals like gold etc. cannot dissolve in any acid. In order to dissolve gold a combination of two acids known an aqua regia is needed which is 3 parts of concentrated HCl (Hydrochloric Acid) mixed with one part of concentrated HNO3 (Nitric Acid). When polishing gold, the jewellery is dipped in aqua regia and as a result of this the outer old covering of gold gets dissolved and the inner shiny covering is revealed. As a result of the dissolution of the outer covering of gold, a slight loss in weight is observed after polishing.
Topics Covered in Chapter 4 Materials:Metals and Non-Metals Class 8 Science :-
- Physical Properties of Metals and Non-metals
- Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-metals
- Uses of Metals and Non-metals
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4-Materials:Metals and Non-Metals:-
Malleability: The property of the metals by which they can beaten into thin sheets of metal is called malleability.
Ductility: The property of the metals by which they can be drawn into wires is known as ductility.
Sonorous: Materials which are capable of producing a deep ringing sound are referred to as sonorous.
Metals: The materials which possess sonority, malleability, ductility, are hard and lustrous and good conductors of heat and electricity are classified as metals.
Non-Metals: Materials which break down into a powdery mass on tapping with a hammer, are soft and brittle, and are poor conductors of heat and electricity are known as non-metals.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
- Crop Production and Management
- Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
- Coal and Petroleum
- Combustion and Flame
- Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Cell Structure and Functions
- Reproduction in Animals
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Force and Pressure
- Friction
- Sound
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Some Natural Phenomena
- Light
- Stars and The Solar System
- Pollution of Air and Water