NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 – Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 3. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 3 – Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 3 – Synthetic Fibres and Plastics |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 – Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 – Synthetic Fibres and Plastics– Solutions to Question 1 to Question 4
Question 1:
Explain why some fibres are called synthetic.
Answer 1.
The fibres which are man-made or artificial and are not naturally obtained are known as synthetic fibres. Nylon, rayon, and polyester are some examples of synthetic fibres.
Question 2:
Mark the correct answer.
Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because
(a) it has a silk like appearance
(b) it is obtained from wood pulp
(c) its fibres can also be woven like those of natural fibres
Answer 2.
(b) it is obtained from wood pulp
Question 3
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
(a) Synthetic fibres are also called ______ or _______ fibres.
(b) Synthetic fibres are synthesised from raw material called ________.
(c) Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a __________ .
Ans 3.
(a) Synthetic fibres are also called man-made or artificial fibres.
(b) Synthetic fibres are synthesised from raw material called petrochemicals.
(c) Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a polymer.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 – Synthetic Fibres and Plastics – Video Explanation
Question 4
Give examples which indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
Answer .
(a) It is used for reinforcement in rubber material like car tires.
(b) It is used in making seat belts, tents, curtains etc.
(c) It is used as a rope in rock climbing and in parachutes.
Question 5
Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food.
Answer 5.
Plastic containers are favoured because of the following reasons:
- Plastic is light-weight, easy to carry and handle, cheaper in price and more convenient than other materials.
- It is non-reactive so does not react with the food in containers.
Question 6
Explain the difference between the thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
Answer 6
| Thermoplastic | Thermosetting Plastics |
|---|---|
| Have week forces of attraction among chains | Have a 3-D network structure with a strong covalent bond |
| Can easily bend on the application of heat and pressure. | Resists strongly on alteration of the structure by application of heat and pressure |
| Softens on heating and solidifies on cooling | It does not soften on heating |
| Soluble in organic solvents | It is insoluble in organic solvents |
| For example – polythene | For Example – Bakelite |
Question 7
Explain why the following are made of thermosetting plastics.
(a) Saucepan handles
(b) Electric plugs/switches/plug boards
Answer 7
(a) Thermosetting plastics are used to make saucepan handles because they are bad conductors of heat, resist fire and do not get softened on heating like other plastics. For example- Melamine.
(b) Thermosetting plastics are used in making Electric plugs/switches/plug boards because they are poor conductors of electricity and heat. For example- Bakelite.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 – Synthetic Fibres and Plastics – NCERT Exercises
Question 8
Categorise the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled’ and ‘cannot be recycled’: Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ball point pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches.
Answer 8.
Can be Recycled:
(a)Plastic chairs
(b)Plastic bowls
(c)Plastic toys
(d)Plastic covering on electrical wires
(e)Carry bags
(f)Ballpoint pens
Cannot be Recycled
(a) Cooker handles
(b) Electrical switches
(c) Telephone
Question 9
Rana wants to buy shirts for summer. Should he buy cotton shirts or shirts made from synthetic material? Advise Rana, giving your reason.
Answer 9.
Rana is advised to purchase a cotton shirt in summer because cotton is a good absorber of sweat and has pores which facilitate easy evaporation of sweat allowing the person to feel cool in summer. On the other hand, synthetic materials do not absorb sweat and therefore are very uncomfortable for wearing in summers.
Question 10
Give examples to show that plastics are noncorrosive in nature.
Ans10.
Plastics are non-corrosive in nature because:
- They do not react with air and water which are essential for corrosion.
- They do not react even in the presence of strong and concentrated chemicals such as acids present in cleansing agents, pickles etc.
- Food can be stored in plastic containers in spite of the chemicals present in the food.
- Buckets which are made of iron rust over time but plastic buckets do not rust.
Question 11
Should the handle and bristles of a tooth brush be made of the same material? Explain your answer.
Ans11.
No. The handles and bristles of a tooth brush should not be made of the same material because the handle should be hard and strong for better handling and grip whereas the bristles should be soft and flexible promoting easy cleanliness and preventing damage to the gums.
Question 12
‘Avoid plastics as far as possible’. Comment on this advice.
Ans12.
We should avoid using plastics as far as possible because they are promoter of environmental pollution. Plastics are non- biodegradable. They take several years to decompose and even upon incineration they produce gases such as carbon monoxide which are hazardous to human health as well as promote global warming. Plastic bags used for carrying groceries and other items are thrown by people into the environment and are later on consumed by stray animals which may result in blocking their respiratory passage and ultimately lead to their deaths.
Question 13
Match the terms of column I correctly with the phrases given in column II.
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| (i) Polyester | (a) Prepared by using wood pulp |
| (ii) Rabi Crops | (b) Used for making parachute and stocking |
| (iii) Chemical fertilizers, urine and plant waste | (c) Used to make non-stick cookware |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Fabrics do not wrinkle easily |
Answer 13.
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| (i) Polyester | (d) Fabrics do not wrinkle easily |
| (ii) Rabi Crops | (c) Used to make non-stick cookware |
| (iii) Chemical fertilizers, urine and plant waste | (a) Prepared by using wood pulp |
| (iv) Organic manure | (b) Used for making parachute and stocking |
Question 14
‘Manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping conservation of forest’.
Comment.
Answer 14.
Yes, manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping in the conservation of forests because synthetic fibres are made from the materials which are not available in the forests and are made from manmade or artificial compounds. On the other hand, natural fibres are derived from plants and animals, so they ultimately lead to the cutting of tress and the killing of animals. Thus, synthetic fibres prevent this from happening and help preserve the ecosystem.
Question 15
Describe an activity to show that the thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
Answer 15.
In order to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity we can make use of a circuit as shown below:
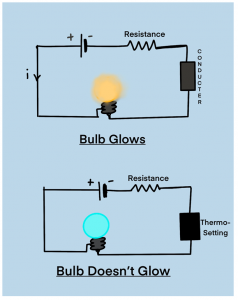
It can be clearly seen in the image above that in one circuit a conductor is used whereas in the other circuit a thermosetting plastic is used in place of it,
The circuit in which the thermosetting plastic is used, the bulb does not glow proving that there is no flow of current providing the conclusion that thermosetting plastic is a poor conductor or insulator of electricity.
Topics Covered in Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Science :-
- What are Synthetic Fibres?
- Types of Synthetic Fibres
- Characteristics of Synthetic Fibres
- Plastics
- Plastics as Materials of Choice
- Plastics and the Environment
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics:-
Synthetic Fibres: These are fibres which are made by the human beings through chemical synthesis and are not obtained naturally.
Polymer: A Polymer is a combination of various repeating sub-units joined together. They may be synthetic and may also occur in nature.
Rayon: It is also known as artificial silk and is a semi-synthetic fibre. Rayon is made from the purified cellulose fibre obtained naturally from wood pulp, but certain chemicals are also used in completing its production.
Nylon: It was first made in 1931 using nothing but coal, air and water. It was the first fully synthetic fibre, made up of long heavy chain of atoms. It is strong, elastic, lustrous, and easy to wash.
PET: It stands for Polyethylene terephthalate and is one of the most commonly used thermoplastic polymer resin used in various applications such as clothing, manufacturing, thermoforming etc.
Petrochemicals: These are the chemical compounds obtained from petroleum by refining. All synthetic fibres are derived from the petroleum origin.
Acrylic: It is more commonly known as ‘plexiglass’. It is a synthetic thermoplastic polymer that has many unique properties such as extreme strength, stiffness etc.
Polythene: It is the most commonly used plastic and is a polymer of ethylene gas. It exists as Low-Density Polythene (LDPE), High-Density Polythene (HDPE) etc. Used for various daily activities.
Thermoplastics: These are the plastic polymers that melt on heating but solidify almost indiscriminately on cooling, regaining its mechanical properties.
Thermosetting: These are cross-linked polymers that become extremely rigid upon heating and cannot be returned back to their original state.
Biodegradable: These are the substances which get degraded and decomposed upon the action of microorganisms such as bacteria. Those which do not get decomposed are known as non-biodegradable.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
- Crop Production and Management
- Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
- Coal and Petroleum
- Combustion and Flame
- Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Cell Structure and Functions
- Reproduction in Animals
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Force and Pressure
- Friction
- Sound
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Some Natural Phenomena
- Light
- Stars and The Solar System
- Pollution of Air and Water