NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 17. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and the application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 13 – Stars and The Solar System |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17-Stars and The Solar System
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System– NCERT Exercises
Question 1
Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
(a) An asteroid
(b) A satellite
(c) A constellation
(d) A comet
Answer 1.
(c) A constellation
Question 2
Which of the following is NOT a planet of the sun?
(a) Sirius
(b) Mercury
(c) Saturn
(d) Earth
Answer 2.
(a)Sirius
Question 3
Phases of the moon occur because
(a) we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
(b) our distance from the moon keeps changing.
(c) the shadow of the Earth covers only a part of moon’s surface.
(d) the thickness of the moon’s atmosphere is not constant.
Answer 3.
(a) we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
Question 4
Fill in the blanks:
(a) The planet which is farthest from the Sun is _______ .
(b) The planet which appears reddish in colour is _______.
(c) A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a _______.
(d) A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as _______.
(e) Shooting stars are actually not _______.
(f) Asteroids are found between the orbits of _______ and _______ .
Answer 4.
(a) The planet which is farthest from the Sun is Neptune.
(b) The planet which appears reddish in colour is Mars .
(c) A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a Constellation.
(d) A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as Satellite.
(e) Shooting stars are actually not stars.
(f) Asteroids are found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
Question 5
Mark the following statements as true (T) or false (F):
(a) Pole Star is a member of the solar system.
(b) Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system.
(c) Uranus is the farthest planet in the solar system.
(d) INSAT is an artificial satellite.
(e) There are nine planets in the solar system.
(f) Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope.
Answer 5.
(a) F
(b) T
(c) F
(d) T
(e) F
(f) F
Question 6
Match items in column A with one or more items in column B:
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| (i) Inner planets | (a) Saturn |
| (ii) Outer Planets | (b) Pole Star |
| (iii) Constellation | (c) Great Bear |
| (iv) Satellite of the Earth | (d) Moon
(e) Earth (f) Orion (g) Mars |
Answer 6.
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| (i) Inner planets | (e) Earth
(g) Mars |
| (ii) Outer Planets | (a) Saturn |
| (iii) Constellation | (c) Great Bear
(f) Orion |
| (iv) Satellite of the Earth | (d) Moon |
Question 7
In which part of the sky can you find Venus if it is visible as an evening star?
Answer 7.
Venus is visible in the western part of the sky after sunset. That is the reason why it is known as the evening star.
Question 8
Name the largest planet of the solar system.
Answer 8.
Jupiter is the largest planet of solar system.
Question 9
What is a constellation? Name any two constellations.
Answer 9.
A constellation is a group of stars forming a particular arrangement in the sky.
Two constellations are :
- Orion
- Great Bear
Question 10
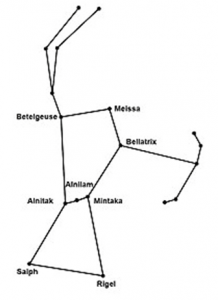
Draw sketches to show the relative positions of prominent stars in
- Ursa Major and (b) Orion
Answer 10.
(a)
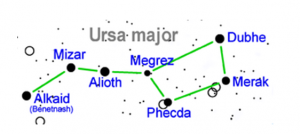
(b)
Question 11
Name two objects other than planets which are members of the solar system.
Answer 11.
Asteroids and Meteors are also a part of the solar system.
Question 12
Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answer 12.
The pole star can be located with the help of Ursa Major by the following steps:
- Locate the Ursa Major and locate the quadrilateral formed by the four stars in it
- Select the two stars on the far side of the quadrilateral
- Join these stars with a line and extend this imaginary line towards the top of the ladle
- A faint star which meets this line is the Pole Star
Question 13
Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain.
Answer 13.
No, all the stars in the sky do not move. They appear to move east to west because of the rotation of the earth from west to east. However, the pole star does no appear to move.
Question 14
Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you understand by the statement that a star is eight light years away from the Earth?
Answer 14.
The distance between stars and planets is very large so it is not convenient to express it in kilometres. That is why a bigger quantity such as a light year is used in expressing the distance between celestial objects. One light year is the distance travelled by light in one year so eight light years mean distance travelled by light in 8 years.
Question 15
The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the Earth. Calculate the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the Earth. How many Earths can Jupiter accomodate?
Answer 15.
For calculating the number of earths that can fit into Jupiter we need to calculate the volume ratio of both the planets
Volume of the earth is (4/3)πR3
And volume of Jupiter is (4/3)π(11R)3
Therefore the ratio of the volumes is
(4/3)π(11R)3 / (4/3)πR3 = volume of Jupiter / Volume of Earth = 1331:1
Therefore, we can fit 1331 earths in one Jupiter.
Question 16
Boojho made the following sketch (Fig. 17.29) of the solar system. Is the sketch correct? If not, correct it.
Answer 16.
No, the sketch is incorrect.
The problems with Boojho’s sketch included-
Neptune is the last planet instead of Uranus and the order of the planets is like Mercury – Venus – Earth – Mars – Jupiter – Saturn – Uranus – Neptune.
The correct sketch is shown below. Now Pluto has been removed as in the consideration of a planet.
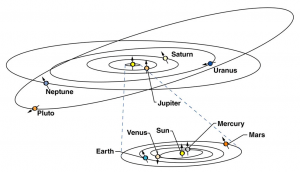
Topics Covered in Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System Class 8 Science :-
- The Moon
- The Stars
- Constellations
- The Solar System
- Some Other Members of the Solar System
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System
Celestial objects: The stars, planets, satellites, moon and many other objects that are present floating around in space are called celestial objects.
Phases of the moon: The various shapes of the bright part of the moon that are seen during any month are called the phases of the moon
Light year: The distance travelled by light in one year is called a light year.
Constellation: The stars forming a particular pattern and group in the sky is known as a constellation.
Orbit: A planet has a definite path in which it revolves around the sun. This path is elliptical in shape and is known as an orbit.
Period of Revolution: The time taken by a planet to complete one revolution around the sun is known as its period of revolution
Period of Rotation: The time taken by a celestial object to complete one rotation around its own axis is called its period of rotation
Asteroids:Small, rocky objects that revolve around the sun are known as asteroids
Meteors: Meteors are the rocky and metallic bodies that fall into the earth’s atmosphere and get heated and burned producing a long shining tail. Also known as a falling star or shooting star.
Meteorite: The meteor which is able to reach the earth is known as a meteorite.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
- Crop Production and Management
- Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
- Coal and Petroleum
- Combustion and Flame
- Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Cell Structure and Functions
- Reproduction in Animals
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Force and Pressure
- Friction
- Sound
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Some Natural Phenomena
- Light
- Stars and The Solar System
- Pollution of Air and Water