NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 15. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 help to check the concept you have learned from detailed classroom sessions and the application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 15 – Some Natural Phenomena |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15-Some Natural Phenomena
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena– NCERT Exercises
Question 1
Which of the following cannot be changed easily by friction?
(a) A plastic scale
(b) A copper rod
(c) An inflated balloon
(d) A woollen cloth.
Ans1.
(b) A copper rod
Question 2
When a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk cloth the rod
(a) and the cloth both acquire positive charge.
(b) becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge.
(c) and the cloth both acquire negative charge.
(d) becomes negatively charged while the cloth has a positive charge.
Answer 2.
(b) becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge
Question 3
Write T against true and F against false in the following statements:
(a) Like charges attract each other
(b) A charged glass rod attract a charged plastic straw
(c) Lightning conductor cannot protect a building from lightning
(d) Earthquakes can be predicted in advance
Answer 3.
(a) F
(b) T
(c) F
(d) F
Question 4
Sometime, a crackling sound is heard while taking off sweater during winters. Explain.
Answer 4.
When a sweater is taken off, it gets charged due to rubbing and friction. Because of this, an electrical discharge takes place and some energy is released in the form of a crackling sound.
Question 5
Explain why a charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand.
Answer 5.
A charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand because our hand provides the charge a passage to the ground like the process of earthing. So the charged body loses its charge on touching it.
Question 6
Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake is measured. An earthquake measures 3 on this scale. Would it be recorded by a seismograph? Is it likely to cause much damage?
Answer 6.
The device used to measure the destructive energy of an earthquake is called a Richter Scale. Yes, it would be recorded by a seismograph. No, a 3 magnitude earthquake is unlikely to cause much damage.
Question 7
Suggest three measures to protect ourselves from lightning.
Answer 7.
Three measures of protection from lightning are:
- Stay away from water. Do no take a bath during a thunderstorm
- Stay away from television and mobile phones during lightning
- Stay under a covered area or inside a room
Question 8
Explain why a charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon whereas an uncharged balloon is attracted by another charged balloon?
Answer 8.
We know that like charges repel each other whereas unlike charges attract each other. A charged balloon has the same type of charged like another charged balloon therefore they repel each other whereas an uncharged balloon is neutral so due to electrostatic induction it is induced with an opposite charge and gets attracted.
Question 9
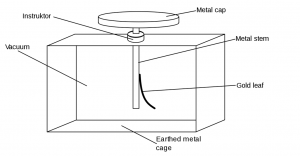
Describe with the help of a diagram an instrument which can be used to detect a charged body.
Answer 9.
An electroscope is a device that is used to detect electric charge.
It works on the principle that like charges repel each other whereas unlike charges attract each other.
Question 10
List three states in India where earthquakes are more likely to strike.
Answer 10.
Earthquakes are most likely to occur in Jammu and Kashmir, Gujarat and Assam.
Question 11
Suppose you are outside your home and an earthquake strikes. What
precaution would you take to protect yourself?
Answer 11.
The precautions to take when an earthquake occurs and we are outside are:
- We should move to an open ground or space and drop on the ground.
- We should stay away from trees and buildings
- If we are in a car or bus, we should ask the driver to slowly move to a clear spot and not come out until the tremors die out.
Question 12
The weather department has predicted that a thunderstorm is likely to occur on a certain day. Suppose you have to go out on that day. Would you carry an umbrella? Explain.
Answer 12.
No, we would not take an umbrella because carrying an umbrella further increases the chance of lightning strike as wider objects are more susceptible to lightning strikes.
Topics Covered in Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 Science :-
- Lightning
- Charging by rubbing
- Types of Charges and their Interaction
- Transfer of Charge
- The Story of Lightning
- Lightning Safety
- Earthquakes
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15-Some Natural Phenomena
Lightning: Lightning is a naturally occurring electrical discharge between storm clouds or between storm clouds and the ground releasing a large amount of energy
Electric charge: Electric charge is basic property of matter that causes it experience a force when kept in an electromagnetic field.
Electroscope: Electroscope is a scientific instrument that is used to measure the presence of electric charge on a body by observing the deflection in the gold leaves placed inside
Earthing: The process of transferring of the charge from a charged body to the ground is known as earthing. It is done to protect us from any leakage of electrical current.
Lightning conductor: Lightning conductor is a device that is used to protect the buildings from an electric discharge or lightning. It consists of a metal rod that is taller than the building itself and serves to transfer the charge from lightning to the ground.
Earthquake: Earthquake is the sudden shaking of the surface of the earth that results due to the release of the seismic waves in the lithosphere of the earth.
Seismic zones: The weak zones of the plates of the earth where the earthquakes are most likely to occur are known as the seismic or fault zones.
Richter scale: Richter scale is a scale that is used to measure the magnitude of an earthquake, that is, how severe an earthquake is. Magnitude above 7 are considered to be really destructive earthquakes.
Seismograph: Seismograph is device that is used to detect the seismic waves taking place under the surface of the earth.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
- Crop Production and Management
- Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
- Coal and Petroleum
- Combustion and Flame
- Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Cell Structure and Functions
- Reproduction in Animals
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Force and Pressure
- Friction
- Sound
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Some Natural Phenomena
- Light
- Stars and The Solar System
- Pollution of Air and Water