NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – Crop Production and Management, contains solutions to various questions in Exercise for Chapter 1. At the end of the Solutions, all the keywords and Notes which are important to understand Science Chapter 1 – Crop Production and Management Class 8, have been explained in a simple and easy to understand manner. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 help to check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and the application of your knowledge.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 1 – Crop Production and Management |
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – Crop Production and Management
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – Crop Production and Management– Solutions to Question 1 and Question 2
Question 1.
Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
a)The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called___.
b)The first step before growing crops is ________of the soil.
c)Damaged seeds would _______on top of water.
d)For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and_____and_____ from the soil are essential.
Answer 1.
a) crop
b) preparation
c) float
d) water, nutrients
Question 2.
Match items in column A with those in column B.
| (i) Kharif Crops | (a) Food for Cattle |
| (ii) Rabi Crops | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilizers, urine and plant waste | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine, and plant waste |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea
(e) Paddy and maize |
Answer 2.
| (i) Kharif Crops | (e) Paddy and Maize |
| (ii) Rabi Crops | (d) Wheat, gram, and Pea |
| (iii) Chemical fertilizers, urine and plant waste | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iv) Organic manure | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine, and plant waste |
Question 3.
Give two examples of each:
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Answer 3.
(a)Kharif crops– Paddy and maize
(b)Rabi crops– Wheat, gram, pea
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – Crop Production and Management – Video Explanation
Question 4.
Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d)Threshing
Answer 4.
(a)Preparation of soil—
The first step in the agriculture and growing of crops is the preparation of soil. Preparation of soil involves the turning and loosening of the soil allowing better penetration of the roots into the soil, adding humus to the soil and improving fertility of soil. This combined process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing.
(b)Sowing—
Sowing of the seeds is a process in which the seeds are placed in the soil and are allowed to germinate over a period of time under stable conditions. While sowing, seeds of high-quality are chosen very carefully to promote better yield of crop. Sowing of the seeds can be done by hand or with the help of a seed-drill.
(c) Weeding—
Weeds are unwanted, valueless plants growing wildly amidst the other useful crops. The process of removal of such unwanted plants is known as weeding.Weeding is usually done during the early stages of crop cultivation to promote better growth of the crops. Weeding has many advantages such as improving fertility of soil and obtaining a better yield.
(d)Threshing—
After 3 or 4 months of hard-work of the farmers comes the season of harvesting. In this season of harvesting, the crops are either pulled out or are cut down carefully to collect the yield. Threshing is the process of separation of the grains from the plant. This process can be carried out by hand and by use of animals or machines.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – Crop Production and Management – NCERT Exercises
Question 5.
Explain how fertilizers are different from manures?
Answer 5.
There are several differences between fertilizers and manures which can be stated as follows-
Fertilizers
- These are made up of inorganic or synthetic materials/salts.
- They typically contain Nitrogen, Phosphorous and potassium along with other minerals in combined forms.
- They are easily absorbed by the plants
- Does not add any humus to the soil.
Manures
- These mostly contain animal faeces, compost etc. and other organic matter obtained by decomposition.
- These are not very rich in plant nutrients compared to the fertilizers.
- They are slowly absorbed by the plants.
- They provide a lot of humus to the soil.
Question 6.
What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer 6.
Irrigation is the process of supplying water to the crops or the plants in an artificial manner according to the crop requirement at necessary intervals of time.
Two methods of irrigation which conserve water are –
- Drip irrigation – In this method of irrigation, the water is supplied directly to the roots of the plants by means of tubes/pipes running underground in the soil.
- Sprinkler irrigation- In this method of irrigation, water is sprinkled over from a central region to the crops on uneven lands.
Question 7.
If wheat is sown in the Kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer 7.
If wheat is sown in the Kharif season, the plants would get wilted and the entire crop may be destroyed. If wheat is supplied with too much water due to rainfall, it would lead to wilting of plants followed by water-clogging in the fields. Also, it needs mediocre amount of sunlight and a comparatively cooler climate, both of which are not available in the Kharif season. Thus, the quality of the harvest produced would be very poor and unsatisfactory if sown in the Kharif season.
Question 8.
Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer 8.
Continuous plantation of crops results in lack of nutrients in the soil such as potassium, nitrogen, and phosphorous. As a result of the lack of these nutrients, the farmers have to add fertilisers and manures for the soil to remain rich in the requisite minerals. If the plant is leguminous, it can replenish itself of nitrogen by nitrogen fixation. Crop rotation and occasional manuring can help diminish this problem.
Question 9.
What are weeds? How can we control them?
Answer 9.
Weeds are the unwanted, valueless plants which grow around the main crop and hinder their growth by competing with them for sunlight, water and absorption of nutrients.
Weeds can be controlled by the process of weeding.Weeding can be done manually by hand which involves the killing of the weeds by uprooting or cutting them or by chemical weedicides.
Question 10.
Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
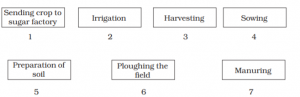
Answer10.
The following sequence is the proper order from top to bottom for sugarcane crop production-
- Preparation of soil.
- Ploughing the field.
- Sowing
- Irrigation
- Manuring
- Harvesting
- Sending crop to sugar factory
Question 11.
Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.

Answer 11.
- IRRIGATION
- STORAGE
- HARVESTOR
- GRAM
- CROP
- WINNOWING
Topics Covered in Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science :-
- Agricultural Practices
- Basic Practices of Crop Production
- Preparation of Soil
- Sowing
- Adding Manure and Fertilisers
- Irrigation
- Protection from Weeds
- Harvesting
- Storage
- Food from Animals
Important Terms Relevant to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management :-
Crop: When plants of the same type are grown and cultivated at the same place on a large scale, they are collectively called as a crop.
Tilling/Ploughing: The process of loosening and turning of the soil is known as tilling or ploughing.
Plough:Plough is a device that is pulled through the ground in order the ground to make it open into furrows for planting.
Hoe:Hoe is a simple tool with a thin, flat blade with a long handle that is used to uproot weeds and loosen the ground around a plant.
Seed drill: Seed drill is a device that is used to sow the seeds uniformly and at regular intervals and distances with the help of a tractor.
Manures:The organic fertilizers that are added by farmers in the soil to improve the fertility of the soil and to enrich the soil with nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorous, etc, are known as manures.
Fertilizers:Fertilizers are chemical, man-made artificial substances or, chemicals that are used by farmers to improve the productivity of the soil and enrich it with nutrients to improve the yield of the crops.
Irrigation:The process of supplying water artificially to the crops in a controlled manner and at needed times is called irrigation. This assists in the production of crops and is a boon to farmers.
Weeds: Weeds are the unwanted valueless plants that grow around the main crop and inhibit their development, growth and compete with them in terms of food, water and sunlight.
Leguminous: The plants that can take atmospheric nitrogen and convert them into usable inorganic compounds, used by the plants, apart from absorbing nitrogen from the soil are known as Leguminous. These are able to do so due to presence of the Rhizobium bacteria present in its nodules.
Weedicides:Weedicides are the chemicals that are used to check the growth of weeds around the plants in the fields. These are sprayed over the fields and inhibit the growth of the weeds.
Harvesting: The process of gathering the useful parts of a plant when the plants are mature is called harvesting.
Animal Husbandry:The process of controlled growth, cultivation and management of the animals to improve the quality of breeds. They are raised for their utility in future such as obtaining wool, fur, food etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
- Crop Production and Management
- Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
- Coal and Petroleum
- Combustion and Flame
- Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Cell Structure and Functions
- Reproduction in Animals
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Force and Pressure
- Friction
- Sound
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Some Natural Phenomena
- Light
- Stars and The Solar System
- Pollution of Air and Water