We may observe many types of substances that are present around us and find that they differ in shapes, size, compositions etc. Substances also differ in their purity. Some substances are pure, they are referred to as elements and compounds and some substances are impure, they are referred to as mixtures. Mixtures are further classified into solutions, colloids and suspensions. So, what is a suspension?
We know that the substances which are soluble in water form solutions or true solutions but those substances which are insoluble in water form suspensions.
Let us now define suspensions.
A suspension is a heterogenous mixture in which the small particles of a solid are spread throughout a liquid without dissolving in it.
Some common examples of suspensions are – chalk water mixture, muddy water, milk of magnesia, sand particles suspended in water, and flour in water. Chalk water mixture is a suspension of fine chalk particles in water, muddy water is a suspension of soil particles in water and milk of magnesia is a suspension of magnesium hydroxide in water. It is to be noted that solid particles and water remain separate in a suspension. The particles do not dissolve in water.
To study the properties of a suspension –
We can find out certain properties of suspensions by observing them.
If we shake some chalk powder with water in a beaker, a milky suspension is formed. We can see the fine particles of chalk suspended throughout the water without dissolving in it. If this suspension of chalk and water is kept undisturbed for some time, the chalk particles settle down at the bottom of the beaker. This means that chalk and water suspension is unstable. If we filter the suspension of chalk and water, the chalk particles are left behind as a residue on the filter paper and clear water is obtained as a filtrate. This means that chalk and water suspension can be separated into chalk and water by filtration. And if a beam of light is passed through a chalk and water suspension, it scatters the beam of light and renders its path visible inside it.
From the above discussion we can very well point out the properties of suspensions. So, all the suspensions have the following properties –
Properties of suspension –
The important characteristic properties of suspensions are:-
- A suspension is a heterogenous mixture.
- The size of solute particles in a suspension is quite large. It is larger than 100 nm in diameter.
- The particles of a suspension can be seen easily.
- The particles of a suspension do not pass through a filter paper. So, a suspension can be separated by filtration.
- The suspensions are unstable which means that if we leave a suspension for some time then we will observe that the solute particles settle down at the bottom of the beaker.
- A suspension scatters a beam of light passing through it because its particles are quite large and they are able to divert the beam of light when it strikes the solute particles.
NCERT textbook Questions –
Page 18
Question 2:-
How are sol, solution and suspension different from each other?
Answer:-
Sol is a colloid in which tiny solid particles are dispersed in a liquid medium. So, in this question, the term ‘sol’ has been used to represent a colloid (or colloidal solution). The main points of difference between solutions, sols (or colloids) and suspensions are:-
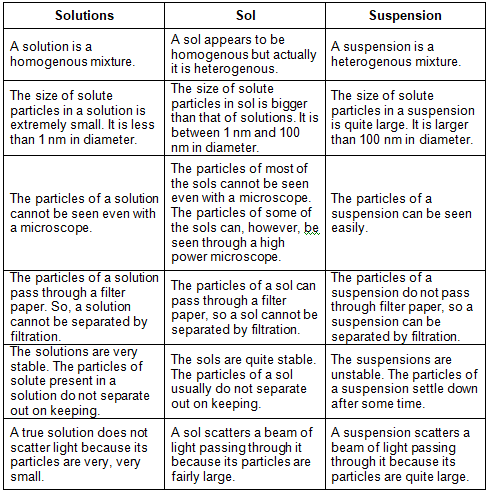
The impure substances present around us are called mixtures and these are further classified into solutions, suspensions and colloids. What is a suspension? The suspensions are heterogenous mixtures of in which small particles of solute are spread throughout a liquid without dissolving in it. Like solutions, suspensions also have some specific properties like – suspensions are heterogenous mixtures, their solute particles can be seen easily, its solute particles are quite large in size and so they are capable of scattering light, suspensions are unstable which means that if we leave them for some time then the solute particles settle down at the bottom, the constituents of a suspension can be separated by filtration.