NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.1 Arithmetic Progressions
Download NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.1 Arithmetic Progressions. Class 10th exercise 5.1 contains 4 questions, for which detailed answers have been provided in this note. If you are a class 10 students then you must be looking for class 10 maths chapter 5 exercise 5.1 solutions. Here we are providing complete solutions for arithmetic progressions class 10 chapter 5. These solutions will help you in preparing your class 10 maths board exams. Arithmetic Progression class 10th math exercise 5.1 NCERT Solutions have been explained in a simple and easy-to-understand language to help you learn and prepare for your upcoming class 10 Maths exams. Here we are sharing Arithmetic Progressions class 10th exercise 5.1 solution.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 10 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 5 |
| Exercise | Exercise 5.1 |
| Chapter Name | Arithmetic Progressions |
NCERT solutions For class 10th exercise 5.1 Maths chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions
1. In which of the following situations, does the list of numbers involved make an arithmetic progression, and why?
(i) The taxi fare after each km when the fare is ₹15 for the first km and ₹8 for each additional km.
Solution: Taxi fare for 1st 1 km = ₹15.
Taxi fare for first 2 km = ₹15 + ₹8 = ₹23
Taxi fare for first 3 km = ₹23+₹8 = ₹31
Taxi fare for first 4 km = ₹31+₹8 = ₹39
Therefore, we observe that 15, 23, 31, 39….. forms an A.P. because the common difference for each km is the same i.e. 8.
Hence, the given situation makes an arithmetic progression.
(ii) The amount of air present in a cylinder when a vacuum pump removes (1/4) of the air remaining in the cylinder at a time.
Solution: Let V be the initial volume of air in the cylinder.
After pump remaining volume of air = V – (1/4)V = (3/4)V.
After pumping 2nd time volume of air = V- (1/4)²V = (9/16)V = (3/4)²V
After pumping 3rd times volume of air = V- (1/4)³V = (3/4)³V
Therefore, we observe that (3/4)V, (3/4)²V, (3/4)³V …… not form arithmetic because the common difference is not the same.
(iii) The cost of digging a well after every meter of digging, when it costs ₹150 for the first meter and rises by ₹50 for each subsequent meter.
Solution:
Cost of digging for 1st meter = ₹150.
Cost of digging for 2nd meter = 150+50 = ₹200
Cost of digging for 3rd meter = 200+50 = ₹250
Cost for 250+50 = ₹300
Therefore, we observe that 150, 200, 250, 300 ……. forms an A.P. because the common difference is same i.e, 50
Hence, the given situation makes an arithmetic progression.
(iv) The amount of money in account every year, when ₹10000 is deposited at compound interest at 8% per annum.
Solution: Here P = 10000, r = 8% t = 1 year
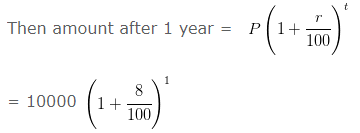
= 10000 x (108/100)
= 10800
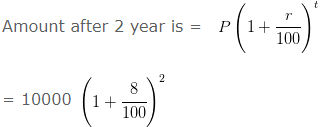
= 10000 x (108 x 108/100 x 100)
= 108×108
= 11664
So the interest after 1 year is = 10800-10000 = 800
Interest after 2 year is = 11664-10000 = 1664
Hence the difference is not the same for both years. So, the given situation is not an arithmetic process.
2. Write the first four-term of AP, when the first term a and the common difference d are given as follows:
Solution: We know that if a be the first term and d be the common difference of an AP then AP is given by
a, a+d, a+2d, a+3d, a+4d, ….
(i) a = 10, d = 10
Solution: The AP is given by
10, 10+10, 10+2×10, 10+3×10, 10+4×10, ….
10, 20, 30, 40, 50, …..
Therefore, the first four terms of this AP are 10, 20, 30, 40.
(ii) a = -2, d = 0
Solution: The AP is given by
-2, -2+0, -2+2×0, -2+3×0,….
-2, -2, -2, -2,…
Therefore, the first four terms of this AP are -2, -2, -2 and -2
(iii) a = 4, d = -3
Solution: The AP is given by
4, 4+(-3), 4+2×(-3), 4+3(-3),…
4, 4-3, 4-6, 4-9,…
4, 1, -2, -5,…
Therefore, the first four terms of the AP are 4, 1, -2 and -5.
(iv) a = -1, d = 1/2
Solution: The AP is given by
-1, -1+ (1/2), -1+2×(1/2), -1+3×(1/2),…
-1, (-1/2), -1+1, -1+ (3/2),…
-1, (-1/2), 0, (1/2), …
Therefore, the first four terms of this AP are -1, (-1/2), 0, and (1/2).
NCERT solutions for class 10th math exercise 5.1
Question 3. For the following APs write the first term and the common difference:
Solution: We know that if a1, a2, a3, a4,… be an AP then the first term is a1 and the common difference is d = (a2- a1)
(i) 3, 1, -1, -3, ….
Solution:
First term = 3
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1 = 1-3 = -2.
(ii) -5, -1, 3, 7, ….
Solution:
First term = -5
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1 = -1-(-5) = -1+5 = 4.
(iii) 1/3, 5/3, 9/3, 13/3, ….
Solution:
First term = 1/3
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1 = (5/3) – (1/3) = 4/3
(iv) 0.6, 1.7, 2.8, 3.9, ….
Solution:
First term = 0.6
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1 = 1.7-0.6 = 1.1
4. Which of the following are APs? If they form AP, find their common difference d and write three more terms.
Solution: We know that if a1, a2, a3, a4,… be an AP then a2– a1 = a3 – a2 = a4– a3 = …= d
(i) 2, 4, 8, 16,…
Solution:
Common difference d is given by
a2-a1 = 4-2 = 2
a3-a2 = 8-4 = 4
a2-a1 ≠ a3-a2
Hence, the given series does not form an AP.
(ii) 2, 5/2, 3, 7/2, ….
Solution:
Common difference d is given by
d = a2-a1= 5/2 – 2 = 1/2
d = a3-a2 = 3-(5/2) = 1/2
d = a4-a3= (7/2) – 3 = (1/2)
a2-a1 = a3-a2 = a4-a3 = (1/2)
Hence, the given series forms an AP.
And three more terms of this AP are given by,
a5= (7/2) + (1/2) = 4
a6= 4+(1/2) = 9/2
a7= (9/2) + (1/2) = 5
(iii) -1.2, -3.2, -5.2, -7.2,…
Solution: Common difference d is given by
d = a2-a1= -3.2-(-1.2) = -3.2+1.2 = -2
d = a3-a2 = -5.2-(-3.2) = -5.2+3.2 = -2
d = a4-a3= -7.2-(-5.2) = -7.2+5.2 = -2
a2-a1 = a3-a2 = a4-a3 = -2
Hence, the given series forms an AP.
And three more terms of this AP are given by,
a5= -7.2-2 = -9.2
a6= -9.2-2 = -11.2
a7= -11.2-2 = -13.2
(iv) -10, -6, -2, 2,….
Solution: Common difference d is given by
a2-a1= -6-(-10) = -6+10 = 4
a3-a2 = -2-(-6) = -2+6 = 4
a4-a3 = 2-(-2) = 2+2 = 4
a2-a1 = a3-a2 = a4-a3 = 4
Hence, the given series forms an AP.
And three more terms of this AP are given by,
a5= 2+4 = 6
a6= 6+4 = 10
a7= 10+4 = 14
(v) 3, 3+√2, 3+2√2, 3+3√2,…
Solution: Common difference d is given by
a2-a1 = 3+√2 – 3 = √2
a3-a2 = (3+2√2) – (3+√2) = √2
a4-a3 = (3+3√2) – (3+2√2) = √2
a2-a1 = a3-a2 = a4-a3 = √2
Hence, the given series forms an AP.
And three more terms of this AP are given by,
a5= 3+3√2+√2 = 3+4√2
a6= 3+4√2+√2 = 3+5√2
a7= 3+5√2+√2 = 3+6√2
(vi) 0.2, 0.22, 0.222, 0.2222,…
Solution:
Common difference d is given by
a2-a1 = 0.22-0.2 = 0.02
a3-a2 = 0.222-0.22 = 0.002
a2-a1 ≠ a3-a2
Hence, the given series does not form an AP.
(vii) 0, -4, -8, -12, ….
Solution:
Common difference d is given by
a2-a1 = -4-0 = -4
a3-a2 = -8-(-4) = -8+4 = -4
a4-a3 = -12-(-8) = -12+8 = -4
a2-a1 = a3-a2 = a4-a3 = -4
Hence, the given series forms an AP.
And three more terms of this AP are given by,
a5= -12-4 = -16
a6= -16-4 = -20
a7= -20-4 = -24
(viii) (-1/2) , (-1/2) , (-1/2) , (-1/2) , …
Solution: Common difference d is given by
a2-a1 = (-1/2) – (-1/2) = 0
a3-a2 = (-1/2) – (-1/2) = 0
a2-a1 = a3-a2 = a4-a3 = 0
Hence, the given series forms an AP.
Three more terms of this AP are given by (-1/2) , (-1/2) and (-1/2).
(ix) 1, 3, 9, 27,….
Solution:
Common difference d is given by
a3-a2 = 3-1 = 2
a4-a3 = 9-3 = 6
a2-a1 ≠ a3-a2
Hence, the given series does not form an AP.
(x) a, 2a, 3a, 4a, …
Solution:
Common difference d is given by
a2-a1 = 2a-a = a
a3-a2 = 3a-2a = a
a4-a3 = 4a-3a = a
a2-a1 = a3-a2 = a4-a3 = a
Hence, the given series forms an AP.
And three more terms of this AP are given by,
a5= 4a+a = 5a
a6= 5a+a = 6a
a7= 6a+a = 7a
(xi) a, a2, a3, a4, …
Solution: Common difference d is given by
a2-a1 = a2-a
a3-a2 = a3-a2
a2-a1 ≠ a3-a2
Hence, the given series does not form an AP.
(xii) √2, √8, √18, √32,…
Solution: The given series can be written as √2, 2√2, 3√2, 4√2,…
Common difference d is given by
a2-a1 = √8 – √2 = 2√2 – √2 = √2
a3-a2 = √18 – √8 = 3√2-2√2 = √2
a4-a3 = √32 – √18 = 4√2-3√2 = √2
a2-a1 = a3-a2 = a4-a3 = √2
Hence, the given series forms an AP.
And three more terms of this AP are given by,
a5= 4√2+√2 = 5√2
a6 = 5√2+√2 = 6√2
a7 = 6√2+√2 = 7√2
(xiii) √3, √6, √9, √12,…
Solution:
Common difference d is given by
a2-a1 = √6-√3
a3-a2 = √9-√6
a2-a1 ≠ a3-a2
Hence, the given series does not form an AP.
(xiv) 12, 32, 52, 72,…
Solution: The given series can be written as 1, 9, 25, 49, …
a2-a1 = 9 – 1 = 8
a3-a2 = 25 – 9 = 16
a2-a1 ≠ a3-a2
Hence, the given series does not form an AP.
(xv) 12, 52, 72, 73
Solution: The given series can be written as 1, 25, 49, 73, …
Common difference d is given by
a2-a1 = 25-1 =24
a3-a2 = 49-25 = 24
a4-a3 = 73-49 = 24
a2-a1 = a3-a2 = a4-a3 = 24
Hence, the given series forms an AP.
And three more terms of this AP are given by,
a5= 73+24 = 97
a6 = 97+24 = 121
a7= 121+24 = 145
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.1 Arithmetic Progressions, has been designed by the NCERT to test the knowledge of the student on the topic Arithmetic Progressions
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Ex. 5.1 Arithmetic Progressions
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Ex. 5.2 Arithmetic Progressions
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Ex. 5.3 Arithmetic Progressions
- Maths – NCERT Solutions Class 10f
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
