What is a colloidal solution?
A colloid is a kind of solution in which the size of solute particles is intermediate between those in true solutions and those in suspensions. The size of solute particles in a colloid is bigger than that of true solution but smaller than those of suspension. Though colloids appear to be homogenous to us but actually they are found to be heterogenous when observed through a high-power microscope. So, a colloid is not a true solution. Some of the examples of colloids are: soap solution, starch solution, milk, ink, blood, jelly and solutions of synthetic detergents. Colloids are also called colloidal solutions.
To study the properties of colloids –
If we shake some soap powder with water in a beaker, we get a colloidal soap solution which is not perfectly transparent, it is somewhat translucent. The soap particles cannot be seen by us. If the soap solution is kept for some time, the soap particles do not settle down. If we filter the soap solution, the whole solution passes through the filter paper and no residue is left behind. All these observations indicate that the soap and water mixture is a true solution. The scattering of light by a soap solution and the examination of soap solution under a high-power microscope, however, show that soap solution is not a true solution.
In a true solution like sugar solution, the solute particles are so small that they cannot scatter light rays falling on them. If a beam of light is put on a true solution kept in a beaker in a dark room, the path of light beam is invisible inside the solution when seen from the side. The beam of light can become visible only when the solute particles are big enough to reflect light falling on them. Since the particles of a true solution do not scatter light, we conclude that they must be very, very small.
In a colloidal solution, the particles are big enough to scatter light. If a beam of light is put on a colloidal solution, kept in a beaker in a dark room, the path of light beam is illuminated and becomes visible when seen from the side. The path of light beam becomes visible because the colloidal particles are big enough to scatter light falling on them in all the directions. This scattered light enters our eyes and we are able to see the path of light beam.
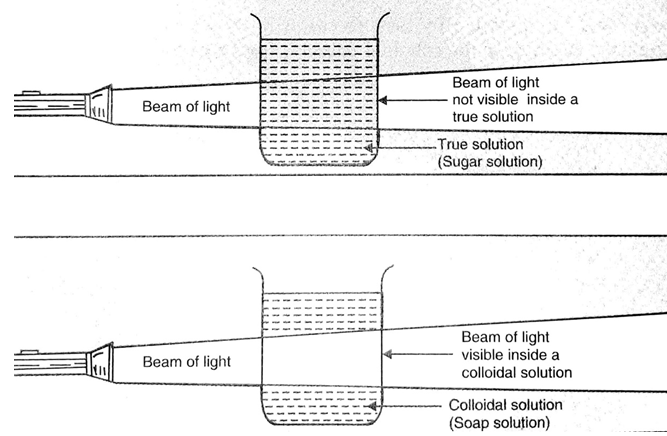
This scattering of light by colloidal particles is known as Tyndall effect. The scattering of light by colloidal solutions tells us that the colloidal particles are much bigger than the particles of a true solutions and hence colloidal solutions are not true solutions. So, a true solution can be distinguished from a colloidal solution by the fact that a true solution does not scatter a beam of light passing through it but a colloidal solution scatters a beam of light passing through it and renders its path visible. In other words, a true solution does not show Tyndall effect but a colloidal solution shows Tyndall effect.
The particles of some of the colloidal solutions can be seen through a high-power microscope. For example, if a drop of milk is examined under a microscope, we can see the small particles of fat floating in the liquid. This observation shows that colloids are heterogenous in nature, though they appear to be homogenous.
Properties of colloids –
The important characteristic properties of colloids (or colloidal solutions) are as follows:-
- A colloid or colloidal solution appears to be homogenous but actually it is heterogenous.
- The size of particles in a colloid is bigger than those in a true solution but smaller than those in a suspension. It is between 1 nm and 100 nm in diameter.
- The particles of most of the colloids cannot be seen even with a microscope.
- The particles of a colloid can pass through a filter paper. So, a colloid cannot be separated by filtration.
- The colloids are quite stable. The particles of a colloid do not separate out on keeping.
- A colloid scatters a beam of light passing through it because its particles are fairly large.
Classification of colloids –
Colloids do not involve only solids and liquids, they may also involve gases. So, colloids are classified according to the physical state of dispersed phase (solute) and the dispersion medium (solvent). Most of the colloids can be classified into the following seven groups.
- Sol
- Solid sol
- Aerosol
- Emulsion
- Foam
- Solid foam
- Gel
All these are the technical names of the groups of colloids. We will now describe all these colloids in brief.
- Sol – Sol is a colloid in which tiny solid particles are dispersed in a liquid medium. The examples of sols are – ink, soap solution, starch solution and most paints
- Solid sol – Solid sol is a colloid in which solid particles are dispersed in a solid medium. The example of a solid sol is – coloured gem stones (like ruby).
- Aerosol –An aerosol is a colloid in which a solid or liquid is dispersed in a gas(including air). The examples of aerosols in which a solid is dispersed in a gas are – smoke (which soot in air) and automobile exhausts. The examples of aerosols in which a liquid is dispersed in a gas are – hairspray, fog, mist and clouds.
- Emulsion – An emulsion is a colloid in which minute droplets of one liquid are dispersed in another liquid which is not miscible with it. Examples of emulsions are – milk, butter and face cream.
- Foam – The foam is a colloid in which a gas is dispersed in a liquid medium. The examples of foam are – fire extinguisher foam, soap bubbles, shaving cream and beer foam.
- Solid foam – The solid foam is a colloid in which a gas is dispersed in a solid medium. The examples of solid foam are – insulating foam, foam rubber, sponge and bread.
- Gel – The gel is a semi solid colloid in which there is a continuous network of solid particles dispersed in a liquid. The examples of gel are – jellies, gelatine and hair gel.
Questions related to topic (What is a Colloidal Solution) from NCERT textbook –
Page 28, 29 and 30
Question 9:-
Which of the following will show ‘Tyndall effect’?
(a) Salt solution
(b) Milk
(c) Copper sulphate solution
(d) Starch solution
Answer:-
Milk and Starch solution
What is a colloidal solution? A colloid is a kind of solution in which the size of solute particles is intermediate between those in true solutions and suspensions. Colloids are heterogenous mixtures which shows all the properties of true solutions except scattering of beam of light. The property of scattering of light by colloidal particles is known as Tyndall effect. The scattering of a beam of light renders its path visible and we are able to see the path of light from the side of the beaker. There are many types of colloids such as – sols, solid sols, aerosol, emulsion, foam, solid foam, gel.