TROPISM
The Growth movement of a plant in response to its stimulus, based on the direction of the stimulus, determines the direction of growth of the plant, referred to as TROPISM.
This Growth pattern of a plant can be based on the nature of the tropism. If the Plant bends or grows towards the stimulus, it has a positive effect on growth termed as Positive Tropism.
If the plant bends and grows away from the direction of stimulus, it has a negative effect on growth termed as Negative Tropism.
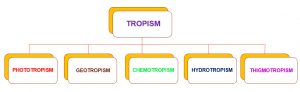
PHOTOTROPISM
This is the movement of the plant in response to light. This is a positive tropism, as the shoot of the plant grows towards sunlight.
GEOTROPISM
This is the movement of the plant in response to Gravity. This is a positive tropism, as the root of the plant grows downwards into the soil.
CHEMOTROPISM
This is when a plant responds to a Chemical. It too is a form of positive tropism. Eg the Pollen tube in a Flower grows toward the Ovules for Fertilization.
HYDROTROPISM
Roots always grow in the direction of the source of water for the development of the plant. In doing so they against the law of Gravity. They can grow upwards or sideways depending on the water source. They are said to be Hydrotropic.
THIGMOTROPISM
We may have come across situations or plants, that which upon touching close their leaves. Some plants have weak stems called Tendrils and use the support of stronger plants by winding around them and helping them grow. This is an example of positive tropism, as the weaker plant (tendril) responds to the stimulus by clinging and winding on it, enabling it to grow.
2 thoughts on “Tropism | Types of Tropism in Plants”
Thank you for the great post
Acha h