Theory of supply class 11 notes are presented in this post for easy access to the students. By taking these notes, you can stay active and engaged throughout your reading, revision, and lectures. They also help with clear thinking and understanding. Choose the most important ideas to focus on. These notes provide a useful record of important information and its sources. You’ll be able to recall better what you heard with these notes.
- Stock
- Supply
- Supply function
- Supply schedule
- Supply Curve
- Law of supply
- Change in quantity supplied
- Change in supply
- Price elasticity
Stock under Theory of supply class 11
The term “stock” refers to the total quantity of a given commodity a company has at any given time.
Or
Stock refers to the total quantity of a particular product available in a firm at a particular time.
Supply under Theory of Supply class 11
Supply refers to the number of products a company is willing to sell at a specific price during a specific period.
- To put it another way, supply is the portion of stock that is actually offered for sale in the market. There can never be less supply than stock.
- For example, a seller has 50 tonnes of sugar in storage. If the seller is prepared to sell 30 tons for Rs. 37 per kilogram, 30 tonnes of supply constitute 50 tonnes of total stock.
The definition of supply highlights the following required elements;
- Quantity of a good
- Willingness to sell
- Price of the good
- Period
Individual Supply determinants under Theory of Supply class 11
- Price of the good- (i) There is a positive relationship between the commodity’s supply and price. ii) This indicates that when the price of a commodity rises, so does the supply of that commodity, and vice versa.
- Prices of other goods- (i) Assume a company uses its resources to produce multiple products. (ii) In order to increase profits, a company produces more of other goods at a higher price than it does of goods whose prices have not changed.
- Prices of the factors of production- (i) Because the cost of producing a commodity is determined by the price of factors (rent, wages, interest, and profit), this also affects supply. (ii) A commodity’s supply curve may shift to the left due to an increase in the price of a factor of production. (iii) On the other hand, if the prices of factors fall, the supply curve moves to the right, and a producer may be able t sell more of a product at a given price.
- State of technology- (i) A company’s profit margin will rise as a result of a decrease in production costs as a result of technological advancement, thereby reversing the supply curve. (ii) The supply curve will shift to the left if goods are produced with outdated, inferior technology, which raises production costs and lowers total output.
- Objectives of the firm- (i) Occasionally, a company may be compelled to increase the supply of a product not because it is more profitable but because the product’s supply is a source of market status and prestige. (ii) A company may also increase production for the sole purpose of maximizing sales or employment.
Market supply determinants under Theory of Supply class 11
- Price of the good- (i) There is a positive relationship between the commodity’s supply and price. ii) This indicates that when the price of a commodity rises, so does the supply of that commodity, and vice versa.
- Prices of other goods- (i) Assume a company uses its resources to produce multiple products. (ii) In order to increase profits, a company produces more of other goods at a higher price than it does of goods whose prices have not changed.
- Prices of the factors of production- (i) Because the cost of producing a commodity is determined by the price of factors (rent, wages, interest, and profit), this also affects supply. (ii) A commodity’s supply curve may shift to the left due to an increase in the price of a factor of production. (iii) On the other hand, if the prices of factors fall, the supply curve moves to the right, and a producer may be able to sell more of a product at a given price.
- State of technology- (i) A company’s profit margin will rise as a result of a decrease in production costs as a result of technological advancement, thereby reversing the supply curve. (ii) The supply curve will shift to the left if goods are produced with outdated, inferior technology, which raises production costs and lowers total output.
- Objectives of the firm- (i) Occasionally, a company may be compelled to increase the supply of a product not because it is more profitable but because the product’s supply is a source of market status and prestige. (ii) A company may also increase production for the sole purpose of maximizing sales or employment.
- The number of firms in the market- Market supply also increases when the number of firms in the industry increases due to the large number of producers producing that commodity. (ii) On the other hand, if some businesses begin to leave the industry due to losses, the market supply will decrease.
- Price Expectations in the Future- (i) Current market supply will decrease to raise supply in the future at higher prices if sellers anticipate a price rise shortly. (ii) On the other hand, to avoid future losses, sellers will increase the current supply if they are concerned that prices will fall in the future.
- Transportation and communication- Maintaining a sufficient supply of the commodity is made easier by proper development of the infrastructure, such as improvements to transportation and communication methods.
Supply function
The supply function shows the functional relationship between the supply of a particular good and the factors that influence it.
- The individual supply function refers to the functional relationship between supply and the factors that influence the supply of goods.
- The market supply function refers to the function between market supply and the factors that influence the market supply of goods.
Supply schedule
The supply schedule is a table showing different quantities of goods delivered at different prices over a specific period.
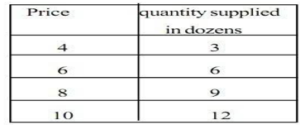
An individual supply schedule is a tabular list of different quantities of goods that a producer is willing to sell at different prices during a particular period.
The Market Supply schedule refers to a tabular list showing the different quantities of goods that all manufacturers are willing to sell at different prices during a particular period.
Supply curve
The supply curve refers to the graph display of the supply schedule.
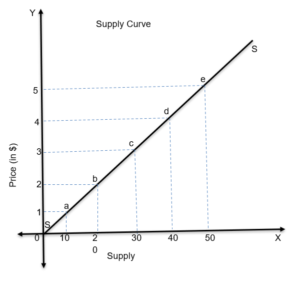
The individual supply curve refers to the graphic representation of individual supply.
The market supply curve refers to the graphical representation of the market supply plan.
Law of supply
The law of supply shows the direct relationship between the price and quantity offered while other factors remain constant.
- Other factors remain constant (Ceteris Paribus), based on the commodity’s price; it is referred to as the Law of Supply. This indicates that as the commodity’s price rises, so does the quantity supplied of it.
- Ceteris Paribus refers to (i) The price of the other product does not change. ii) Production technology shouldn’t change. (iii) Production costs remain constant. (iv) The government’s tax policy shouldn’t change. (v) The company’s goal remains constant.
Assumptions of the law of supply under Theory of Supply class 11
- Prices of other commodities are constant
- The latest technology does not change
- Factors of production prices do not change
- Taxation does not change
- Producer’s goals do not change
Important points
- A positive relationship between prices offered and Quantity is assumed to be free of changes.
- It is a quantitative statement
- It does not establish a proportional relationship
- This law is one-sided
Causes of The Law of Supply
The supply curve has a left-to-right slope because there is a positive relationship between the commodity’s price and the quantity supplied.
This is due to the following factors:
(a) Stock fluctuation: (i) As a result of the commodity’s rising price, sellers are prepared to sell more of their accumulated inventory. (ii) On the other hand, when a commodity’s price drops, sellers want to increase their inventory to avoid losing money.
(b) Loss and gain: Producers typically increase production in response to rising prices to reap greater profits, and vice versa.
c) Companies entering or exiting: (i) When a commodity’s price rises, new businesses enter the market hoping to make a profit, which increases supply. (ii) On the other hand, when prices begin to fall, marginal businesses—also known as inefficient businesses—leave the market to avoid anticipated losses, thereby reducing supply.
Exceptions of The Law of Supply under Theory of Supply class 11
- Future expectation- (i) If future price fluctuations are anticipated, the law will not apply. (ii) For instance, sellers would be prepared to sell more, even at low prices, if they anticipate further price declines in the future.
- Perishable goods- The availability of perishable products like milk, vegetables, fish, and eggs, among others, is also unaffected by the prices they charge. These items cannot be held for long by sellers.
- Agricultural goods- Natural disasters like droughts, floods, and other natural disasters have a greater impact on agricultural product supply with lower prices.
- Rare Commodities- (i) The law of supply does not apply to some precious and rare goods as well. (ii) This category includes high-quality artistic products and poems written by outstanding poets. Even when their prices rise, there is no way to increase their supply.
- Underdeveloped countries- (i) When production and supply cannot be increased due to price increases, backward countries render the law of supply inapplicable. (ii) In this case, production-critical resources are lacking.
Change in quantity supplied or movement along the supply curve.
- If other factors remain constant and the quantity of the goods on sale changes due to changes in the price itself, this is known as a change in the quantity supplied. It is also known as movement along the same demand curve.
- There can be either a downward movement or an upward movement along the same demand curve.
Expansion in supply refers to increased supply due to higher commodity prices while other factors remain constant.
Contraction in supply refers to a decline in quantity offered due to a decline in commodity prices, and other factors remain constant.
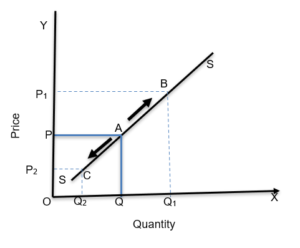
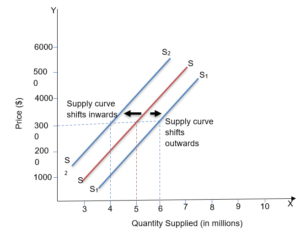
Change in supply or shift in the supply curve
- When the supply of goods changes due to changes in factors other than the price of the goods themselves, this is called a change in supply. It is also known as a shift in the supply curve.
- Changes can be made either to the right or to the left.
An increase in supply refers to an increase in the supply of goods caused by factors other than the price of the goods.
A decrease in supply refers to a decrease in the supply of the cost of goods due to factors other than the own price of the goods.
Price elasticity
The price elasticity of a supply refers to the degree to which the offer of the product reacts to price fluctuations of this product.
OR
The degree to which the quantity supplied responds to changes in supply determinants (such as the price of other commodities, production factors, technology, etc.) is referred to as supply elasticity.
- In other words, the Price elasticity of supply is the degree to which the quantity supplied response to changes in the commodity’s price.
- It is a quantitative statement indicating the magnitude of the price-related change in the quantity supplied.
Percentage method
The percentage method or the flux method is used to calculate supply price elasticity:
- According to this method, elasticity is measured as the rate of change of the quantity offered and the percentage of the price change.
- The ratio of the percentage change in the price to the percentage change in the quantity supplied is how elasticity is measured using this approach.
Es = percentage change in quantity supplied/Percentage change in price
Factors affecting Price elasticity of Supply under Theory of Supply class 11
- The nature of the product: The nature of the commodity affects supply elasticity in some way. (i) Perishable goods, on the other hand, have an inelastic supply because they cannot be increased or decreased, whereas durable goods have an elastic supply. Similarly, the supply of agricultural goods is not elastic, whereas the supply of industrial goods is.
- Production costs; (i) When production costs rise rapidly in tandem with output, there is less incentive to raise supply in response to price increases. Supply will be inelastic in such cases. (ii) On the other hand, supply will rise with price increases if production costs rise slowly with output. Supply will be more flexible in this scenario.
- Time period; (i) During the market period, a commodity’s supply is perfectly inelastic because it cannot be changed in response to a price change. (ii) Because the firm is able to alter the supply by altering the variable factors, supply is relatively less elastic over a brief period. (iii) Supply is more elastic over a long period of time because all factors can be changed, and supply can be easily adjusted in response to price changes.
- Method of production (i) A commodity’s supply will be flexible if simple production methods are used to produce it. (ii) On the other hand, complex production methods make it extremely challenging to alter supply in response to price changes.
- The availability of resources and facilities; (i) The production of a product necessitates the availability of sufficient resources as well as additional facilities like banking, power, transportation, and so on. If they are lacking, the producers feel disabled. As a result, supply becomes inflexible. (ii) On the other hand, producers can easily respond to price changes if these resources and facilities are readily available and adequate.
Types of supply elasticity under Theory of Supply class 11
- If there is an infinite supply at a certain price when the supply of such goods is called perfectly elastic, the supply will be zero, and the price will drop slightly. The perfectly elastic supply curve is a horizontal state line parallel to the x-axis
- If the supply does not change with price changes, the supply of such products is called perfectly inelastic. The perfectly inelastic supply curve is a vertical straight line parallel to the Y-axis.
- If you find that the rate of change is greater than the rate of change, then the supply of such products is considered highly elastic.
- When the percentage change in quantity supplied is less than the percentage change in price, supply is less elastic.
- If the change in quantity offered is equal to the rate of price change, then the offer of such goods is called unitary elasticity, and the supply curve is straight from the origin.
Theory of supply class 11 notes give a wholesome definition of supply and various related concepts. These notes also provide the factors affecting the price elasticity of demand. You can stay active and engaged throughout your reading, revision, and lectures by taking these notes. Additionally, they aid in clear thinking and comprehension. Selectively identify important ideas. A useful record of important information and its sources can be found in these notes. These notes will help you remember what you heard better.