There are some changes during which no new substances are formed. On the other hand, there are some other changes during which new substances are formed. So, on the basis of whether new substances are formed or not, we can classify all the changes into two groups: physical and chemical changes. We will now discuss physical and chemical changes in detail one by one.
Let us start with the physical changes.
Physical changes
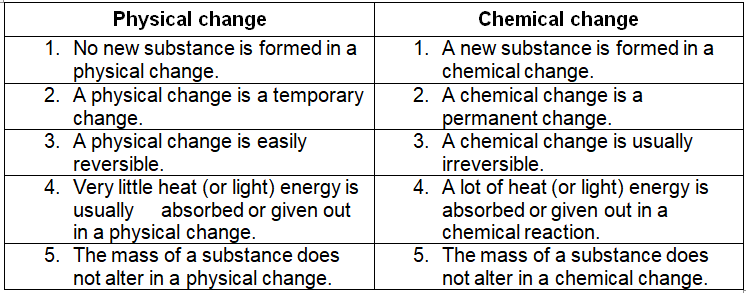
Those changes in which no new substances are formed, are called physical changes. In a physical change, the substances involved do not change their identity. They can be easily returned to their original form by some physical process. This means that the physical changes can be easily reversed. The changes in physical state, size and shape of a substance are physical changes. Some common examples of a physical changes are: Melting of ice (to form water); Freezing of water (to form ice); Boiling of water (to form steam); Condensation of steam (to form water); Making a solution; Glowing of an electric bulb; and Breaking of a glass tumbler.
The detailed explanation of some of these physical changes are given below:
- When ice is heated, it melts to form water. Though ice and water look differently, they are both made of water molecules. Thus, no new chemical substance is formed during the melting of ice. So, the melting of ice to form water is a physical change. When water is cooled (as in a refrigerator), then water solidifies to from ice. This is called freezing of water. The freezing of water to form ice is also a physical change.
- When water is heated, it boils to form steam. Though steam and water look different, they are both made of water molecules. Thus, no new chemical substance is formed during the boiling of water. So, the boiling of water to form steam is a physical change. When steam is cooled, it condenses (liquifies) to form water. The condensation of steam to form water is also a physical change.
- When an electric bulb is switched on, an electric current passes through its filament. The filament of bulb becomes white hot and glows to give light. When the current is switched off, the filament returns to its normal condition and the bulb stops glowing. No new substance is formed in the bulb during this process. So, the glowing of an electric bulb is a physical change.
- We take water in a china dish and dissolve some common salt in it. The salt disappears in water and forms a salt solution. So, a change has taken place in making salt solution. Let us now heat this china dish containing salt solution on a burner till all the water evaporates. A white powder is left behind in the china dish. If we taste this white powder, we will find that it is common salt. This means that no new substance has been formed by dissolving salt in water to make salt solution. Thus, making of a solution is a physical change.
- When a glass tumbler breaks, it forms many pieces. Each broken piece of glass tumbler is still glass. So, during the breaking of a glass tumbler, only the size and shape of glass has changed but no new substance has been formed. So, breaking of a glass tumbler is a physical change.
The physical changes are temporary changes which can be reversed easily to form the original substance. For example – the melting of ice to form water is a temporary change. We can reverse this physical change easily by cooling water to form the original substance, ice.
Chemical changes
Those changes in which new substances are formed, are called chemical changes. In a chemical change, the substances involved change their identity. They get converted into entirely new substances. The new substances usually cannot be returned to their original form. This means that chemical changes are usually irreversible. Some common examples of chemical changes are: Burning of a magnesium wire; Burning of paper; Rusting of iron; Ripening of fruits; Formation of curd from milk; and Cooking of food.
The detailed explanation of some of these physical changes are given below:
- When a magnesium wire is heated, it burns in air to form a white powder called ‘magnesium oxide’. This magnesium oxide is an entirely new substance. Thus, a new chemical substance is formed during the burning of a magnesium metal wire. So, the burning of a magnesium wire is a chemical change.
- If we burn a piece of paper with a lighted match stick then an entirely new substance like carbon dioxide, water vapour, smoke and ash are produced. So, the burning of paper is a chemical change.
The chemical changes are permanent and usually irreversible. For example – burning of paper is a permanent change which cannot be reversed. This is because we cannot combine the products of burning of paper to form the original paper once again.
Difference between Physical changes Chemical changes:-
NCERT textbook Questions–
Page 24
Question 1:-
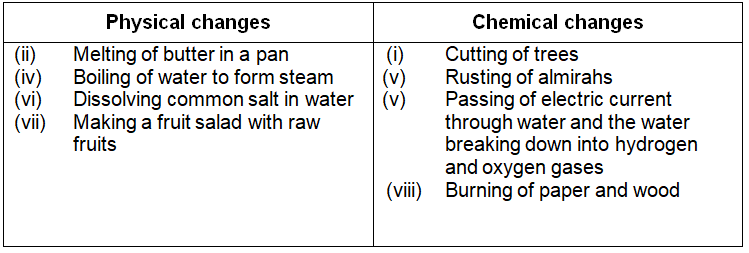
Classify the following as physical or chemical changes:
- (i) Cutting of trees
- (ii) Melting of butter in a pan
- (iii) Rusting of almirahs
- (iv) Boiling of water to form steam
- (v) Passing of electric current through water and the water breaking down into hydrogen and oxygen gases
- (vi) Dissolving common salt in water
- Making a fruit salad with raw fruits, and
- Burning of paper and wood
Answer:-
Page 28, 29 and 30
Question 11:-
Which of the following are chemical changes?
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Mixing of iron filings and sand
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
(f) Freezing of water
(g) Burning of a candle
Answer:-
Chemical changes: Growth of a plant, Rusting of iron, Cooking of food, Digestion of food and Burning of a candle.
Many changes take place around us. In some of them new substances are formed and in others no new substances are formed. These changes can be classified as physical and chemical changes. Those changes in which new substances are formed are called physical changes and in which no new substances are formed are called chemical changes. Examples of physical changes are – melting of ice, making of a solution, glowing of a bulb etc. Examples of chemical changes are – cooking of food, digestion of food, burning of magnesium wire in air etc.