Neurons
Neurons are structural and functional units of the Nervous System that carry messages (impulses) in the form of Electrical Impulses.
Parts of a Neurons
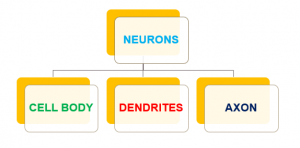
The Cell Body is the roughly round part of a neuron that contains the nucleus, mitochondria, and most of the cellular organelles.
Small tree-like structures called Dendrites extend from the cell body to pick up stimuli from the environment, other neurons, or sensory receptor cells.
Long transmitting processes called Axons extend from the cell body to send signals onward to other neurons or effector cells in the body.
Neuron Function
When a single neuron in an Effector detects a Stimulus, the Receptor sends a signal or impulse to the Dendrites which are connected to the Axon, which in turn relays the message to a next Neuron. Between each neurons is a gap called a Synapse.
This gap contains a chemical substance called a Neurotransmitter, present only on one side of the gap. Synapses act and behave like a one way street, where impulse from a neuron can only be relayed in the direction the chemical substance is present. Its in this way that impulses from millions of neurons are relayed to the Brain and Spinal Cord.
Types of Neurons
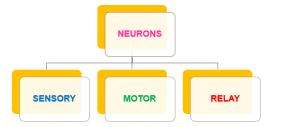
- Sensory Neurons that transmit impulses from sensory cells (receptors) to the CNS (Brain and Spinal Cord)
- Motor Neurons that transmit impulses from the CNS (Brain and Spinal Cord) towards the Effectors or muscle cells
- Relay Neurons which exist in the Brain and Spinal Cord (CNS) and serve as a link between other Neurons