Description: This article focuses on the major landforms of the earth, how they were formed and where are the places, these landforms are situated in.
Major Landforms of The Earth: Landforms are features of the earth which forms a part of the terrain and has a slope, elevation (height), special characteristic that defines the landform. The major landforms of the earth are:
- Mountain
- Hills
- Plateau
- Plains
These major landforms are formed on the surface of the earth either due to plate tectonic movements, volcanism, erosion and deposition by the rivers, winds or glacier.
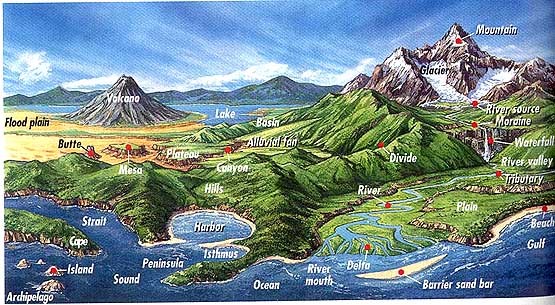
Figure 1: Showing the major landforms
It takes millions of years for these landforms to form on the surface of earth and slowly erode away. The highest landform on the surface of the earth is Mt Everest (8848m) which is part of the Himalayan mountain system.
Let us discuss about the major landforms of the earth in detail:
Mountain: Mountains and hills are conical shaped landforms produced either due to plate tectonic movements (Himalayas, Andes, Alps, Rockies Mountains) or due to volcanism. Some of the mountains and hills are also known as residual hills which are a result of erosion.
Mountains generally have a steeper slope and has an elevation higher than 2000m, while hills have gentle slopes and have a low elevation. Mountains are mostly covered by snow due to their extreme heights.
There are three category of mountains which are discussed in the following paragraphs:
1. Fold Mountains: Fold mountains are formed when two plates collide with each other, and one plate rises above the other. This gives result to crumpling of the landform. Geographers classify the fold mountains into ‘young fold mountains’ are the ‘old fold mountains’ depending upon the age of the mountains
- The young fold mountainsare between 10 and 25 million years old such as the Himalayas in Nepal, the Alps in Europe and the Andes in South America.
- Now, the old fold mountainsare older than 200 million years old such as the Aravalli mountains in India (Rajasthan) Ural mountain in Russia.
2. Block Mountains: Block mountains or horsts are also formed due to plate tectonics when the two plates move apart. Some parts of the Earth are pushed upward and others collapse down. The uplifted blocks are known as block mountains or horsts while the lowered blocks are called grabens . The examples of block mountains are the Rhine valley, Vindhya and Satpuras in India and the Vosges mountain in Europe.

3. Volcanic Mountains: Volcanic mountains are formed when the hot magma rising from the centre of the earth solidifies and cools down to form layers on the earth’s crust. It takes millions of years for volcanic mountains to form. The example of volcanic mountains is Kilimanjaro and Mount Fuji.
Plateau: A fairly level high ground with a flat top and steep sides is known as a Plateau. Plateaus are also known as a table land due to its flat top and are found mostly in drier areas.
The elevation of plateaus range between a few hundred meters to several thousand meters.
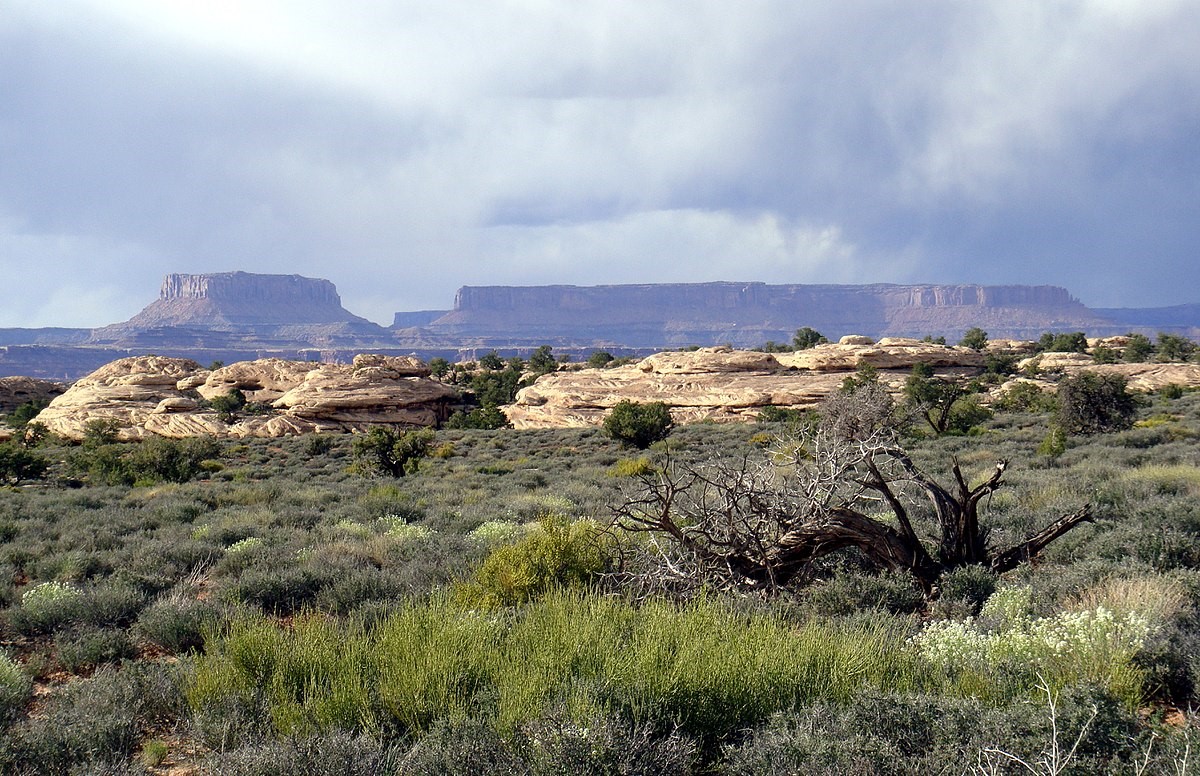

Figure 2: Showing a flat topped plateau
Plateaus mostly form due to volcanic action, for example the Deccan Plateau of India, the Tibetan Plateau which is the highest plateau in the world is also formed due to volcanic action within the earth.
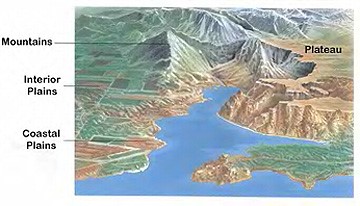
Figure 3: Showing the different landorms
Plains: Plains are level land formed mostly due to the deposition of silt and clay carried down by the rivers. This is the most fertile area where most of the population of the world lives and agriculture is the main occupation.
Many minerals are found in plains. Plains occur as lowlands along the rivers and their tributaries, for example the Indo Gangetic Plain is formed due to the deposition of silt by Ganga. Other categories of plains are coastal plains which are found along the shore lines.
Forests, Deserts and grasslands mostly occur on plains.
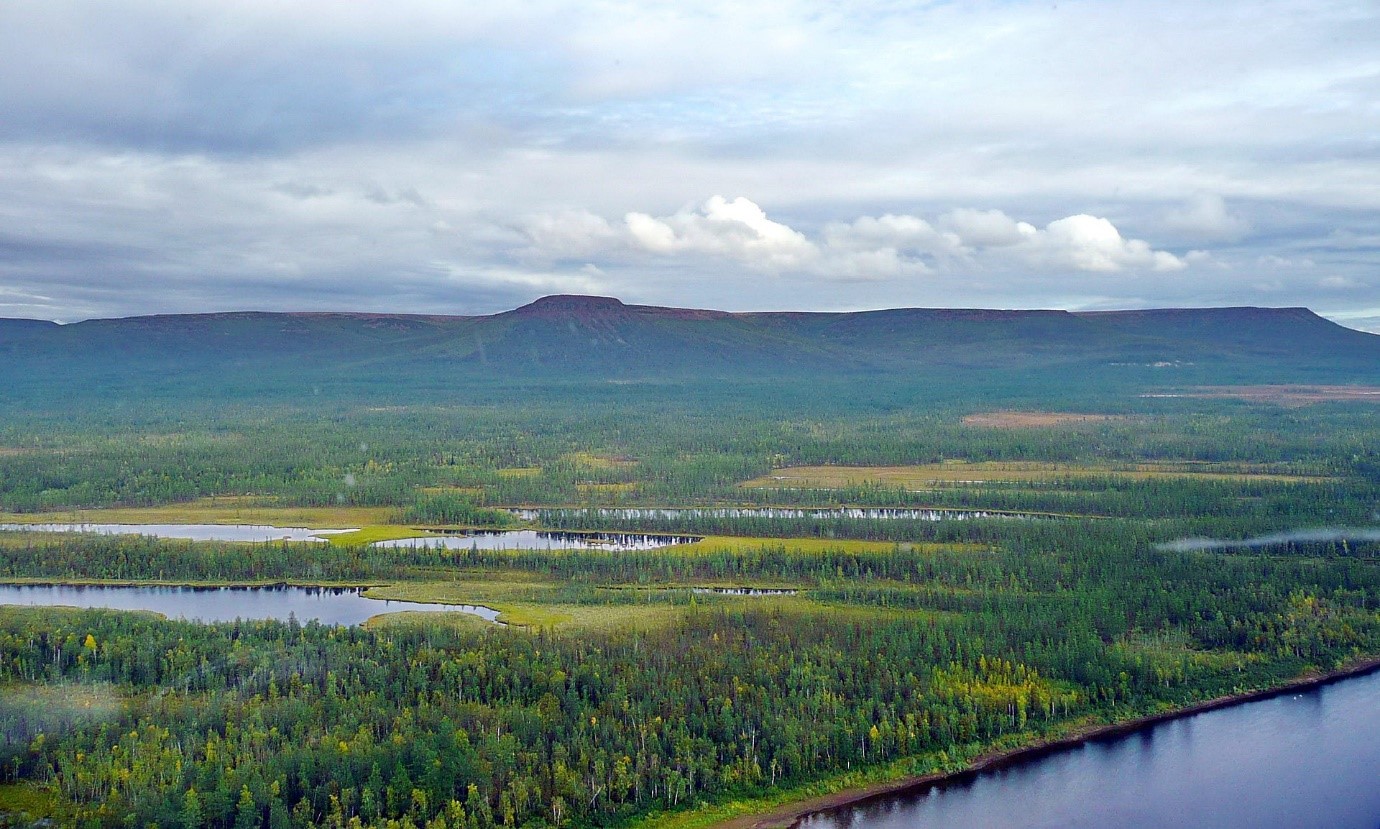

Figure 4: Image of a plain land
Landforms and the people: Since the beginning of life, people had been exploring earth and the different landforms. It has been noticed that the major section of the population prefers to stay in the plain lands rather than the hilly terrain.
The fertile lands of the plains promote cultivation, transportation lines can also be easily built. Industries and mining are also practiced with ease in the plain lands.
Mountain and plateaus are rich in many minerals such as granite, calcite, basalt, all which are hard rocks required for building purposes. Forestry, lumbering, cattle rearing are the major occupation of people living in the mountain and plateau regions.
Therefore, we now understand the various major landforms the earth has and how it is formed. We also must understand how these landforms affect the lives of people, as it is seen that, usually in the mountainous regions the climate is too cold, whereas in the plains, the weather is pleasant all around the year.