When we take a look around us, we find that substances around us are of various forms and quality. Some may be made up of one type of molecules while some may be made up of two or more types of molecules, some may be pure while some may be impure. Thus, we will look at elements, compounds and mixtures which form the base of all materials around us.
All the elements and compounds are pure substances because they contain only one kind of particles. A pure substance is homogenous throughout its mass.
Elements –
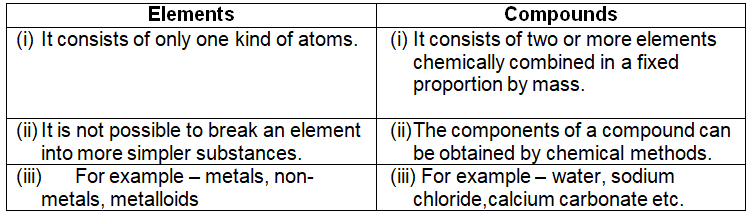
An element is a substance which cannot be split up into two or more simpler substances by the usual chemical methods of applying heat, light or electric energy. For example – hydrogen is an element because it cannot be split up into two or more simpler substances.
An element is a substance made up of only one kind of atoms. For example – copper metal is made up of only one kind of atoms.
Every substance in this world is made up of one or more of these elements. Elements can be solid, liquid or gases. Elements can be further divided into metals, non-metals and metalloids.
Compounds –
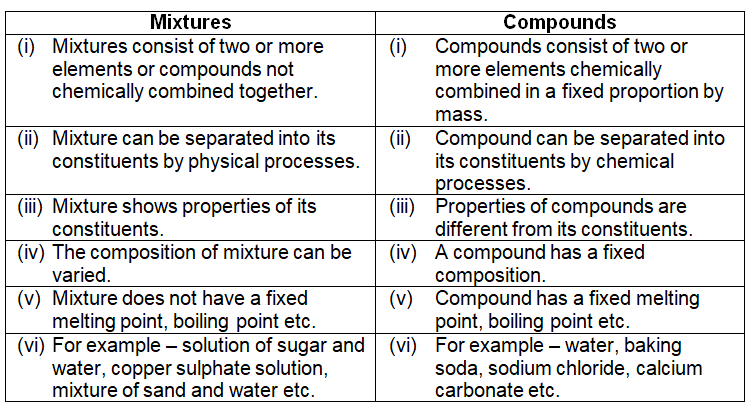
A compound is a substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion by mass. For example – water is a compound made up of two elements, hydrogen and oxygen, chemically combined in a fixed proportion 1:8 by mass.
A compound is a homogenous substance. Properties of compounds are entirely different from their constituent elements. They cannot be separated into its components by physical methods. Energy in the form of heat, light etc. is usually either given out or absorbed during the preparation of a compound. The composition of a compound is fixed, the constituents are present in a fixed proportion by mass. It has fixed melting point, boiling point etc.
Mixtures –
A mixture is a substance which consists of two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together. For example – air is a mixture of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, argon, carbon dioxide, water vapour etc., all solutions are mixtures.
The various substances present in a mixture are known as “constituents of the mixture” or “components of a mixture”. A mixture can be separated into its constituents by physical processes. It shows the properties of all the constituents present in it. Preparation of a mixture is a physical change i.e. energy is neither given out nor absorbed. In a mixture the constituents may be present in any proportion by mass. It does not have definite melting or boiling point.
There are two types of mixtures – homogenous mixtures and heterogenous mixtures
Homogenous mixtures and heterogenous mixtures –
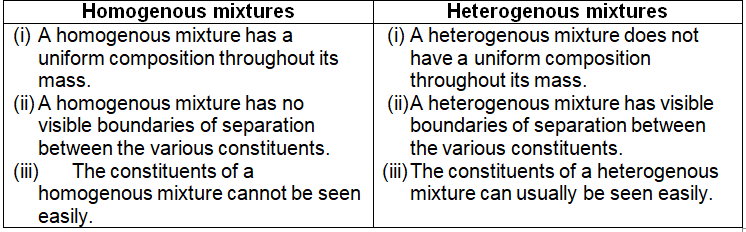
The mixture in which the substances are completely mixed together and are indistinguishable from one another are called homogenous mixtures. All homogenous mixtures are called solutions. A homogenous mixture has uniform composition throughout its mass. It has no visible boundaries of separation between its various constituent.
Those mixtures in which the various substances remain suspended and one substance is spread throughout the other substance as small particles, droplets or bubbles, are called heterogenous mixtures. A heterogenous mixture does not have uniform composition throughout its mass. It has visible boundaries of separation between the various constituents. The suspension of solids in liquids are also heterogenous mixtures.
Examples of homogenous mixture –
A solution of Sugar and water is a homogenous mixture because its components are indistinguishable from each other. There no visible boundary that separates sugar from water. The mixture has sugar distributed in it evenly. There is uniformity in its composition. Similarly, solution of salt and water, copper sulphate solution, lemonade, vinegar, alloys, air, kerosene etc. are all homogenous mixtures.
Examples of heterogenous mixture –
A mixture of oil and water is a heterogenous mixture because its components do not mix well with each other. We can easily distinguish oil layer in water as there is visible boundary between the two. Since oil does not mix with water therefore, its composition is not uniform in water. Similarly, sugar and sand mixture, polluted air, gunpowder, milk, ink, petroleum, paint, dyes, milk of magnesia etc. are all examples of heterogenous mixture.
Difference between element and compounds –
Difference between mixtures and compounds –
Questions related to the topic Elements, Compounds and Mixtures from NCERT textbook – Page 15
Question 2:-
List the points of differences between homogenous and heterogenous mixtures.
Solution:-
Questions related to the topic Elements, Compounds and Mixtures from NCERT textbook – Page 18
Question 1:-
Differentiate between homogenous and heterogenous mixtures with examples.
Solution:-
- Homogenous mixtures are those mixtures which have uniform composition throughout their mass and have no visible boundaries of separation. For example – the mixture of sugar and water is homogenous because all parts of sugar and water have same sugar-water composition. There is no boundary of separation in the mixture.
- Heterogenous mixtures are those mixtures which do not have a uniform composition throughout their mass and have visible boundaries of separation. For example – mixture of sugar and sand is heterogenous mixture because some parts will have more sugar while some parts will have more sand in them. There is also a visible boundary between the two.
Page 24
Question 2:-
Try segregating the things around you as pure substances or mixtures.
Solution:-
Pure substances – naphthalene balls, sodium chloride, distilled water, alum, graphite, baking soda
Mixtures – tap water, milk, air, gold ornaments, ice-cream, brass, salt solution, steel, wood
Questions related to the topic Elements, Compounds and Mixtures from NCERT textbook – Page 28, 29 and 30
Question 5:-
Classify each of the following as a homogenous or heterogenous mixture:
Soda water, wood, air, soil, vinegar, filtered tea
Solution:-
Homogenous mixtures – soda water, air, vinegar, filtered tea
Heterogenous mixtures – wood, soil
Question 10:-
Classify the following into elements, compounds and mixtures:
(a) sodium
(b) soil
(c) sugar solution
(d) silver
(e) calcium carbonate
(f) tin
(g) silicon
(h) coal
(i) air
(j) soap
(k) methane
(l) carbon dioxide
(m) blood
Solution:-
Elements – sodium, silver, tin, silicon
Compounds – calcium carbonate, soap, methane, carbon dioxide
Mixtures – soil, sugar solution, coal, air, blood
All types of matter present around us can be pure or impure. Substances can be classified into elements, compounds and mixtures.Elements are substances that are made up single type of atoms. For example – metals, non-metals, metalloids. Compounds are substances that are made up of two or more elements which are chemically combined in fixed proportion. For example – water, sodium chloride etc. mixtures are substances made up of two or more elements which are physically combined but not in fixed proportion.
Mixtures are of two types – homogenous and heterogenous. Homogenous mixtures are uniform in composition and have no visible boundaries. For example – solution of sugar and water. Heterogenous mixtures are non-uniform in composition and have visible boundaries between their constituents. for example – mixture of sand and water.