Whole Numbers Examples, deals with various concepts which are as under:-
- Whole Numbers Definition
- Successor of a Whole Number
- Predecessor of a Whole Number
- Consecutive Whole Numbers
- Compare numbers on whole number line
- Division algorithm
- Distributive Law Of Multiplication Over Addition
- Distributive Law of Multiplication over Subtraction
Whole Numbers Definition
Whole Numbers are non-negative number. The set of natural numbers, denoted N, can be defined in either of two ways: N = {0, 1, 2, 3……….}. So 0 is the smallest whole number and only non-negative natural numbers are known as whole numbers but all whole numbers are natural numbers.
Whole Numbers Examples – Successor of a Whole Number
The “Successor” of any whole number is the number, obtained by adding 1 to that number.
Example 1
Find the successor of 85265
Explanation
The “Successor” of any whole number is the number, obtained by adding 1 to that number
So, the successor of 85265 is 85265 + 1 = 85266
Whole Numbers Examples – Predecessor of a Whole Number
The “Predecessor” of any whole number is the number obtained by subtracting 1 from it
Example 2
Find the predecessor of 85265 ?
Explanation
The “Predecessor” of any whole number is the number obtained by subtracting 1 from it
So, the predecessor of 85265 is 85265 – 1 = 85264
Whole Numbers Examples – Consecutive Whole Numbers
Example 3
Write the three whole numbers occurring just after 40053
Explanation
The next three whole number of 40053 can be obtained by adding 1, 2 and 3 to 40053
that is,
40053 + 1 = 40054
40053 + 2 = 40055
40053 + 3 = 40056
Hence the next three whole numbers of 40053 are 40054 , 40055 , 40056 respectively
Whole Numbers Examples – Compare numbers on whole number line
The smaller number comes on the left side of the whole number line and bigger number comes on the right side of the whole number line.
Example 4
In the following pairs of number, state which number will be on right hand side of the whole number line?
( 589 , 362 )
Explanation
We know that the smaller number comes on the left and bigger number comes on right on the whole number line.
So between 589 and 362
362 is smaller number
So, 362 will be on left hand side while 589 will be on right hand side
362 < 589
Hence, 589 will be on right hand side of the whole number line
Example 5
In the following pairs state which number will be on left hand side of the whole number line?
( 563 , 693 )
Explanation
We know that the smaller number comes on the left and bigger number comes on right on the whole number line.
So, between 563 and 693
563 is smaller number
Since, 563 will be on left hand side while 693 will be on right hand side
563 < 693
Hence, the number on the left hand side would be 563
Whole Numbers Examples – Division algorithm
According to Division Algorithm,
dividend = (divisor x quotient) + remainder
Example 6
Find the number which when divided by 89 gives 4 as quotient and 6 as remainder
Explanation
Given,
Divisor = 89
Quotient = 4
Remainder = 6
In this question we have to use division algorithm
dividend = (divisor x quotient) + remainder
= ( 89 x 4 ) + 6
= 356 + 6
= 362
Hence, the dividend is 362
Example 7
If the Dividend = 6451 , quotient = 7 and remainder = 4 , find the Divisor ?
Explanation
Given,
Dividend = 6451
Quotient = 7
Remainder = 4
In this question we have to use division algorithm
dividend = (divisor x quotient) + remainder
dividend – remainder = divisor x quotient
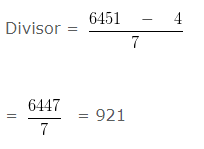
Hence, the divisor is 921
Whole Numbers Examples – Distributive Law Of Multiplication Over Addition
According to Distributive law of multiplication over addition, If a, b and c are Whole Numbers then,
a x (b + c ) = (a x b) + (a x c )
Example 8
Find the value of the following:-
( 635 x 63 ) + ( 67 x 635 )
Explanation
It follows Distributive law of multiplication over addition
Which states that a x (b + c ) = (a x b) + (a x c )
Here, a = 635
b = 63
c = 67
This question is in the form of (a x b) + (a x c )
That is, ( 635 x 63 ) + ( 67 x 635 )
( 635 x 63 ) + ( 635 x 67 ) ( NOTE : Whole number satisfy commutative property under multiplication)
i.e (a x b) = (b x a)
Here, we have 67 x 635 = 635 x 67
By distributive law, = 635 x ( 63 + 67 )
= 635 x 130
= 82550
Whole Numbers Examples – Distributive Law of Multiplication over Subtraction
According to Distributive law of multiplication over subtraction, If a, b and c are Whole Numbers then,
a x ( b – c ) = (a x b) – (a x c)
Example 9
Solve:
11 x ( 9 – 5 )
Explanation
Here, we have two method to solve this question
By Distributive law of multiplication over subtraction a x ( b – c ) = (a x b) – (a x c)
here,
a = 11
b = 9
c = 5
1 Method
a x (b – c)
11 x ( 9 – 5 )
= 11 x 4
= 44
2 Method
(a x b) – (a x c)
( 11 X 9 ) – ( 11 x 5 )
= 99 – 55
= 44