This Article discusses the following : –
- What is a map,
- Different types of maps,
- Various uses of maps ; and
- Key components which help us understand different symbology within a map.
What is a Map?
What are Maps ?
Maps are 2-Dimensional representation of the spherical earth on a flat surface. Maps are usually made on paper and depicted with various symbols and colours.
Main function of a Map ?
The main function of a map is to illustrate and describe a particular area in detail.
There are various kinds of maps such as physical maps, political maps, topographical maps etc. They represent various features of the earth- both natural and man-made.
A list showing natural and man-made features that are depicted in maps are given below:
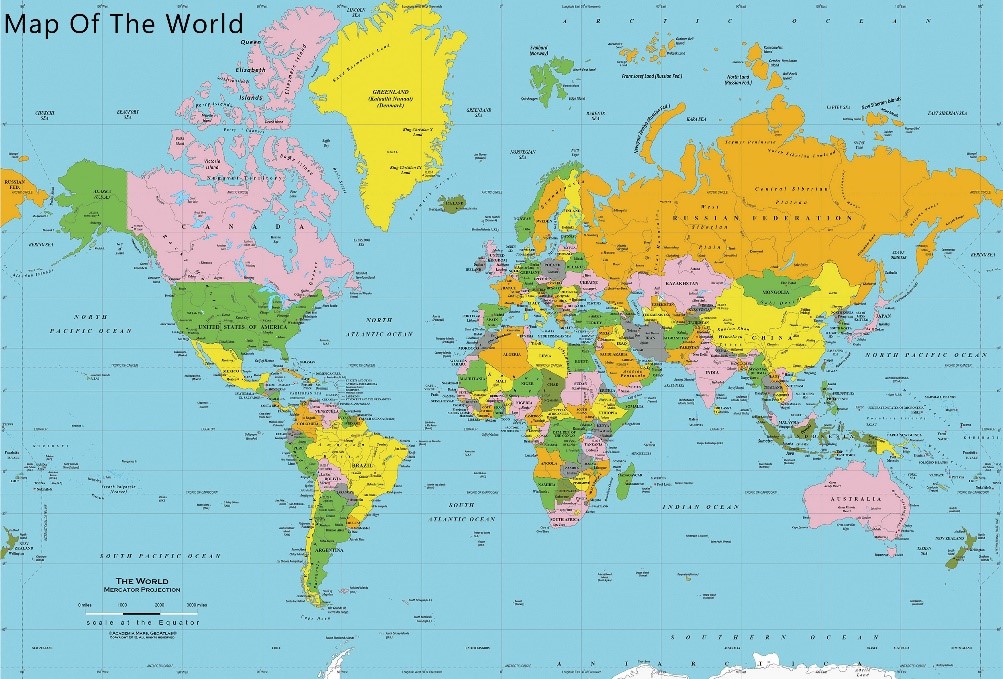
Figure 1:Map of the World
Uses of Maps:
Maps are of great importance not only to geographers but also, navigators, planners, researchers, soldiers and so on. Some of the prime uses of maps are given below:
- We can represent a vast number of objects on a small surface.
- We can also estimate the time and distance needed to travel from one place to another.
- We can understand how the population is spread over the land.
- We understand the natural relief of a place with the help of topographical maps.
- It is vital for planning purposes.
Different Types of Maps:
There are various categories of maps, some which represent the topography of a place and are called physical maps. The other category deals with administrative boundaries, capitals of states, important cities and roads. This type is called a political map.
-
What is a physical map?
Physical maps aim to show the terrain, relief, slope, natural vegetation, rivers, lakes and oceans of a place. This is extremely important for us, geographers, to determine the ruggedness of a place.
Whether a country or state is located on the mountainous region of Himalayas, whether it is located close to the sea or is it on the plain lands. Physical maps also help us to understand whether the city or state will have a cold climate or will it be extremely hot. Rivers are also present in physical maps.
The physical map of India below shows the different aspects of relief in India. Note the Legend, Title and the Northline.
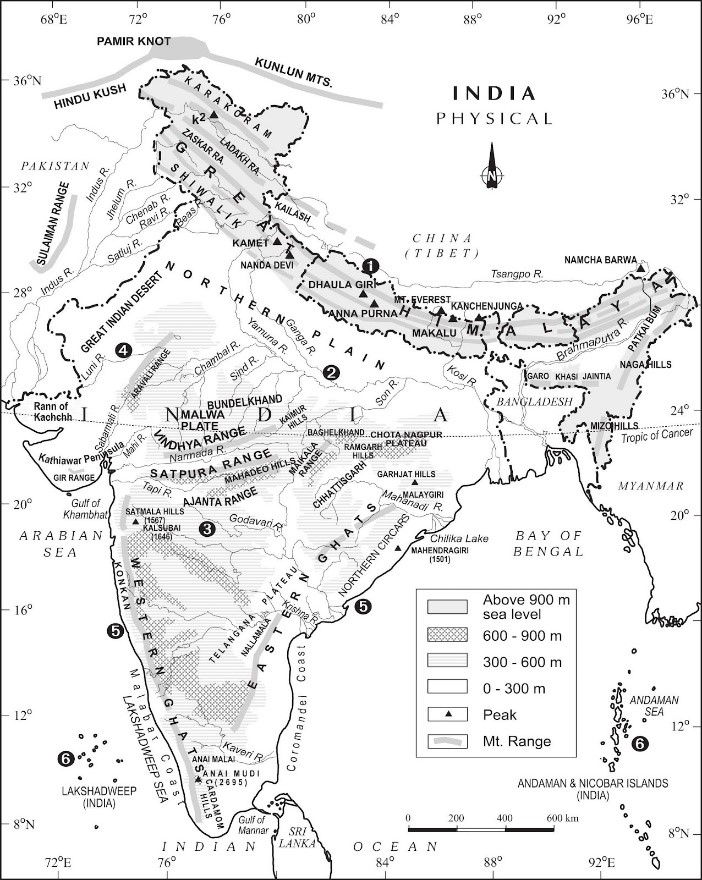
Figure 2: Physical Map of India
-
What is a political map?
Political maps comprise of important administrative boundaries like international boundaries for example, the boundary between India and Pakistan or India and Bangladesh help us differentiate between the territory of two different countries.
State boundaries separate the different states and are important aspects in regional planning. Political maps may also contain the important cities and capitals.
The image below shows a Political Map of India with the neighbouring countries and the international boundaries.
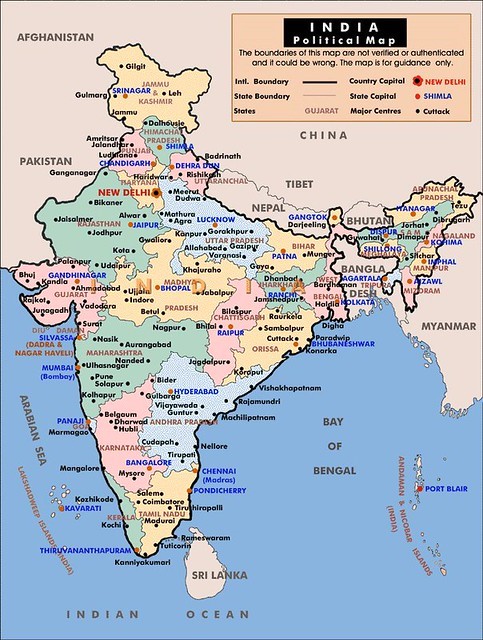
Figure 3: Political Map of India
Components of Map:
A map does not only have the image or a picture of a state there are some other important components of a map such as the title, the date when it was published, the scale, the latitudes and longitudes etc.
- Title: This state whether the Map is a physical map, a political map or a special map depicting a particular feature for example: Population Map of India. The title must possess the name of the country or state which is represented on the map. Example: Drainage Map of India, Political Map of Australia, Topographical Map of Orissa.
- Legend (or Key): Many maps are represented either by colours or symbols because it may look extremely clustered to put in all details on the map itself. Therefore, in the bottom left or right corner, there are legends to explain what a particular colour or symbol means. For example, Yellow depicts desert area, Green depicts plain land, Brown depicts hilly region.
- Scale: Maps may show and illustrate as big a feature as the world or it may depict a small area such as a city. Accordingly the scales of a map is either a large scale map or a small scale map.
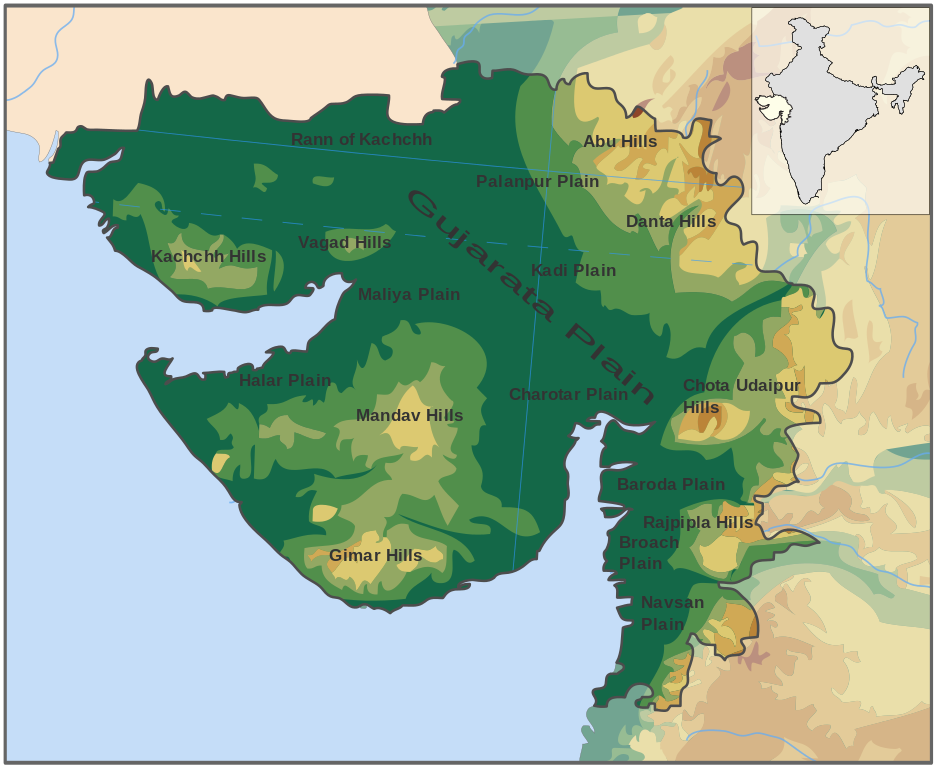
Figure 4: Map Showing the Physical Aspects of Gujarat
- Compass Direction: A map contains latitudes and longitudes, which are imaginary lines to locate any point on the earth. Some maps may only contain a North arrow such as Ꙟ to show the Direction of North.
- Date: This important aspect, explains when the map was created or published.
Thus we understand that maps are extremely important for us geographers to understand the physical as well as cultural features of the world. It helps us to calculate and estimate the area, perimeter, distance to travel from one place and the other. Modern cartographic tools now make map making extremely interesting.
1 thought on “What is Map – Uses of Maps, Types of Maps, Components of Maps”
Use full for students