NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 – Lines and Angles. This Exercise contains 6 questions, for which detailed answers have been provided in this note. In case you are looking at studying the remaining Exercise for Class 9 for Maths NCERT solutions for Chapter 6 or other Chapters, you can click the link at the end of this Note.
To practice Lines and Angles Class 9 Exercise 6.2, you may have to clear you concept for the Basic terms used in Lines and Angles Class 6. We have explained important terms, concepts and definitions , which are used for Lines and Angles Class 9 in an interesting and easy-to-understand manner. Every effort has been made to clear every concept in a simple or easy language. To understand basic terms and definitions Click here .
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Lines and Angles

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 – Lines and Angles, has been designed by the NCERT to test the knowledge of the student on the following topics:-
Important terms and Definitions for Lines and Angles Class 9
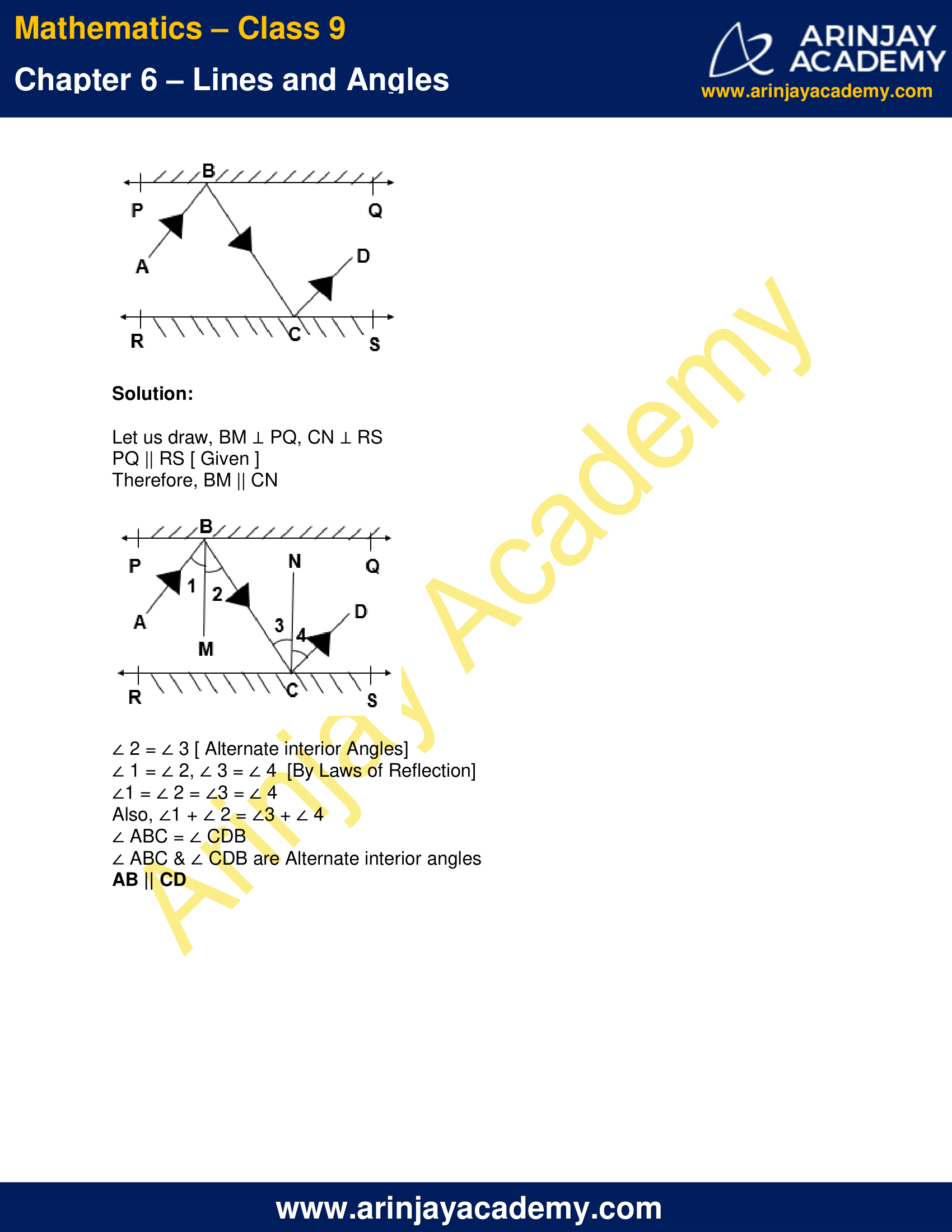
- INTERSECTING LINES
Two lines are said to be intersecting if they have a common point.
Let say two lines ‘l’ and ‘m’ are intersecting to each other and they have a common point ‘O’. This point is called Point of Intersection.
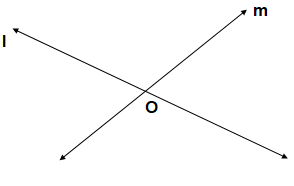
- PARALLEL LINES
Two lines l and m are said to be parallel if:
They lie on the same plane
They do not intersect however far they are extended.
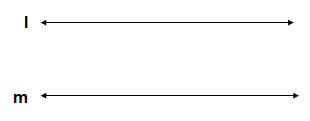
- TRANSVERSAL
A line which intersects two or more lines at distinct points is called transversal.
- ANGLES FORMS BY TRANSVERSAL LINES:
Let two parallel lines ‘l’ and ‘m’ cut by a transversal line ‘p’, forming angles as shown below:
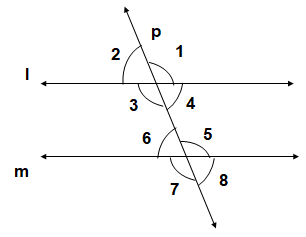
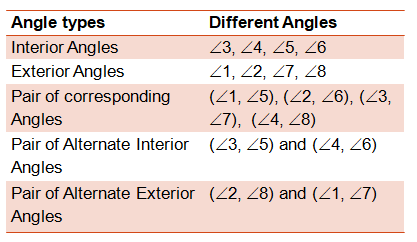
The next Exercise for NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.3 – Lines and Angles can be accessed by clicking here.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Lines and Angles
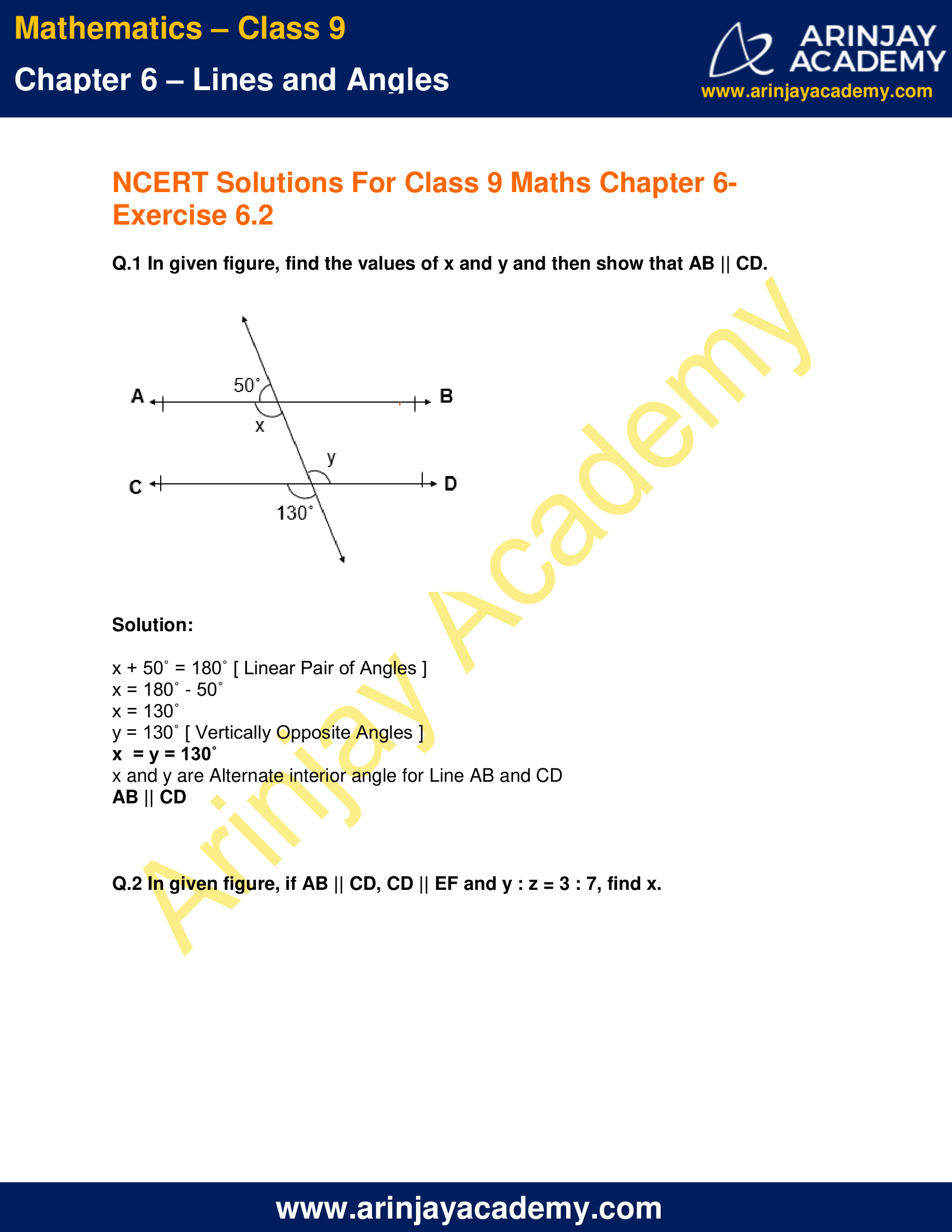
Q.1 In given figure, find the values of x and y and then show that AB || CD.
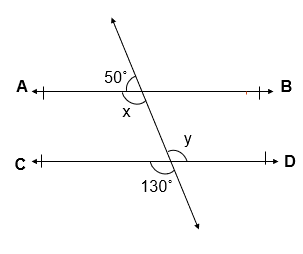
Solution:
x + 50˚ = 180˚ [ Linear Pair of Angles ]
x = 180˚ – 50˚
x = 130˚
y = 130˚ [ Vertically Opposite Angles ]
x = y = 130˚
x and y are Alternate interior angle for Line AB and CD
AB || CD
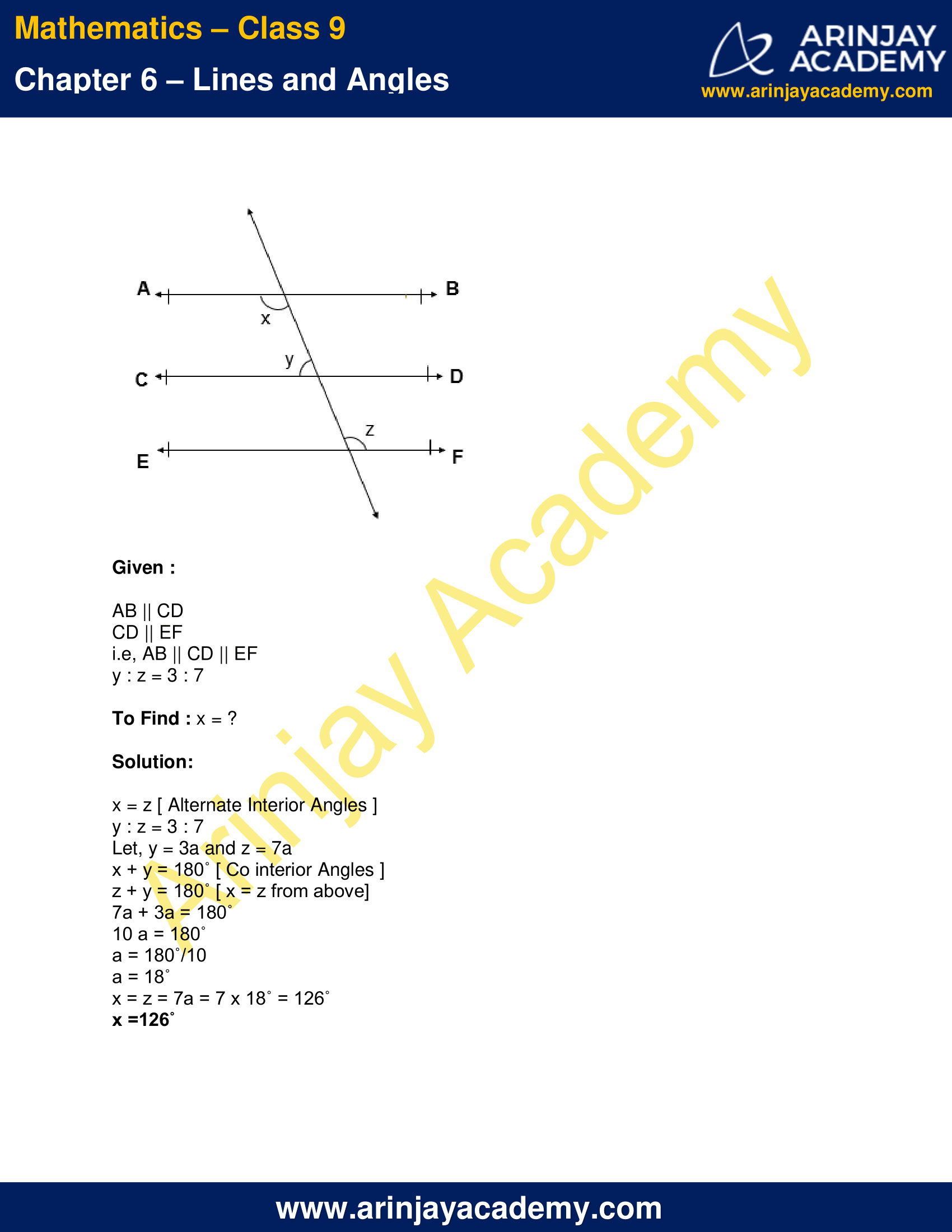
Q.2 In given figure, if AB || CD, CD || EF and y : z = 3 : 7, find x.
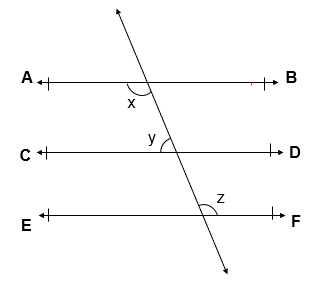
Given :
AB || CD
CD || EF
i.e, AB || CD || EF
y : z = 3 : 7
To Find : x = ?
Solution:
x = z [ Alternate Interior Angles ]
y : z = 3 : 7
Let, y = 3a and z = 7a
x + y = 180˚ [ Co interior Angles ]
z + y = 180˚ [ x = z from above]
7a + 3a = 180˚
10 a = 180˚
a = 180˚/10
a = 18˚
x = z = 7a = 7 x 18˚ = 126˚
x =126˚
Q.3 In given figure, if AB || CD, EF ⊥ CD and ∠ GED = 126°, find ∠ AGE, ∠ GEF and ∠ FGE
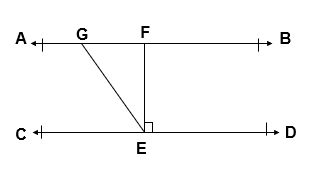
Given :
AB || CD
EF ⊥ CD
∠ GED = 126°
To Find :
∠ AGE = ?
∠ GEF = ?
∠ FGE = ?
Solution:
∠ AGE = ∠ GED = 126° [ Alternate Interior Angles ]
∠ GED = 126° [ Given ]
∠ GEF + ∠ DEF = 126°
∠ GEF + 90° = 126°
∠ GEF = 126° – 90°
∠ GEF = 36°
∠ AGE + ∠ FGE = 180° [ Linear Pair of Angles ]
126° + ∠ FGE = 180°
∠ FGE = 180° – 126°
∠ FGE = 54°
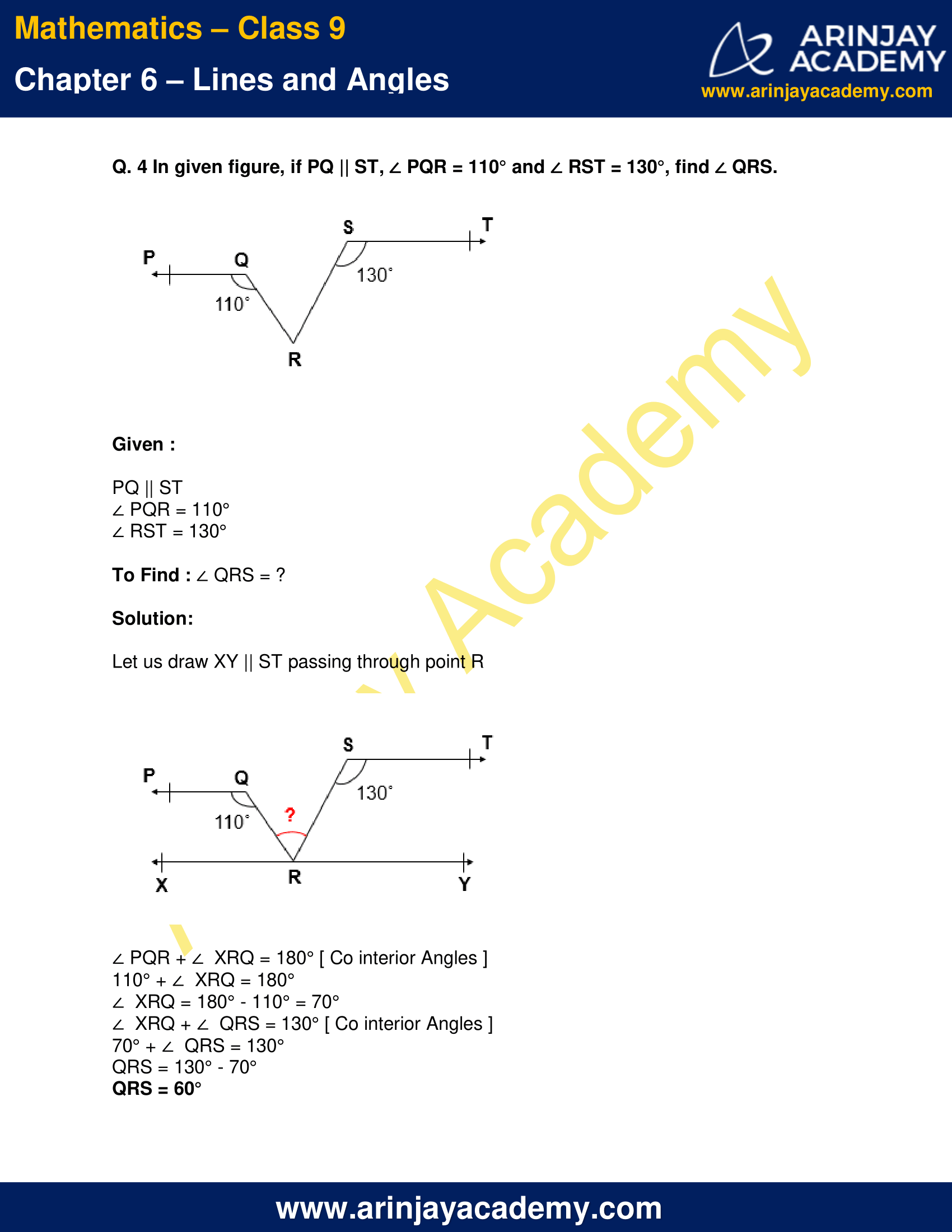
Q. 4 In given figure, if PQ || ST, ∠ PQR = 110° and ∠ RST = 130°, find ∠ QRS.
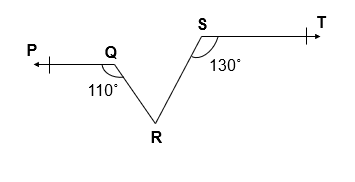
Given :
PQ || ST
∠ PQR = 110°
∠ RST = 130°
To Find : ∠ QRS = ?
Solution:
Let us draw XY || ST passing through point R
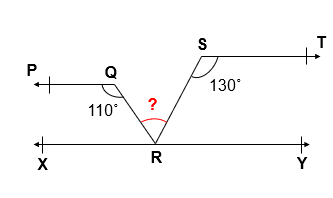
∠ PQR + ∠ XRQ = 180° [ Co interior Angles ]
110° + ∠ XRQ = 180°
∠ XRQ = 180° – 110° = 70°
∠ XRQ + ∠ QRS = 130° [ Co interior Angles ]
70° + ∠ QRS = 130°
QRS = 130° – 70°
QRS = 60°
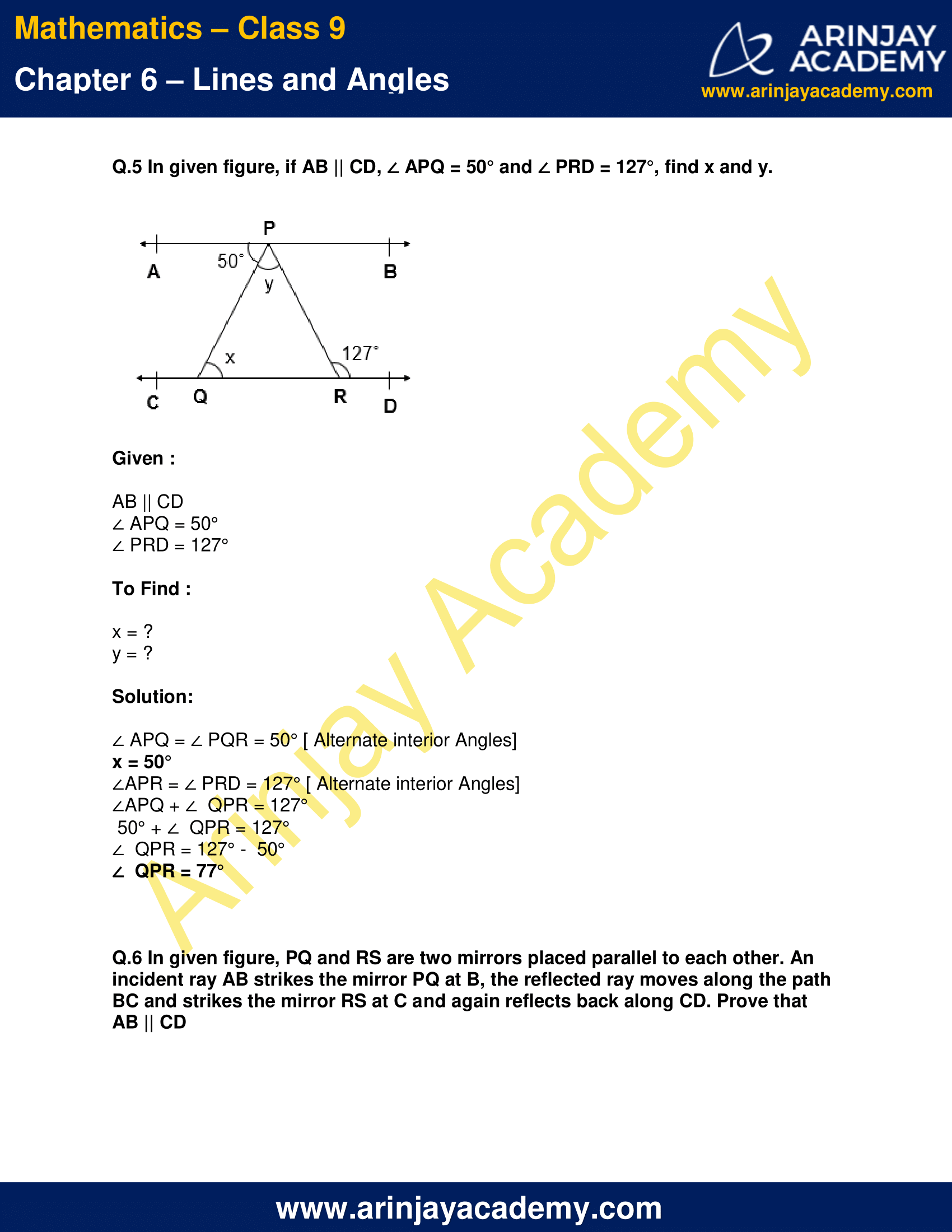
Q.5 In given figure, if AB || CD, ∠ APQ = 50° and ∠ PRD = 127°, find x and y.
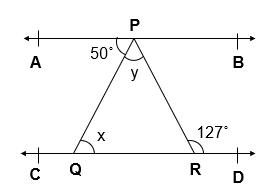
Given :
AB || CD
∠ APQ = 50°
∠ PRD = 127°
To Find :
x = ?
y = ?
Solution:
∠ APQ = ∠ PQR = 50° [ Alternate interior Angles]
x = 50°
∠APR = ∠ PRD = 127° [ Alternate interior Angles]
∠APQ + ∠ QPR = 127°
50° + ∠ QPR = 127°
∠ QPR = 127° – 50°
∠ QPR = 77°
Q.6 In given figure, PQ and RS are two mirrors placed parallel to each other. An incident ray AB strikes the mirror PQ at B, the reflected ray moves along the path BC and strikes the mirror RS at C and again reflects back along CD. Prove that AB || CD
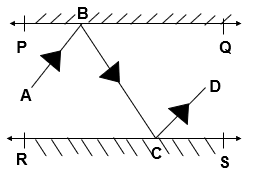
Solution:
Let us draw, BM ⊥ PQ, CN ⊥ RS
PQ || RS [ Given ]
Therefore, BM || CN
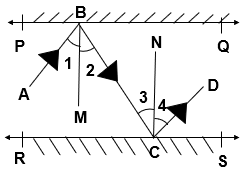
∠ 2 = ∠ 3 [ Alternate interior Angles]
∠ 1 = ∠ 2, ∠ 3 = ∠ 4 [By Laws of Reflection]
∠1 = ∠ 2 = ∠3 = ∠ 4
Also, ∠1 + ∠ 2 = ∠3 + ∠ 4
∠ ABC = ∠ CDB
∠ ABC & ∠ CDB are Alternate interior angles
AB || CD
The next Exercise for NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.3 – Lines and Angles can be accessed by clicking here.
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 – Lines and Angles
