NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.2 Circles
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.2 Circles. This ex 10.2 class 10 contains 13 questions, for which detailed answers have been provided in this note. In case you are looking at studying the remaining Exercise for Class 10 for Maths NCERT solutions for other Chapters, you can click the link at the end of this Note.
| Category | NCERT Solutions for Class 10 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 10 |
| Exercise | Exercise 10.1 |
| Chapter Name | Circles |
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.2 Circles
1. From a point Q, the length of the tangent to a circle is 24 cm and the distance of Q from the centre is 25 cm. The radius of the circle is
(A) 7 cm
(B) 12 cm
(C) 15 cm
(D) 5 cm
Let P be the point of contact and O be the centre of the circle with radius r
∴ PQ=24 cm
OQ=25 cm
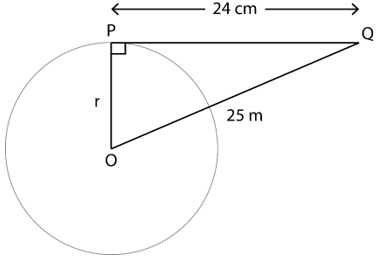
∵ Tangent and radius are perpendicular to each other at point of contact
∴ In △OPQ, ∠P=90°
OP2 + PQ2 = OQ2 (By Pythagorean Theorem)
r2 + 242 = 252
r2 = 252 – 242
r2 = (25 – 24)×(25 + 24)
r2 = 49
r = 7 cm
Therefore, the correct option is (A)
2. In the given figure, if TP and TQ are the two tangents to a circle with centre O so that ∠POQ=110°, then ∠PTQ is equal to
(A) 60°
(B) 70°
(C) 80°
(D) 90°
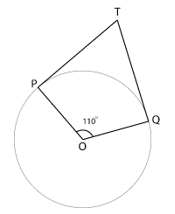
∵ Tangent and radius are perpendicular to each other at point of contact
∴ ∠TPO = ∠TQO = 90°
∵ Sum of angles of a quadrilateral = 360°
∴ In quadrilateral TPOQ
∠TPO + ∠POQ + ∠OQT + ∠QTP = 360°
90° + 110° + 90° + ∠QTP = 360°
290° + ∠QTP = 360°
∠QTP = 360° – 290°
∠QTP = 70°
Therefore, the correct option is (B)
3. If tangents PA and PB from a point P to a circle with centre O are inclined to each other at an angle of 80°, then ∠POA is equal to
(A) 50°
(B) 60°
(C) 70°
(D) 80°
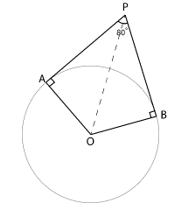
∵ Tangent and radius are perpendicular to each other at point of contact
∴ ∠PAO = ∠OBP = 90°
∵ Sum of angles of a quadrilateral = 360°
∴ In quadrilateral PAOB
∠PAO + ∠AOB + ∠OBP + ∠BPA = 360°
90° + ∠AOB + 90° + 80° = 360°
260° + ∠AOB = 360°
∠AOB = 360° – 260°
∠AOB = 100°
In △OPA and △OPB
∠PAO = ∠OBP = 90°
PO = PO [Common]
AO = OB [Radius]
∴ △OPA ≅ △OPB (RHS Congruency Rule)
⇒ ∠AOP = ∠BOP = ∠AOB =
x 100° = 50°
Therefore, correct option is (A)
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Circles Exercise 10.2 Solutions
4. Prove that the tangents drawn at the ends of a diameter of a circle are parallel
Given: PQ and RS be the two tangents drawn at the end points of the diameter AB of circle with centre O
To Prove: PQ and RS are parallel to each other
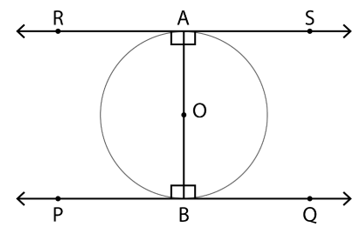
Proof:
∵ Tangent and radius are perpendicular to each other at point of contact
∴ ∠PBO = ∠QBO = 90°
∠RAO = ∠SAO = 90°
⇒ ∠RAO = ∠QBO
∠PBO = ∠SAO
∵ Alternate angles are equal
∴ PQ and RS are parallel to each other
5. Prove that the perpendicular at the point of contact to the tangent to a circle passes through the centre.
Given: A circle with O as the centre of the circle and AB is a tangent to the circle with point of contact at P
To Prove: Perpendicular to the tangent AB passes through the centre O
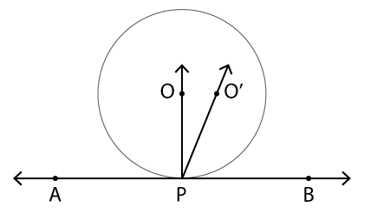
Proof (by contradiction):
Let the perpendicular to the tangent AB at P does not pass through O but passes through a point O’, not lying on the line joining O and P
∴ ∠O’PB = 90° …(i)
∵ Tangent and radius are perpendicular to each other at the point of contact
∴ ∠OPB = 90° …(ii)
From equation (i) and (ii)
∠O’PB = 90° = ∠OPB
This is possible only if O’, O and P lie on the same line
It is in contradiction to the earlier assumption
Therefore, O’ lies on the line joining O and P
Hence, the perpendicular to the tangent AB at P passes through O
Therefore, the perpendicular at the point of contact to the tangent to a circle passes through the centre
6. The length of a tangent from point A at a distance of 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle.
Let B be the point of contact and O be the centre of the circle with radius r
∴ BA = 4 cm
OA = 5 cm
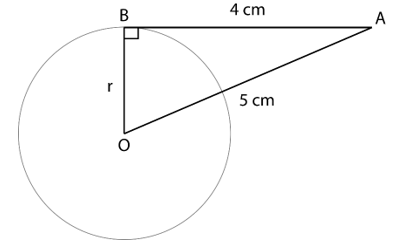
∵ Tangent and radius are perpendicular to each other at point of contact
∴ In △OAB, ∠B=90°
OB2 + BA2 = OA2 (By Pythagorean Theorem)
r2 + 42 = 52
r2 = 52 – 42
r2 = 25 – 16
r2 = 9
r = 3 cm
Therefore, the radius of the circle is 3 cm.
7. Two concentric circles are of radii 5 cm and 3 cm. Find the length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle.
Let AC be the chord of the bigger circle and is a tangent to the smaller circle with point of contact B, both circles have common centre O
∴ OA = 5 cm
OB = 3 cm
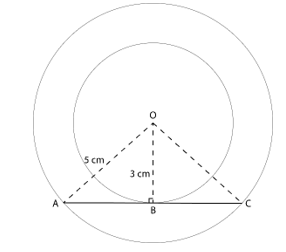
∵ Tangent and radius are perpendicular to each other at point of contact
∴ In △OBA, ∠B=90°
OB2 + BA2 = OA2 (By Pythagorean Theorem)
32 + BA2 = 52
BA2 = 52 – 32
BA2 = 25 – 9
BA2 = 16
BA = 4 cm
AC = 2×AB (Perpendicular to the chord from the centre bisects it)
AC = 2×4 = 8 cm
Therefore, the length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle is 8 cm.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.2
8. A quadrilateral ABCD is drawn to circumscribe a circle. Prove that AB + CD = AD + BC
The points P, Q, R and S are the point where the circle is touched by the sides AB, BC, CD and DA, respectively.
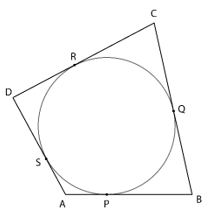
∵ Tangents from an external point to a circle are of equal length
∴ AP = AS …(i)
BP = BQ …(ii)
DR = DS …(iii)
CR = CQ …(iv)
Adding equations (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
AP + BP + DR + CR = AS + BQ + DS + CQ
(AP + BP) + (DR + CR) = (AS + DS) + (BQ + CQ)
⇒ AB + CD = AD + BC
9. In the given figure, XY and X’Y’ are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O and another tangent AB with the point of contact C intersecting XY at A and X’Y’ at B. Prove that ∠AOB=90°.
Join the centre of the circle with the point of contact of the tangent AB
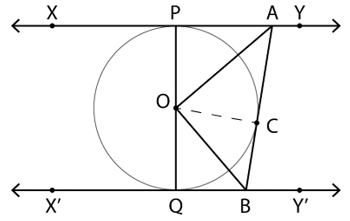
In △OPA and △OCA
∠OPA = ∠OCA = 90° (Tangent and radius are perpendicular to each other at the point of contact)
AO = AO [Common]
PO = CO = Radius
∴ △OPA ≅ △OCA (RHS Congruence Rule)
⇒ ∠POA = ∠COA …(i)(By CPCT)
Similarly, △OQB ≅ △OCB
⇒ ∠QOB = ∠COB …(ii)(By CPCT)
∵ PQ is a straight line
∴ ∠QOB = 180°
∠POA + ∠COA + ∠QOB + ∠COB = 180°
Substituting values from equations (i) and (ii)
2∠COA + 2∠COB = 180°
⇒ ∠AOB = 90°
Ex 10.2 Class 10 NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
10. Prove that the angle between the two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle is supplementary to the angle subtended by the line segment joining the points of contact at the centre.
Given: A and B are the points of contact of the tangents from the external point P to the circle with centre O
To Prove: ∠APB + ∠AOB = 180°
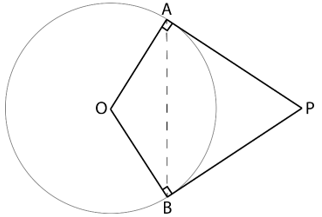
Proof:
∵ Tangent and radius are perpendicular to each other at point of contact
∴ ∠PAO = ∠PBO = 90°
∵ Sum of angles of a quadrilateral = 360°
∴ In quadrilateral PAOB
∠PAO + ∠AOB + ∠OBP + ∠APB = 360°
90° + ∠AOB + 90° + ∠APB = 360°
180° + ∠AOB + ∠APB = 360°
∠AOB + ∠APB = 360° – 180°
∠APB + ∠AOB = 180°
Hence, it is proved that the angle between the two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle is supplementary to the angle subtended by the line-segment joining the points of contact at the centre.
11. Prove that the parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus.
ABCD is a parallelogram and the points P, Q, R and S are the point of where the circle is touched by the sides AB, BC, CD and DA, respectively
∴ AB = CD …(i)
BC = AD …(ii)
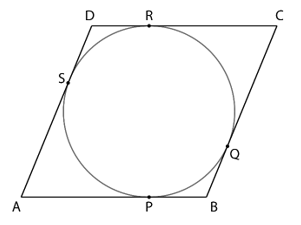
∵ Tangents from an external point to a circle are of equal length
∴ AP = AS …(iii)
BP = BQ …(iv)
DR = DS …(v)
CR = CQ …(vi)
Adding equations (iii), (iv), (v) and (vi)
AP + BP + DR + CR = AS + BQ + DS + CQ
(AP + BP) + (DR + CR) = (AS + DS) + (BQ + CQ)
⇒ AB + CD = AD + BC
Substituting values from equation (i) and (ii)
AB + AB = BC + BC
2AB = 2BC
AB = BC …(vii)
From equation (i), (ii) and (vii)
AB = BC = CD = DA
⇒ All sides of the parallelogram circumscribing a circle are equal
Since, a parallelogram with sides of equal length is a rhombus
Therefore, a parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus.
12. A triangle ABC is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius 4 cm such that the segments BD and DC into which BC is divided by the point of contact D are of lengths 8 cm and 6 cm respectively. Find the sides AB and AC.
Let the sides AB and AC touch the circle at E and F respectively
Let AF = x
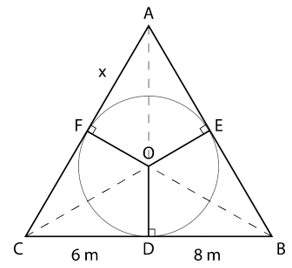
∵ Tangents from an external point to a circle are of equal length
∴ AE = AF = x
BD = BE = 8 cm
CF = CD = 6 cm
AB = AE + EB = x + 8
BC = BD + CD = 8 + 6 = 14 cm
CA = CF + FA = 6 + x
Semi-perimeter of △ABC (s) =(AB + BC + CA) =
(x + 8 + 14 + 6 + x) = x + 14
Area of △ABC = (Heron’s Formula)
Area of △ABC =
Area of △ABC =
Area of △ABC = …(i)
Area of △ABC = ar(△AOB) + ar(△BOC) + ar(△COA)
= (AB×OE) +
(BC×OD) +
CA×OF)
= (x + 8)×4 +
(14×4) +
(x + 6)×4 (OD = OE = OF = 4 cm)
= 2×(x + 8) + 2×14 + 2×(x + 6)
= 2×(x + 8 + 14 + x + 6)
= 2×(2x + 28)
= 4(x + 14) …(ii)
From equation (i) and (ii)
48x(x + 14) = 16(x + 14)2 (Both sides squared)
Dividing by common factors
3x = (x + 14)
3x – x = 14
2x = 14
x = 7 cm
AB = x + 8 = 7 + 8 = 15 cm
BC = 14 cm
CA = x + 6 = 7 + 6 = 13 cm
Therefore, AB = 15 cm and AC = 13 cm.
13. Prove that opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the centre of the circle.
Consider the quadrilateral ABCD circumscribing a circle with centre O. AB, BC, CD and DA touch the circle at points P, Q, R and S respectively
Join the centre of the circle to the points of contact and the vertices of the quadrilateral
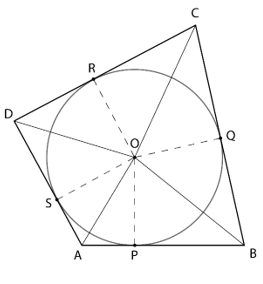
In △POA and △SOA
∠OPA = ∠OSA = 90° (Tangent and radius are perpendicular to each other at point of contact)
AO = AO [Common]
OP = OS [Radius]
∴ △POA ≅ △SOA (RHS Congruency Rule)
⇒ ∠POA = ∠SOA (By CPCT) …(i)
Similarly, △SOD ≅ △ROD
⇒ ∠SOD = ∠ROD …(ii)
△ROC ≅ △QOC
⇒ ∠ROC = ∠QOC …(iii)
△QOB ≅ △POB
⇒ ∠QOB = ∠POB …(iv)
∠POA + ∠SOA + ∠SOD + ∠ROD + ∠ROC + ∠QOC + ∠QOB + ∠POB = 360°
Substituting values from equation (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
2∠POA + 2∠POB + 2∠ROD + 2∠ROC = 360°
2[(∠POA + ∠POB) + 2(∠ROD + ∠ROC)] = 360°
2(∠AOB + ∠COD) = 360°
⇒ ∠AOB + ∠COD = 180°
Similarly, ∠AOD + ∠BOC = 180°
Hence, the opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the centre of the circle.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.2 – Circles, has been designed by the NCERT to test the knowledge of the student on the topic – Number of Tangents from a Point on a Circle
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Ex. 10.1 Introduction to Trigonometry
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Ex. 10.1 Introduction to Trigonometry
- Maths – NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
