Working of Institutions Class 9 Civics Chapter 4 Extra Questions and Answers covers various types i.e. Very short, Short and Long questions, related to the topic so as to help the students with their preparation by helping them do an in-depth study of the topic.
- This chapter talks about the different types of government institutions of the country and how they work.
- It talks about how the institutions have to deal with the disputes related to the decisions that are made and how are they tackled.
- The Chapter introduces the students to three important bodies of our country the executive, the legislature and the judiciary and also talks about their nature and features.
- Overall, this chapter helps the students to get a better view of how the government functions at different levels and which institution plays a crucial role in the process.
Class 9 Civics Chapter 4 Extra Questions are Answered in detail by our team of experts which includes teachers and professionals. These solutions have been compiled in an easy to understand manner, keeping in mind, the perspective of strong, and weak students. We are providing NCERT Solutions for Class 9 all subjects which can be accessed by clicking here.
Class 9 Civics Chapter 4 Extra Questions and Answers – Very Short Type Questions: [1-2 marks]
1. SEBC stands for _______.
Ans) Socially and Educationally Backward Classes
2. An _________ explains the verdict taken by the government that has been issued by a suitable expert witness.
Ans) Office Memorandum
3. President is known as the head of the _________ while prime minister is defined as the head of the ___________.
Ans) State, Government
4. In the year 1979 the second backward classes commission was headed by _______ and was also known as the _________.
Ans) BP Mandal, Mandal Commission
5. Which party came to power after the 1989 elections? Who became the prime minister then?
Ans) Janata Dal, VP Singh
6. _________ has the final authority for making laws in the country.
Ans) Parliament
7. Which house of the parliament is known as the upper chamber?
Ans) Rajya Sabha
8. The government of India is elected for _______ number of years.
Ans) 5
9. _________ are government functionaries who take major decisions and are elected for a fixed time period.
Ans) Political executives
10. Permanent executives also known as _______ remain in office even after the ruling party changes.
Ans) Civil servants
11. Who is the most powerful member of the cabinet?
Ans) Prime Minister
12. _______ form of government is followed in our country.
Ans) Parliamentary
13. When the supreme court is said to maintain the judicial administration of a particular country then it is known as _______.
Ans) Integrated judiciary
14. Chief Justice __________ assisted our current president Shri. Ram Nath Kovind to take the oath of president’s office.
Ans) Shri. Justice K.H. Khehar
15. In the central hall of parliament in Delhi on ________ the oath ceremony of the current president of India took place.
Ans) 25th July 2017
16. ______, ________ and _________ are the three categories of council of ministers.
Ans) Cabinet ministers, Ministers of state with independent charge, Ministers of state.
17. _________ are provisions made in modern democracies to run the government.
Ans) Institutions
Class 9 Civics Chapter 4 Extra Questions and Answers – Short Type Questions: [2-4 marks]
1. Political institutions in India play a very crucial role. Explain.
Ans) Political institutions can be defined as a set of measures for regulating the demeanor of government and political life in the country. It plays a very crucial role in our country as it is responsible for providing facilities like security, health, education, and implementing other welfare schemes for the citizens of the country. It also helps in tax collection and creating budget for different programs like administration, defence etc. of the country.
2. Parliament is the final authority in making laws and also plays a very crucial role to maintain our country’s democratic nature. Point out two other major roles it plays.
Ans) Parliament can be defined as the highest forum where discussions related to public affairs and welfare schemes take place. It plays a number of roles and a few of them are as follows:
- Parliament plays a crucial role in the law making of the country. It has the final power for making laws and can carry out amendments if necessary.
- It is responsible for taking decisions on money and financial matters and also exercises authority over the people working for government.
3. Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha are the two houses of our country. Which house of the two is more powerful? Give two reasons for your answer.
Ans) Even though Rajya Sabha is known as the Upper House of our country, yet Lok Sabha seems to be more powerful owing to number of reasons, a few of which are stated below:
a) Lok Sabha plays a very important role in case of monetary bills as once a bill is passed by Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha cannot reject it but can only delay by 14 days or suggest changes.
b) Lok Sabha is responsible for controlling the council of ministers and also possesses the power to pass a low confidence motion, forcing the prime minister and his council to resign.
4. Prime Minister is the head of the government and, as a result possesses a number of powers to run the country. However, if the ruling party is a coalition government then there are a number of problems that the leader has to face. Mention any two such problems that he has to face.
Ans) Prime Minister, being the head of the government, possesses a number of powers.However, if he happens to be the leader of a party which did not receive majority and as a result of which had to form a coalition government, then he faces a number of constraints.
Firstly, he has to accommodate all the members, including members of different parties whose help he sought to emerge victorious and listen to their suggestions and demands.
Secondly, he cannot take up decisions on his own and there is often a situation of chaos as there are a number of parties with different ideologies and and as a result of which the primary problems get neglected and there is a situation of internal competition.
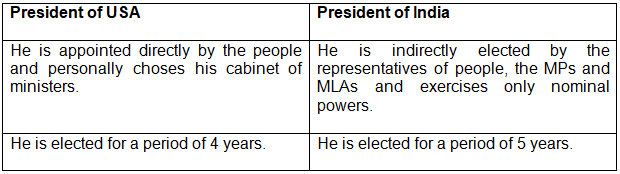
5. State two points of differences between the president of our country and that of USA. State one reason as to why these differences are present.
Ans) The president of India and that of USA has a number of distinguishing powers some of them are as follows.
6. What is a PIL and what are its functions?
Ans) PIL or public interest litigation is issued by any individual for public’s interest at large. It is often issued to check malpractices of public officials or to seek remedies against any tragedy which impacted the public at large. It is a way in which public can seek redressal for their demands from the courts via one petition.
7. Which commission became a controversial issue in our country? State two reasons as to why did it happen.
Ans) The Mandal Commission became a controversial issue in our country owing to a number of reasons. Few of them are as follows:
a) Different opinions of the media and press leading to widespread protests among the masses made it a controversial issue. Some felt due to all this the national unity of the country was hampered.
b) Few were in favour of reservations while others were not.This created conflicts and this clash of thoughts led to severe violence and wide scale demonstrations.
8. Prime Minister is the head of the government and possesses a number of powers. Mention any three of his most important powers.
Ans) Prime Minster is the head of the state and possess a number of powers to run the country.Few of them are follows:
- He is the leader of the majority party, and commands and presides over cabinet meetings.
- His consent is mandatory for decisions of the cabinet and he has the power to choose his ministers.
- He also acts as an adviser for the appointment of president, and judges of the Supreme Court and decisions are taken under his leadership.
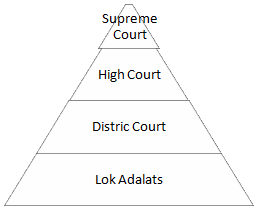
9. State the composition of Indian Judiciary in a pictorial manner.
Ans)
Class 9 Civics Chapter 4 Extra Questions and Answers – Long Type Questions: [4-6 marks]
1. Mandal Commission was one of the most controversial issue of our country. State 4 reasons as to how was this issue resolved.
Ans) The Mandal Commission became a controversial issue in our country owing to a number of reasons like differentiated public opinions, public protests, high media coverage creating conflicts etc. However, this issue was resolved with the help of these measures that are mentioned below:
A number of cases were filed in the courts opposing the matter and the conflict and all the cases were named under one i.e. Indira Sahaye Vs UOI.
In the year 1992, most courts declared this government order as valid leading to closing of the topic.
The original order was also sent for modification according to the demand of removing the creamy layer of the backward classes from the benefits of reservation.
A new memorandum was issued by the Department of Personnel and Training which was one of the final steps taken after which the conflict was resolved to a great extent.
2. Mention 4 powers of the parliament of our country. Which among its powers according to you is the most unique and why?
Ans)National gathering of chosen legislatures can be defined as parliament and it possesses a number of powers like executive, legislative, judicial, constitutional etc. among which a few are mentioned below:
- Parliament plays a very crucial role in the law making process of our country and it also is the final authority and has the power to make amendments in this field.
- It possesses the power to remove the government by passing a no-confidence motion against it which will force the cabinet of ministers along with the prime minister to resign.
- Parliament plays a very crucial role in the monetary and finance related matters and it also plays an important role in distribution and allocation of the funds for different projects and other public affairs.
- The parliament has the power of impeachment and it can remove the vice president, president, judges and other important personalities.
However, out of all the powers a parliament possesses, the most unique and important power seems to be the financial power as it can decide the finance related sectors and also play a crucial role in making the budget every year and progress with the implementation of various developmental projects and other public welfare measures.
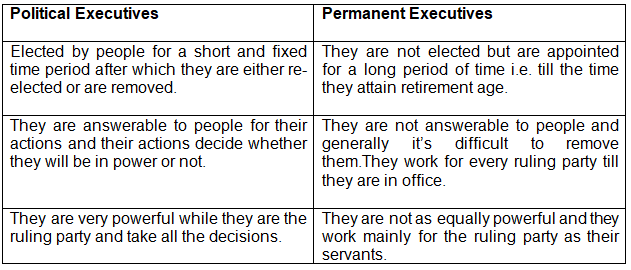
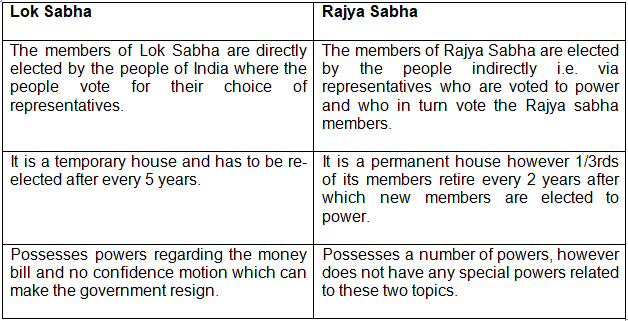
3. State three points of differences for each of the following.
a) Political and Permanent Executives.
b) Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha
Ans) a)
b)
4. Mention any four powers of the head of the state.
Ans)President is known as the head of the state and even though he is the de facto or nominal head of the country, still he possesses a number of powers, a few of which are mentioned below:
- He possesses the power to choose his own ministers and also has the power to summon and preside over meetings.
- He leads the cabinet and also gives his assent to important bills after which they get passed.
- He is the supreme commander of the defense forces of India. He also actively participates and gives assent to the international agreements and treaties.
- He acts like a supervisor of all the political institutions and also plays the role of an advisor for major appointments like Supreme Court judges etc.
5. State two reasons as to why judiciary in India is so powerful. Also describe the procedure or conditions as to how the judges can be removed after they are appointed.
Ans) India has a system of independent judiciary and as a result, judiciary has a number of powers in order to maintain the system of checks and balances in the country. They have the power to interpret the laws and the constitution of the country and also has the power to amend them. It protects the citizens by providing them equality of justice and can intervene with the government policies if they seem unreasonable. As a result, the judiciary and the judges are among the most powerful people of the country.
It is difficult to remove a judge once appointed in the Supreme Court or the High Court and is nearly impossible to remove him from the position. However, he or she can be removed by the process of impeachment only if majority, i.e.2/3rds of the members of both the houses unanimously vote against him and in favour of his removal.
If you have any feedbacks on Working of Institutions Class 9 Civics Chapter 4 Extra Questions and Answers please write us on comment box.