Introduction of Government Budget and the Economics Class 12th
Meaning of Government Budget
A statement which is prepared annually, showing estimated expenditure and receipts of the government over the fiscal or financial year is termed as GOVERNMENT BUDGET.
A financial year or fiscal year runs from April 1 to March 31.
Objectives of Government Budget Class 12
Redistribution of Resources
The first and foremost objective of government budget is the redistribution of resources in the Indian economy with a motive to achieve both “Economic and Social welfare” in the economy.
By providing tax concessions or subsidies government encourages investment in the economy.
By providing public utility services like water supply, health facilities etc. Govt creates social welfare in the economy.
Reducing Disparities in Income and Wealth
Govt imposes tax on the rich and spends more on the welfare of the poor as to reduce disparities in the Income and wealth of the economy.
Growth and Development of the Economy
Govt make provisions in the govt budget to spend on technology, health, Infrastructure and it will develop the economy and will increase the real GDP of the nation which leads to growth in the Economy.
Regional Equality
Govt encourages setting up of production units in the economically backward regions by providing tax holidays and other benefits so that regional equality can be achieved.
Operation of public sector
Govt Budget is prepared with the objective for making various provisions for the management and operation of public sector. Financial assistance is also provided as this sector will create social welfare in the economy.
Components of Government Budget – Economy Class 12 Notes
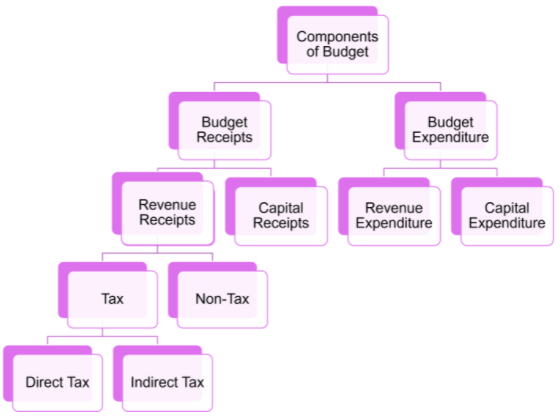
Meaning and Types of Budget Receipt
Budget Receipt – It is the estimated receipts of the government from all the sources during a given financial year.
TYPES OF BUDGET RECEIPT
- Revenue Receipt
- Capital Receipt
Revenue Receipt
The receipts which neither creates liability nor reduces assets of the government is termed as REVENUE RECEIPT. They are regular and recurring in nature.
For Example:- Tax income
Sources of Tax Revenue
- Tax revenue
- Non Tax revenue
Tax Revenue:- It includes the receipts from the taxes and other duties which are imposed by the government.
It is a compulsory payment to the government . The revenue received from the taxes is used by the government for the welfare of the general public.
Tax can be categorized as
- Direct tax
- Indirect tax
Direct tax– When the liability and burden to pay the tax falls on the same person, the tax is called Direct Tax.
For eg. Income tax, Corporation tax etc.
Indirect tax– When the liability and burden to pay tax falls on different persons, the tax is called Indirect tax.
For eg. GST, Custom Duties.
Non Tax Revenue :- Non tax revenue is the income earned by the Govt from all the sources other than taxes.
Sources of Non Tax Revenue
- Profits and Dividends: Public sector is a source to earn profits for the govt. It also receives dividend by investing in other companies.
- Fines and Penalties : The Govt imposes fines and penalties on people for maintaining or following the laws of the country. The objective of the imposition of fines and penalties is not generate revenue but to maintain law & order in the Nation.
- Fees : The fee is paid is paid in return for the services provided by the government. For eg. Registration fee, Education fee.
- License Fee : License fee is charged by the government for granting permission.
- Gifts and Grants : The government also receives gifts & grants from the foreign govt and institutions but these sources are not a fixed source of revenue as it is usually received at the time of crisis.
Capital Receipt
The receipts which either creates liability or reduces assets of the government is termed as CAPITAL RECEIPT. They are non recurring in nature.
For Example:-
Sources of Capital Receipt
- Borrowings: This includes funds raised by the govt through loans from the public,Reserve Bank of India etc. It is a capital receipt for the govt as it creates liability for the Govt as the fund raised need to be repaid by the Govt in future.
- Recovery of loan : Repayment of loan by the state and union territory to the govt falls under this category. Recovery of loan is a capital receipt as it reduces the financial asset of the Govt.
- Other Receipts : This includes capital receipts from Disinvestment and Small Savings.
Budget Expenditure – Government Budget and the Economy Class 12 Notes
Budget expenditure is the estimated expenditure to be incurred by the Govt during a given financial year.
Types of Budget Expenditure
- Revenue expenditure
- Capital Expenditure
1. Revenue Expenditure: Revenue expenditure refers to the expenditure which neither creates assets nor reduces liability of the government.
For eg. Expenditure on administration, Payment of salary etc.
2. Capital Expenditure : Capital expenditure refers to the expenditure which either creates assets or reduces liability of the govt.
For eg. Repayment of loan, construction of dams.
Measures of Government Deficit
Budget Deficit can be defined as the situation when the estimated revenues are less than the estimated expenditure.
Types of Deficit:-
There are mainly three types of deficit in Govt Budget
Revenue Deficit
The revenue deficit is the excess of government’s revenue expenditure over revenue receipts.
FORMULA – Revenue Deficit= Revenue Expenditure – Revenue Receipts
Revenue Deficit represents that the government’s own earnings are insufficient to meet the day-to-day operations of its various departments.
Implications
- It shows that the Govt is using savings to meet the govt expenditure.
- It also signifies that govt has to meet its deficit from capital receipts. This will reduce the asset of the Govt or will increase the liability of the govt.
- Use of capital receipt will create a situation of inflation in the Economy.
- It implies a repayment burden in future.
Measures to Reduce Revenue Deficit
- Govt should take same major steps as to reduce its expenditure.
- Govt should try to increase their source of revenue receipts and should take some serious steps to control tax evasion.
Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal Deficit refers to the excess of total expenditure over total receipts excluding borrowings during a given fiscal year.
Formula – Fiscal Deficit = Total expenditure – Total receipts excluding borrowings
The extend of the fiscal deficit is an indication of how far the government is spending beyond its means.
Implications
- It indicates the total borrowing requirements of the Govt. The borrowing will not just increase the loan repayment amount(Principal amount) but will also increase the obligation to pay interest.
- Interest payment will increase the revenue expenditure which will lead to revenue deficit.
- To meet the deficit the RBI will print new currency which will increase the money supply and creates inflationary pressure in the economy.
- Because of borrowings financial burden will increase and this will hamper the growth and development process in the economy.
Measures to Reduce Fiscal Deficit
- By borrowing from external or internal sources fiscal deficit can be reduced.
- RBI will issue new currency and will lend it to the Govt against securities as to meet the fiscal deficit. This process is called ‘DEFICIT FINANCING’
Primary Deficit
Primary deficit refers to the difference between fiscal deficit and interest payment.
Formula – Primary Deficit = Fiscal Deficit – Interest Payment
It indicates how much government borrowing is going to meet expenses other than interest payment.
Implications
It reflects the extend to which current govt policy is adding to future burdens originating from past policy. If primary deficit is zero then it shows that fiscal deficit is equal to interest payment.
CBSE Economics Class 12 Notes Term I Syllabus
Part A: Introductory Macroeconomics
Part B: Indian Economic Development
Development Experience (1947-90) and Economic Reforms since 1991:- 12 Marks
- Indian Economy on the eve of Independence Notes
- Indian Economy (1950-90) Notes
- Economic Reforms since 1991 Notes
Current challenges facing Indian Economy – 10 Marks