| Category | Accountancy Class 12 Notes |
| Chapter | Chapter 1 – Accounting for Share Capital |
| Topic | Accounting Treatment |
Accounting Treatment –
The books of accounts of a partnership firm are closed consequent to the order of dissolution passed by the court or mutual agreement between the partners. When a firm is dissolved it calls for settlement of its accounts.
In this process, the assets of the firm are disposed of off to meet the obligations of the firm. The profit or loss derived post the settlement of accounts is divided between the partners in their profit sharing ratio.
To ascertain such profit or loss, a Realisation account is prepared. It records both realizations of assets and payment of liabilities. If realizations are in excess of payments it results in profit and if payments are in excess of realizations it generates a loss.
What is a Realisation account?
A realization account is a nominal account that is prepared while shutting down an agreement of partnership business. It includes the details of all the assets and liabilities. The realization account is credited with all the incomes and debited with all the expenses. It is prepared once for a firm at the time of its closure.
Why is the Realisation Account prepared?
The realization account is prepared to record all the assets and settlements of liabilities at the time of termination of the partnership business or a firm. The main motive of the preparation of the Realisation account is to evaluate the total profit or loss realized by a firm.
All the assets except cash are transferred to the debit side of the realization account and liabilities (not capital accounts) to the credit side of the realization account. When the assets are sold, cash or bank account is debited and the Realisation Account is credited. On settling the liabilities, the Realisation Account is debited and the Cash or Bank Account is credited.
At last, if the total of the credit side exceeds that of the debit side, it means there is profit that is transferred to the partners’ capital account. In case of loss, the partners’ capital accounts are debited while the Realization Accounts are credited.
How to prepare a Realisation account?
- All asset accounts are closed by transferring their book value to the debit of the Realisation account. However, cash, bank, and fictitious assets are not transferred to this account. Also, for any asset for which a provision is in existence, the gross value of such asset will be posted to the debit of Realisation account and the provision amount is recorded on the credit side of this account. For eg – Sundry debtors and provision for doubtful debts, fixed assets, and provision for depreciation, etc.
- Similar to assets, all liabilities accounts are closed by transferring them to the credit side of the Realisation account.
- Next, any sale of assets and settlement of liabilities are recorded. These entries are routed through the Bank account.
- Any expenses incurred to carry out the process of realization of assets and payment of liabilities are also recorded.
- Any other expenses or unrecorded assets or liabilities are also taken into account while preparing the Realisation account.
- The balance after the posting of the above entries is either profit or loss on realization. This is transferred to the partner’s capital accounts in the profit-sharing ratio.
Format of Realisation Account –
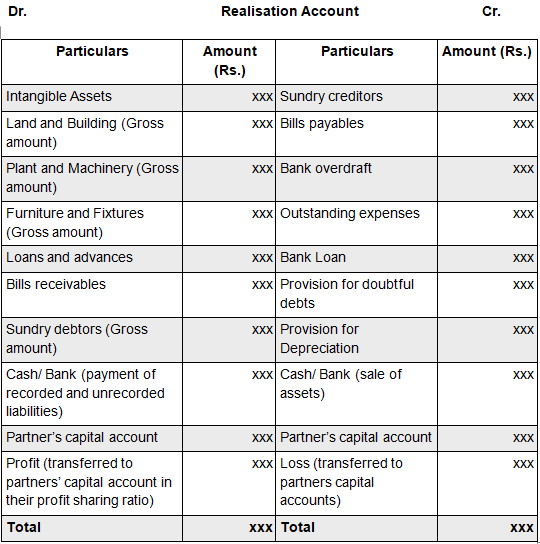
Thus, to close all accounts of a partnership firm in the event of dissolution, a Realisation account is prepared. All assets and liabilities are posted at the book value and all realizations and settlements are recorded.
Chapter 5 Dissolution of Partnership Firm
- Dissolution of Partnership
- Dissolution of a Firm
- Settlement of Accounts
- Accounting Treatment