Meaning of Share:
When the total capacity of a company is divided into smaller units, then each smaller unit is known as Share. A share is a document, which acknowledges an ownership in a company.
Types of Shares:
There are two types of shares:
- Preference Shares
- Equity Shares
Preference Shares:
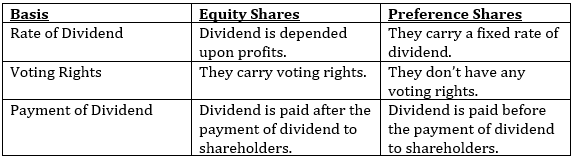
Preference Shares are those shares, which carry certain privileges with them. A fixed rate of dividend is paid, which is usually mentioned in name. E.g. 6% preference shares and so on. Their dividend is paid before equity shareholders. But they have no voting rights attached to them. At the time of wining up of a company their capital is paid before the equity shareholder capital.
Types of preference shares:
- Cumulative Preference shares
- Non-Cumulative Preference shares
- Participating Preference shares
- Non-participating shares
- Convertible Preference shares
- Non-convertible preference shares
- Redeemable preference shares
- Irredeemable preference shares
Equity Shares:
These shares do not have any rights over dividend or at the time of winding up of company. But they carry voting rights with them. Every shareholder has a voting right to elect director of the Company. Their dividend is depended upon the profit of the company.
Difference between Equity and Preference Shares
Meaning of Share Capital:
The capital raised by the company through the issue of shares is known as Share capital. The capital raised by equity shares is known as Equity share capital. Preference share capital is known as capital rose by issue of preference shares.
Kinds of Share Capital:
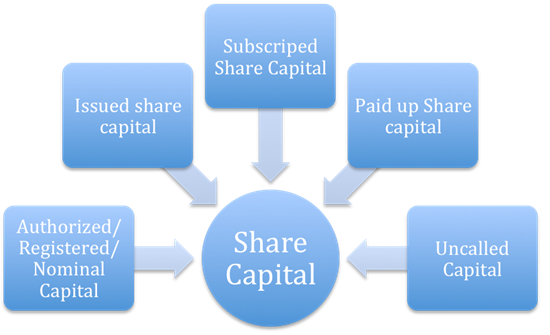
Authorised Capital:
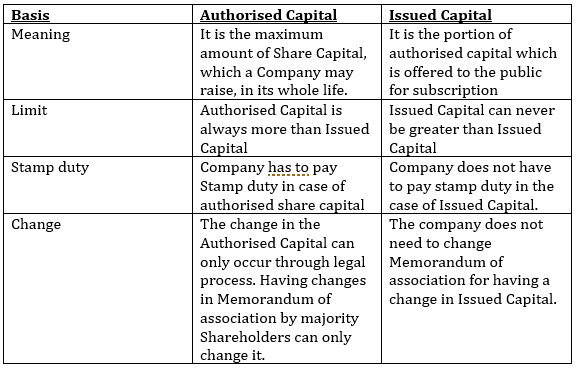
The maximum amount of share capital that a Company is authorised as it states in Memorandum of Association or Articles of Incorporation to raise from the public throughout its life is known as Authorised Share Capital. Following the process under Companies Act, 2013, can only increase it
Issued Share capital:
The part of authorised capital, which it is issued to public, is known as Issued Share capital. Usually a Company doesn’t issue all of its Authorised Capital all at once.
Subscribed Capital:
The part of the Issued Share Capital, which is subscribed by the public, is known as Subscribed Share Capital. Not every part of Issued Share Capital is part of Subscribed Share capital.
Paid up Share Capital:
The part of the called up capital, which has been received by the company from the shareholders, is known as paid up Share Capital.
Uncalled Capital:
The unpaid portion of the subscribed Capital is known as Uncalled Capital. It is the reminder of the Subscribed Capital, which has not been called up yet. The Company can call up for this, when they want subjected to terms and conditions at the time of Issue.
Difference Between Authorised Capital and Issued Capital
Capital Reserve:
This is that reserve which is created out of Capital profits. These are not normal profits of a Company but profits created by selling of Machinery, issue of debentures at premium etc. They are not distributed as dividends and are there to strengthen the business.
Examples of Capital profits are:
- Profit on sale of fixed assets and investments
- Issue of Share/Debentures at Premium
- Forfeitures of Shares
- Redemption of Shares at Discount
- Revaluation of Assets and Liabilities
Chapter 1 – Accounting for Share Capital