National income and related aggregates class 12 notes CBSE, would cover various aggregates of national income such as GDPMP, NDPFC, etc…. and Methods of Calculating National Income and its Aggregates Class 12. We will also study about Gross Domestic Product “GDP” and the various manner in which it contributes to welfare.
| Category | CBSE Economics Class 12 Notes |
| Subject | Economics |
| Topic | National income and related aggregates class 12 notes |
These national income notes provide the Definition, Factor Income, measurement of national income class 12, Measurement Problems, and Estimate (With Diagram)! Go through these national income notes if your goal is to secure good marks in class 12 Economics.
National Income and its Related Aggregates Notes
National Income and its related aggregates are an important concept of macroeconomics.
What is National Income?
National income is the sum total of the entire Factor incomes, of a country generated by normal residents of that country. It is the net national product at factor cost in the market.
Question and Answers for doubts on Factor Incomes
1. What are Factor incomes?
Factor incomes are rewards received by owners of Factors of Production (Land, Labour, Capital, and entrepreneurship) from the firms who use the factor services. These can be in the form of compensation like rent for use of Land, Salaries for employees for providing Labour, interest on capital, and profit for Entrepreneurs).
2. Is there any difference between Factor Incomes and Factor Payments?
Since Factor Incomes are paid by firms, they are also called Factor Payments.
3. National Income includes Factor Income and Transfer Payments. Is this statement true?
National Income includes only Factor Income and hence this statement is False.
4. Transfer Payments are rewards for use of Services. Is this statement true?
Transfer Payments are not rewards for use of Services but are one-sided payments like Charity etc, where the payor may not get any economic returns.
Question and Answers on Normal residents in Economics: –
Aggregates of National Income
Aggregates of National Income are similar factors that can also be called national income in the economy.
Question and Answers on Aggregates of National Income in Economics: –
Define the various aggregates of national income?
There are 8 aggregates of national income which are broadly classified as Domestic aggregates of national income and National aggregates of national income. These aggregates of national income are defined as under: –
Aggregate 1 – What is GDPMP or Gross Domestic Product at Market Price?
Gross Domestic Product at Market Price refers to the gross value added by all final goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country during a period of time. It is computed based on market price.
The following aspect needs to be considered in respect of Gross Domestic Product at Market Price.
- Gross Domestic Product – “Gross” in Gross Domestic Product means the value is computed without making any provision of depreciation.
- Gross Domestic Product – Domestic in Gross Domestic Product means that the goods and services are produced within the domestic territory.
- Market price – Market price means the price of goods and services in the market, including net indirect taxes.
Additional Questions: –
1. State which of the following are true : –
- Gross Domestic Product at Market Price refers to the net value added by all final goods and services – False
- Gross Domestic Product at Market Price is in respect of goods produced in the domestic territory – True
- Gross Domestic Product at Market Price includes gross value added by all final and intermediate goods and services – False
Aggregate 2 – What is Net Domestic Product at Market Price or NDPMP?
Net Domestic Product at Market Price refers to the net value-added, by all final goods and services at market price, which is produced within the domestic territory of a country, during a given period of time.
The following aspect needs to be considered in respect of Net Domestic Product at Market Price.
- Net Domestic Product – Net Domestic Product means the value is computed after deducting depreciation.
- Domestic in Net Domestic Product – Domestic in Net Domestic Product means that the goods and services are produced in the domestic territory.
- Market Price – Market price means the price of goods and services in the market, including net indirect taxes.
Aggregate 3 – What is Gross National Product at Market Price or GNPMP?
Gross National Product at Market Price refers to the gross value added by all final goods and services at market price produced by the normal resident of a country during a period of time.
The following aspect needs to be considered in respect of Gross National Net Domestic Product at Market Price.
- “Gross” in Gross National Product means the value is computed without making any provision of depreciation.
- National in Gross National Product – National means goods and services are produced by normal resident
- Market Price – Market price means the price of goods and services in the market, including net indirect taxes.
NNPMP or Net National Product at Market Price
It refers to the net value added by all final goods and services at market price produced by a normal resident of a country during a period of time.
- Net means that depreciation is deducted from the value.
- National means goods and services are produced by normal residents.
- Market price means goods and services include net indirect taxes.
GDPFC or Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost
It refers to the gross value added by all final goods and services at money value (factor cost) produced within the domestic territory of a country during a period of time.
- Gross means there is no provision of depreciation.
- Domestic means goods and services are produced in the domestic territory.
- Factor cost means goods and services do not include net indirect taxes.
NDPFC or Net Domestic Product at Factor Cost
It refers to the net value added by all final goods and services at money value (factor cost) produced within the domestic territory of a country during a period of time. It is also called DOMESTIC INCOME.
- Net means depreciation is deducted from the value.
- Domestic means goods and services are produced in the domestic territory.
- Factor cost means goods and services do not include net indirect taxes.
GNPFC or Gross National Product at Factor Cost
It refers to the gross value added by all final goods and services at money value (factor cost) produced by the normal resident of a country during a period of time.
- Gross means there is no provision of depreciation.
- National means goods and services are produced by the normal resident.
- Factor cost means goods and services do not include net indirect taxes.
NNPFC or Net National Product at Factor Cost
It refers to the net value added by all final goods and services at money value (factor cost) produced by the normal resident of a country during a period of time. It is also called NATIONAL INCOME.
- Net means depreciation is deducted from the value.
- National means goods and services are produced by the normal resident.
- Factor cost means goods and services do not include net indirect taxes.
HOW TO CALCULATE NNPFC FROM GDPMP?
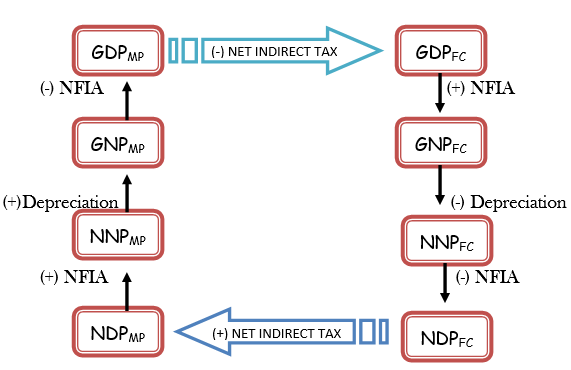
DIFERENCE BETWEEN NATIONAL AND DOMESTIC INCOME
| S.NO | BASIS | NATIONAL INCOME | DOMESTIC INCOME |
| 1 | Nature of Concept | It is a TERRITORIAL concept as it includes all goods and services produced in domestic territory. | It is a NATIONAL concept as it includes all goods and services produced by a normal resident. |
| 2 | Category of Producers | It considers all producers within domestic territory. | It considers all producers who are normally residents. |
| 3 | NFIA | It includes NFIA. | It does not include NFIA. |
METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME AND ITS AGGREGATES CLASS 12
METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12 – VALUE-ADDED METHOD
This method is used to calculate national income from the various phases of the circular flow of income. It shows the contribution of each production unit in producing goods and services. This method is also known as the Product Method, Production Method, or Net Output Method.
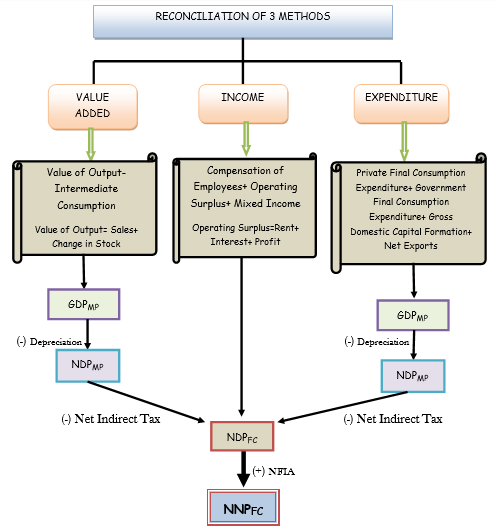
VALUE ADDED refers to the addition of value to the raw materials by a firm through its production activities. It is calculated as the difference between the value of output and the value of intermediate consumption. The value-added method gives us the result as GDPMP(an aggregate of national income).
Value Added= Value of Output- Intermediate Consumption
INTERMEDIATE CONSUMPTION is not included while calculating national income. Therefore it is deducted from the value of output. If intermediate consumption is given, then imports are not separately included as they are a part of intermediate consumption.
VALUE OF OUTPUT is the market value of all goods and services produced in an economy during a period of one year. Value of output includes the sales made during a particular year and the unsold stock of goods left out during that year. Sales are calculated by multiplying output with a price. Exports are not separately included in national income through this method as they are already a part of sales of that year.

*Value Added Method*
PRECAUTIONS OF VALUE-ADDED METHOD
- Intermediate goods are not included in calculating national income.
- The sale and purchase of second-hand goods are not included.
- Production of services for self-consumption is not included.
- Production of goods for self-consumption is included.
- Change in the stock of goods will be included.
- The imputed value of the house occupied by the owner is taken as the rent of that place.
While measuring national income, only the value of final goods is to be included to avoid the problem of double-counting while passing through various stages of the production process.
METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12 – INCOME METHOD
According to this method, all the income received or accrued to be received by the factors of production through wages, salaries, interests, rent, royalty, profits, etc…. are summed up to get the national income. The income methods give NDPFC (an aggregate of national income). This is also called “domestic income”. This method includes all the incomes earned by the normal resident of our country during the year. This method is also known as the “factor payment method”.
COMPONENTS OF INCOME METHOD
- Compensation of Employees: It is the amount paid by employers to their employees for giving production services. It includes payment in cash as well as kind, directly or indirectly received by the employees. It includes “wages and salaries in cash”, “wages and salaries in kind” and “employers contribution to social security schemes”.
- Operating surplus: It refers to the sum total of income received by factors of production (land, capital, and entrepreneur). It includes “rent and royalty”, “interest” and “profit”. Interest income includes the interest taken for production purposes only. Profit includes corporate tax, retained earnings, and dividends.
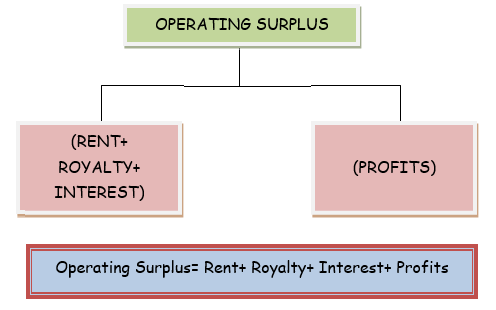
- Mixed-Income: It is the income earned by self-employed persons and has components of more than one type of income from factors of production. For example, farmers produce wheat on their own farming land.
NDPFC = Compensation of Employees+ Operating Surplus+ Mixed-Income
PRECAUTIONS OF INCOME METHOD
- Transfer incomes are not included in national income.
- Income from the sale of second-hand goods is not included in national income.
- Income from the sale of shares, bonds, debentures, etc…. is not included. However, the brokerage on the sale is included.
- Windfall gains such as lottery incomes are not included.
- Payment out of the previous savings is not included in national income.
- Indirect taxes are not included in national income.
- The imputed value of factor services provided by the owners for production purposes is included.
METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12 – EXPENDITURE METHOD
The factor income earned by the factors of production is spent in the form of consumption expenditure and received back by the firms. The expenditure is made by the households, business firms, government, and the foreign sector. This final expenditure is a sum totaled to get GDPMP(an aggregate of national income). This method is also known as the “Income Disposable Method”.
COMPONENTS OF EXPENDITURE METHOD
- Private Final Consumption Expenditure: It refers to all the expenditure made by households and private non-profit organizations on all types of goods (durable, semi-durable, non-durable, and services) earned by the normal resident of India.
- Government Final Consumption Expenditure: It refers to the expenditure made by the government on administration services such as defense, law, and order, education, etc….
- Gross Domestic Capital Formation: It refers to the addition to the capital stock of the economy. It includes- Gross Fixed Capital Formation and Inventory Investment. Gross Fixed Capital Formation refers to the expenditure made on the purchase of fixed assets. It includes Gross business fixed investment, gross residential construction investment, and gross public investment. Inventory Investment refers to the change in the stock of raw materials or goods kept with the producer.
Gross Domestic Capital Formation= Gross Fixed Capital Formation+ Inventory Investment
Gross Fixed Capital Formation= Gross Business Fixed Investment+ Gross Residential Construction Investment+ Gross Public Investment
Inventory Investment= Closing Stock- Opening Stock
- Net Exports: It refers to the difference between the exports and imports of a country during a period of time. Exports refer to the purchase of domestic goods by a foreign country. Imports refer to the purchase of foreign goods by a domestic country.
GDPMP= Private Final Consumption Expenditure+ Government Final Consumption Expenditure+ Gross Domestic Capital Formation+ Net Exports
PRECAUTION OF EXPENDITURE METHODS
- Expenditure on intermediate goods is not included in national income.
- Transfer incomes are not included in national income.
- Purchase of second-hand goods is not included in national income.
- Purchase of financial assets is not included in national income but the brokerage or commission on the sale is included in national income.
- Expenditure on goods produced for self-consumption will be included in national income.
GDP AND WELFARE
GDP refers to all the goods and services produced by a domestic country in a financial year. There are TWO types of GDP: Real GDP and Nominal GDP.
Nominal GDP: – It is also called GDP at the current year price. It is estimated on the basis of the prices of the same year in which the output is produced. It is inclusive of the inflation in the market.
Real GDP: – It is also called GDP at base year/ constant price. It is estimated on the basis of prices of some base year in which there was no or less inflation. It tells us the real increase in the GDP. It truly reflects the growth of the Economy.
Real GDP is better than Nominal GDP as it shows the true economic growth.

GDP DEFLATOR: – It measures the average price level of all goods and services produced in the economy that constitute the GDP. It is also known as “PRICE INDEX”.

GDP is often considered as a measurement of welfare. Higher GDP means higher welfare. But it may not stand true all the time. Following are certain situations: –
1. Distribution of income: Due to the rise in GDP, the gap between rich and poor may also increase, As GDP does not consider inequalities in the distribution of income. . So, welfare does not rise with rising in GDP.
2. Non- monetary exchanges: Some of the transactions may not be measured in monetary terms i.e., they will not be included in the GDP of the economy but these activities influence the welfare of the economy in a positive way. For example, work done by the housewife.
3. Externalities: These refer to the benefits or harms caused by the external factors which are not recorded in GDP. For example, a factory set up near a residential area causes pollution which harms the welfare but at the same time increases the GDP. On the other hand, a public park set up near a residential area does not affect the GDP but at the same time increases the welfare of the people.
4. Rate of population growth: GDP does not take into account population growth. If the population rises at an increase in comparison to the increase in the GDP then it will lead to less availability of goods and services for an individual. This will adversely affect the welfare of the economy.
5. Change in prices: Due to an increase in prices the nominal GDP will rise but it will lead to inflation in the market. This will decrease the economic welfare adversely as there is no increase in the physical output available.
RECONCILIATION OF METHODS OF NATIONAL INCOME AND ITS AGGREGATES
CBSE Class 12 Economics Notes Term II Syllabus
Part A: Introductory Macroeconomics
- Circular Flow of Income Class 12 Notes
- Basic Concepts of Macroeconomics Class 12 Notes
- National Income and Related Aggregates Class 12 Notes – 10 Mark
- National Income and Related Aggregates Class 12 Numericals
- Determination of Income and Employment Class 12 Notes
Part B: Indian Economic Development
Current challenges facing Indian Economy – 12 Marks
Development Experience of India – A Comparison with Neighbours – 6 Marks