An economy as a whole, comprises of various individuals, companies various commodities etc. , like individual income, output of a particular commodity by a company etc. When each of such units are combined, we get the aggregate of such attributes for the entire economy. In this light, let us understand the meaning of Micro and Macro Economics.
Micro and Macro Economics – Meaning of Microeconomics :-
The term ‘micro’ has been derived from the Greek word ‘mikros’ which means “small”.
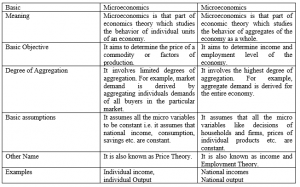
Microeconomics is that part of economic theory, which studies the behavior of individual units of an economy. For example, Individual income, individual output, price of a commodity etc. The main tools of Microeconomics are Demand and supply.
Micro and Macro Economics – Meaning of Macroeconomics :-
The term ‘macro’ has been derived from the Greek word ‘makros’ which means ‘large’.
Macroeconomics deals with overall performance of the economy and is concerned with study of problems of the economy like inflation, unemployment, poverty etc. Macroeconomics is that part of economic theory which studies the behavior of aggregates of the economy as a whole.
For example : – National income, aggregate output, aggregate consumption etc. Its main tools are Aggregate Demand and Aggregate supply.
Difference between Micro and Macro Economics
Microeconomics and microeconomics are not independent of each other and there is a lot of common ground between them.
Microeconomics depends on Macroeconomics
- Law of demand came into existence from the analysis of the behavior of a group (aggregate) of people.
- Law of commodity is influenced by the general price level prevailing in the economy.
Macroeconomics depends on Microeconomics
- National income of a country is nothing but the sum total of incomes of individuals units of the country.
- Aggregate demand depends on demand of individual households of the economy.