Market Mechanism MCQ Class 12 – Equilibrium Price and Quantity in a Competitive Market, covers certain important topics, which are covered under syllabus for ISCE Class 12 and are coming in Term I examination for the academic year 2022-23. Market Mechanism Class 12 MCQ Test contains 52 questions. MCQ on Economics Class 12 ISC have been made for Class 12 students to help check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
Market Mechanism MCQ Class 12
1.The price at which Quantity Demanded = Quantity Supplied is
(a) Market Price
(b) Equilibrium Price
(c) Consumer’s Price
(d) Supply Price
Answer
Answer: (b) Equilibrium Price
2. The maximum price a consumer will pay for a good is equal to its
(a) Total Utility
(b) Income of the Consumer
(c) Marginal Utility
(d) Reserve Price
Answer
Answer: (c) Marginal Utility
3. The minimum limit of price which producers will offer a good for sale is their
(a) Final Price
(b) Marginal Utility
(c) Marginal Cost of Production
(d) Equilibrium Price
Answer
Answer: (c) Marginal Cost of Production
4.________ and ______ curves tell us about different quantities that are demanded by a consumer at different prices
(a) demand, price
(b) price, supply
(c) demand, supply
(d) supply, output
Answer
Answer: (c) demand, supply
5.equilibrium refers to a state of
(a) discomfort
(b) rest
(c) supply
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) rest
6.When the quantity demanded is not equal to the quantity supplied, we say the market is ____
(a) collapsing
(b) in stable equilibrium
(c) in equilibrium
(d) in disequilibrium
Answer
Answer: (d) in disequilibrium
7.At equilibrium, ________ are in equilibrium
(a) price
(b) demand
(c) supply
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the above
8.Buyer demands a commodity because it possesses ______
(a) utility
(b) satisfaction
(c) purchasing power
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) utility
9.Sellers aim at ______
(a) achieving equilibrium
(b)earning profits
(c) selling below equilibrium price
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) earning profits
10.Lowest limit of Price is the
(a) Average Cost
(b) Marginal Utility
(c) Marginal Cost of Production
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Marginal Cost of Production
11.When the price equals the equilibrium price and quantity bought and sold equals the equilibrium quantity, is called
(a) Consumer equilibrium
(b) Market equilibrium
(c) Mechanized equilibrium
(d) Suppliers’ Equilibrium
Answer
Answer: (b) Market equilibrium
Market Mechanism MCQ Class 12
Equilibrium Price and Quantity in a Competitive Market – Price Determination
12.What kind of a situation arises at point A
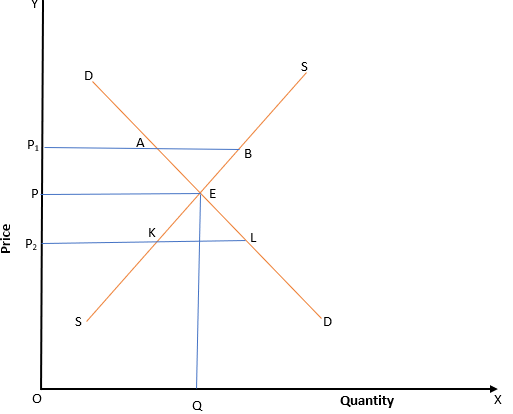
(a)Excess Supply
(b) Excess Demand
(c) Demand > Supply
(d) Equilibrium
Answer
Answer: (a)Excess Supply
13.Which of the following is NOT True about Determination of Equilibrium
(a) Amount by which quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied is called Excess Demand
(b) Equilibrium falls between Marginal Utility and Marginal Cost of Production
(c) Both sides have to compromise/budge from their price to attain Equilibrium
(d) Graphically, equilibrium is where the demand and supply curve do not intersect
Answer
Answer: (d) Graphically, equilibrium is where the demand and supply curve do not intersect
14. Equilibrium price is also called as ______ price
(a) ideal
(b) optimum
(c) supply-demand
(d) market clearing
Answer
Answer: (d) market clearing
15.In a competitive market, price is determined through the interaction of market
(a) price and demand
(b) demand and supply
(c) price and supply
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) demand and supply
| Price
(Rs per Shirt) |
Quantity Demanded
(000 Shirts per month) |
Quantity Supplied
(000 Shirts per month) |
Market Position |
| 1000 | 30 | 56 | |
| 900 | 40 | 50 | |
| 800 | 45 | 45 | |
| 700 | 55 | 35 | |
| 600 | 70 | 20 |
Answer the following with reference to the given demand and supply schedule of shirts
16.At what price is market equilibrium found
(a) 800
(b) 900
(c) 1000
(d) 850
Answer
Answer: (a) 800
17.When price is 600, there emerges
(a) excess supply
(b)excess demand
(c) shortage of demand
(d) equilibrium
Answer
Answer: (b) excess demand
18.When the price is 1000, what must happen to the quantity demanded for it to achieve equilibrium
(a) it should remain the same
(b)it should decrease
(c) it should increase
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) it should decrease
19.The amount by which the quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied is referred to as
(a) excess consumer demand
(b) excess supply
(c) excess demand
(d) equilibrium
Answer
Answer: (c) excess demand
20.Whenever there is shortage of goods in the market, ____ compete against each other for the limited goods offered for sale
(a) sellers
(b) producers
(c) buyers
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) none of the above
21.The demand and supply curve together
(a) are parallel to each other
(b) are always perpendicular to each other
(c) intersect each other and are in a diagonal plus shape
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) intersect each other and are in a diagonal plus shape
Market Mechanism MCQ Class 12
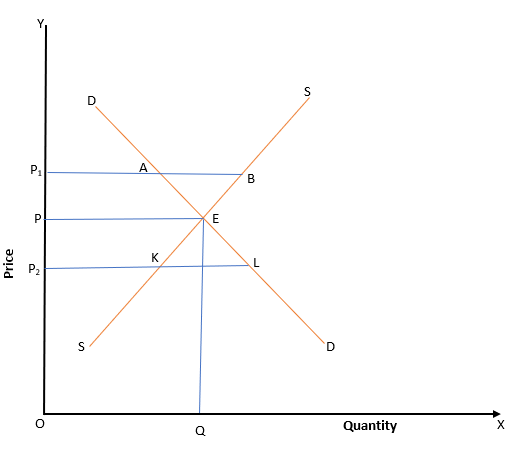
Answer questions based on the following diagram
22.What does point A represent
(a) Excess Supply
(b) Shortage in Demand
(c) None of the above
(d) Both a and b
Answer
Answer: (d) Both a and b
23.What does Point L represent
(a) Excess Supply
(b) Shortage of Demand
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) None of the above
24._________ equilibrium is one which, if displaced due to some small disturbance, brings forces in operation which restore the initial equilibrium position.
(a) unstable
(b)stable
(c) equal
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) stable
25._______ has described the two forces of demand and supply as the two blades of a scissor which are necessary to cut a piece of cloth.
(a) Parets
(b) Hicks and Allen
(c) Adam Smith
(d) Alfred Marshall
Answer
Answer: (d) Alfred Marshall
Market Mechanism MCQ Class 12
Effects of Changes and simultaneous changes in demand and supply on the equilibrium price along with special cases of equilibrium
26.If supply remains constant, a Leftward Shift in demand curve will lead to
(a) fall in equilibrium price and quantity bought
(b) rise in equilibrium price and quantity bought
(c) fall in equilibrium price but increase in demand
(d) fall in demand but increase in price of good
Answer
Answer: (a) fall in equilibrium price and quantity bought
27.With demand being constant, an increase in supply of the commodity causes
(a) decrease in equilibrium price and quantity
(b) increase in equilibrium price and quantity
(c) decrease in equilibrium price and increase in the equilibrium quantity
(d) increase in the equilibrium price and decrease in the equilibrium quantity
Answer
Answer: (c) decrease in equilibrium price and increase in the equilibrium quantity
28.When demand and supply increase in the same proportion,
(a) Price Increases
(b) Price is same
(c) Price decreases
(d) No constant value of price
Answer
Answer: (b) Price is same
29.What happens here, with respect to equilibrium (P is initial Price)
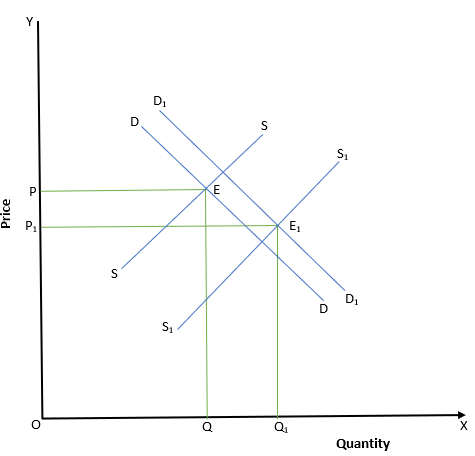
(a) Price remains same
(b) Price rises
(c) Price falls
(d) Increase in demand > Increase in Supply
Answer
Answer: (c) Price falls
30.When the demand curve is perfect elastic,
(a) increase in supply leads to decrease in quantity bought and sold
(b) decrease in supply leads to increase in quantity bought and sold
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) None of the above
31.Identify this diagram
(a) Perfectly Elastic Supply Curve
(b) Unitary Elastic Demand Curve
(c) Perfectly Inelastic Demand curve
(d) Demand curve where Elasticity is Infinite
Answer
Answer: (c) Perfectly Inelastic Demand curve
32.When supply curve is perfectly inelastic, an increase in demand leads to
(a) fall in price and quantity
(b) rise in price but fall in quantity
(c) fall in price but same quantity
(d) rise in price but same quantity
Answer
Answer: (d) rise in price but same quantity
33.A leftward shift of the demand curve will lead to ______ in equilibrium price and _____ in equilibrium quantity bought and sold
(a) rise, fall
(b) fall, rise
(c) rise, rise
(d) fall, fall
Answer
Answer: (d) fall, fall
34.When demand curve shifts to the right, competition among producers and consumers cause price to
(a) rise
(b) fall
(c) remain constant
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) rise
35.When demand remains constant, an increase in supply leads to ________ in price and ________ in quantity bought and sold
(a) rise, fall
(b) fall, rise
(c) rise, rise
(d) fall, fall
Answer
Answer: (b) fall, rise
36.When the relative increase in demand is smaller than the relative increase in supply, price ______ and equilibrium quantity _____
(a) rises, falls
(b) falls, rises
(c) falls, falls
(d) rises, rises
Answer
Answer: (b) falls, rises
37.When demand curve is parallel to the X-axis, an increase in supply leads to a ______
(a) decrease in quantity demanded
(b) increase in quantity demanded and sold
(c) change in price
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) increase in quantity demanded and sold
38.The given diagram below shows a change in quantity demanded when ________ is _______
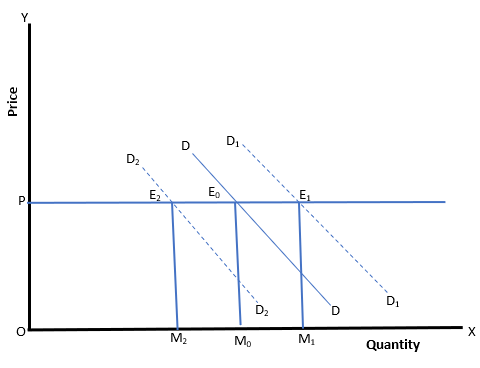
(a) demand, perfectly elastic
(b) supply, perfectly elastic
(c) demand, perfectly inelastic
(d) supply, perfectly inelastic
Answer
Answer: (b) supply, perfectly elastic
Market Mechanism MCQ Class 12
IMPORTANCE OF TIME ELEMENT IN DETERMINATION OF PRICE IS CANCELLED
Applications of Tools of Demand and Supply – Price Control
39.Maximum Price Legislation is also known as
(a) Price Ceiling
(b) MRP
(c) Price Floor
(d) Price Control
Answer
Answer: (a) Price Ceiling
40.Which of these is true about Price Ceiling
(a) There is no rationing
(b) Price ceiling is set below equilibrium price
(c) Price ceiling is used for goods like Gold, Luxury Cars
(d) It mainly benefits higher income groups
Answer
Answer: (b) Price ceiling is set below equilibrium price
41._____ is a system of distribution of a specified quantity of a product at price fixed by the government
(a) Black Market
(b) Allocation by Seller’s Preference
(c) Rationing
(d) First come, first serve
Answer
Answer: (c) Rationing
42.What happens when the price of a product is fixed at Floor Price
(a) Excess Demand
(b) Excess Supply
(c) Rationing
(d) Quantity Bought and sold rises
Answer
Answer: (b) Excess Supply
43.________ is the maximum legal price which the suppliers can charge for a particular good or service
(a) Price Ceiling
(b) Price Floor
(c) Price Mechanism
(d) Price Surface
Answer
Answer: (a) Price Ceiling
44.Price ceiling is imposed on goods like
(a) wheat
(b) oil
(c) rice
(d) all of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) all of the above
45.Price ceiling is usually more favorable for
(a) Rich people
(b) Upper middle-class groups
(c) Low-income groups
(d) Both a and c
Answer
Answer: (c) Low-income groups
46.Price ceiling is set below equilibrium. Why does this happen?
(a) To create a shortage of the good
(b) To create excess demand
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Both a and b
47.A seller may sell a scarce product only to his regular customers, this is called
(a) rationing
(b) allocation by sellers’ preference
(c) First come, First served
(d) Black Market
Answer
Answer: (b) allocation by sellers’ preference
48.______ is a place where goods are sold illegally at prices higher than a legally fixed price by the government
(a) White bazaar
(b) Ration Market
(c) Black Market
(d) Piracy market
Answer
Answer: (c) Black Market
49.What is floor price also known as
(a) Minimum Support Price
(b) Minimum Price Legislation
(c) None of the above
(d) Both a and b
Answer
Answer: (d) Both a and b
50.Fixing minimum price causes
(a) surplus
(b) shortage
(c) equilibrium
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) surplus
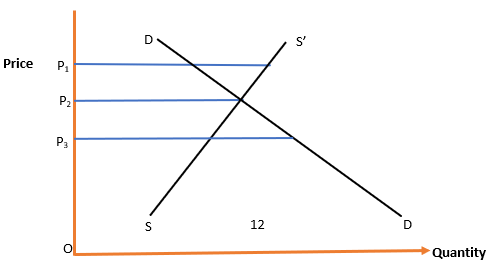
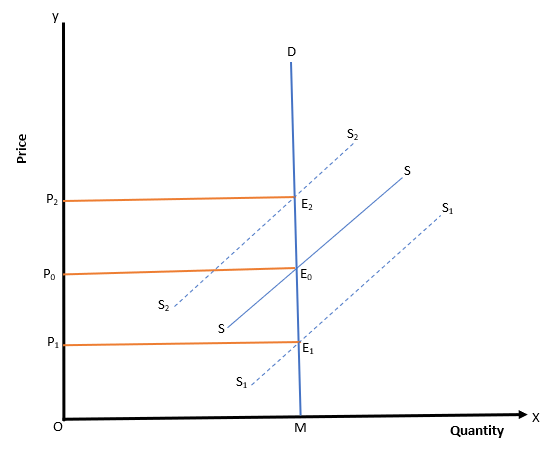
Answer the following questions with reference to the diagram given below
51.At what price is the floor price set
(a) OP1
(b)OP2
(c)OP3
(d) None of the options
Answer
Answer: (a) OP1
52.At what price is the ceiling price set
(a) OP1
(b)OP2
(c)OP3
(d) None of the options
Answer
Answer: (c)OP3
Economics Class 12 ISC MCQs – Term 1
- Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12
- Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ
- Elasticity of Demand
- Supply – Law of Supply and Price Elasticity of Supply
- Market Mechanism
- Law of Returns
- Cost and Revenue Analysis
- Forms of Market
- Producer’s Equilibrium
- Determination of Equilibrium Price and Output under Perfect Competition