Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12 Questions covers certain important topics, which are covered under syllabus for ISCE Class 12 and are coming in Term I examination for the academic year 2022-23. Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12 Test contains 59 questions. MCQ on Economics Class 12 ISC have been made for Class 12 students to help check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12
Introduction
1. Which of the following statements about free goods are correct?
a) Present in Unlimited quantity
b) Do not command a price
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Scarce in nature.
Answer
Answer: c) Both (a) and (b)
2. Economic goods are;
a) Unlimited
b) Scarce
c) Free
d) All of the following
Answer
Answer: b) Scarce
3. Prices of goods and services in an economy are determined by_____.
a) Demand
b) Supply
c) Predetermined
d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
Answer: d) Both (a) and (b)
Meaning and types of demand
4. Which one of the following is True about the Meaning of Demand:
(a) Demand is an Effective Desire
(b) Demand in Economics is always at Price
(c) Demand is expressed with reference to a particular time period
(d) All of the Above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
5. Taste and preferences of the customer depend on
a) Social customs
b) Habits of the consumer
c) Lifestyle of people
d)All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
6. _______ refers to the number of goods that consumers want to buy at a particular point of time.
a) Planned consumption
b)Unplanned consumption
c) Ex post demand
d) Ex-ante demand
Answer
Answer: d) Ex-ante demand
7._______ refers to the number of goods and services that consumers actually buy.
a) Actual consumption
b) Ex-ante demand
c) Ex post demand
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Ex post demand
8. _________ refers to the demand for two or more goods that are purchased together.
a) Combined consumption
b) Joint demand
c) Ex post demand
d) Ex-ante demand
Answer
Answer: b) Joint demand
9. The demand for a commodity that arises due to demand of some other commodity is called
a) Derived demand
b) Joint demand
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Derived demand
10. Demand for goods that have multiple uses is called
a) Derived demand
b) Joint demand
c) Composite demand
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Composite demand
11. The functional relationship between the demand of a commodity and the income of the consumer is known as
a) Price demand
b) Income demand
c) Composite demand
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Income demand
Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12
12. ________ goods can be used in place of each other
a) Income goods
b) Price goods
c) Substitute goods
d) Complementary goods
Answer
Answer: c) Substitute goods
13. Which of the following are Complementary Goods
(a) Pencil and Pen
(b) McDonald’s and Burger King
(c) Tea and Sugar
(d) Tea and Coffee
Answer
Answer: (c) Tea and Sugar
14. The functional relationship between demand for a commodity and income of consumer is called
(a) Income demand
(b) Price demand
(c) Money demand
(d) Consumer demand
Answer
Answer: (a) Income demand
15. As the income of a consumer increases, the demand for goods like jowar/maize will _____
(a) increase
(b) remain constant
(c) decrease
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) decrease
16. _________ are those goods which are used jointly or consumed together to satisfy a given want
(a) Joint goods
(b) Composite Goods
(c) Complementary Goods
(d) Derived Goods
Answer
Answer: (c) Complementary Goods
17. Individual demand is the same as –
(a) Household demand
(b) Market Demand
(c) Industry Demand
(d) Both (c) and (b)
Answer
Answer: (a) Household demand
18. If distribution of income in a country is uneven, then there will be more demand for _______
(a) normal goods
(b) luxury goods
(c) necessities
(d) None of the Above
Answer
Answer: (b) luxury goods
Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12
Determinants of demand
19. Which of the following are determinants of demand for a commodity.
a) Price of the commodity
b) Income of the consumer
c) Consumer’s taste
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
20. The demand for a quantity Y increases with a decrease in the price of a product X. The product Y is a:
(a) Substitute Good
(b) Complementary Good
(c) Giffen Good
(d) Luxury Product
Answer
Answer: (b) Complementary Good
21. Which one of the following is not a determinant of demand:
(a) Consumers’ Expectations
(b) Climatic Factors
(c) Input Prices
(d) Distribution of Income
Answer
Answer: (c) Input Prices
22. There is a ______ relationship between the price of the commodity and quantity demanded
a) Inverse.
b) Direct
c) No relationship
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Inverse.
23. ______ refers to different quantities of a commodity purchased at different prices.
a) Composite demand
b) Joint demand
c) Price demand
d) Income demand
Answer
Answer: a) Composite demand
24. The three types of goods when talking about income and purchasing power of consumer are
a) Inferior goods.
b) Normal goods
c) Inexpensive necessities of life
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
25. The demand for ____ goods increases with an increase in income.
a) Normal goods
b) Inferior goods
c) Inexpensive necessities of life
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Normal goods
26. Which of the following are examples of inferior goods
a) Black and white tv
b) Coarse cloth
c) Coarse cereals
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
27. Which of the following is an example of inexpensive necessities
a) Salt
b) Matchbox
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Both (a) and (b)
28. The given diagram shows the relation between the quantity demanded of X and the price of Z, what type of goods are X and Z
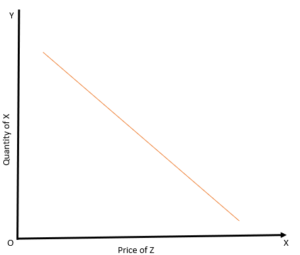
(a) Unrelated Goods
(b) Substitute Goods
(c) Complementary Goods
(d) None of the Above
Answer
Answer: (c) Complementary Goods
Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12
Law of demand
29. People often tend to buy expensive clothes such as Gucci and Prada despite their extremely high price, just to emulate the consumption style of other people, this is called
(a) Income Effect
(b) Price Effect
(c) Demonstration Effect
(d) Substitution Effect
Answer
Answer: c) Demonstration Effect
30. Relationship between the demand for a product and its various determinants is called
a) Demand
b) Demand function
c) Price demand
d) Income function
Answer
Answer: (b) Demand function
31. A graphic presentation of levels of demand is called
a) Demand curve
b) Demand schedule
c) Demand function
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Demand curve
32. ________ is the effect that a change in relative prices of substitute goods has on the quantity demanded
a) Demand effect
b) Price effect
c) Substitution effect
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Substitution effect
33. Which of the following decides the Law of demand
a) Law of diminishing Marginal utility
b) Income effect
c) Substitution effect
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
34. The Law of Demand states that other things remaining equal, the quantity demanded of a commodity ______ when its price falls and decreases when it’s price ______
(a) Increases, rises
(b) decreases, rise
(c) Increases, falls
(d) Decreases, falls
Answer
Answer: (a) Increases, rises
35. Which one of these is a reason for the downward slope of the demand curve
(a) Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
(b) Emergency Situations
(c) Expectation that prices will rise in the future
(d) Quality-Price Relationship
Answer
Answer: (a) Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
36. The sum total of Income Effect and Substitution Effect is called
(a) Money Effect
(b) Cost Effect
(c) Price Effect
(d) Demand Effect
Answer
Answer: (c) Price Effect
37. If the price of a commodity is rising now at a high pace and is expected to rise even more than what it is worth today in the future, then despite the high price, the demand for the commodity will
(a) increase
(b) decrease
(c) Be unchanged
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) increase
38. Movement along the demand curve leads to
(a) Increase in demand
(b) Decrease in demand
(c) Contraction of Demand
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Contraction of Demand
39. Name this movement along the demand curve
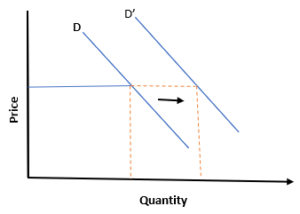
(a) Increase in Demand
(b) Expansion of Demand
(c) Leftward Shift of demand
(d) None of the Above
Answer
Answer: (a) Increase in Demand
40. A _______ in demand means that the entire demand curve shifts to the _____, indicating a smaller amount purchased at every price
(a) Increase, left
(b) decrease, right
(c) increase, right
(d) decrease, left
Answer
Answer: (d) decrease, left
41. The relationship between the demand for a product and its various determinants is called
a) Demand
b) Demand function
c) Price demand
d) Income function
Answer
Answer: b) Demand function
Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12
42. A graphic presentation of levels of demand is called
a) Demand curve
b) Demand schedule
c) Demand function
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Demand curve
43. ________ is the effect that a change in relative prices of substitute goods has on the quantity demanded
a) Demand effect
b) Price effect
c) Substitution effect
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Price effect
44. Which of the following decides the Law of demand
a) Law of diminishing Marginal utility
b) Income effect
c) Substitution effect
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
45. A change in demand on account of a change in the real income resulting from a change in price of a commodity is called ____
(a) Income effect
(b) Price effect
(c) Substitution Effect
(d) Change effect
Answer
Answer: (a) Income effect
46. Substitution effect is the effect that a change in ____ of substitute goods has on quantity demanded
(a) total prices
(b) external cost
(c) relative prices
(d) utility
Answer
Answer: (c) relative prices
47. ______ Is the horizontal summation of the demand curves of all households
(a) Individual Demand Schedule
(b) Market Demand Curve
(c) Market Schedule
(d) Market Demand Map
Answer
Answer: (b) Market Demand Curve
48. Sometimes, consumers assume that high-priced goods are of higher quality than lower-priced goods which leads to an increase in demand even when the price of the commodity is high. This is known as the
(a) Veblen Effect
(b) Demonstration Effect
(c) Conspicuous Effect
(d) All of the Above
Answer
Answer: (a) Veblen Effect
49. When a commodity goes out of fashion, consumers will not purchase a larger amount of the commodity even if the price is ______
(a) increased
(b) reduced
(c) doubled
(d) unchanged
Answer
Answer: (b) reduced
50. Which of the following is not True about Human wants: –
(a) Unlimited
(b) Insatiable
(c) Multiple
(d) Competitive
Answer
Answer: (b) Insatiable
51. If consumers are able to get credit facilities or borrowings from the bank for purchasing a certain good, the demand for that goodwill ______
(a) Decrease
(b) Remain unchanged
(c) Increase
(d) Cannot be said
Answer
Answer: (c) Increase
Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12
52. A reduction in the size of the population will lead to _______ in demand
(a) increase
(b) decrease
(c) no change
(d) cannot be determined
Answer
Answer: (b) decrease
53. In the summer season, the demand for thick cotton clothes will ____
(a) decrease
(b) increase
(c) remain unchanged
(d) cannot be specified
Answer
Answer: (a) decrease
54. If the government imposes taxes on a commodity, the price of that commodity will _____ and the demand for it will________
(a) decrease, decrease
(b) increase, increase
(c) increase, decrease
(d)decrease, increase
Answer
Answer: (c) increase, decrease
55. Which of the following are assumptions to the Law of Demand
(a) The commodity should be a normal commodity
(b) There should be some changes in taste and preference of the consumer
(c) Size and population should change
(d) Prices of related commodities may change
Answer
Answer: (a) The commodity should be a normal commodity
56. Given below are 2 individual demand schedules for Mangoes at given prices. Fill in the Market Demand Schedule for quantity of mangoes demanded by A and B
| Price per Kg | Quantity demanded by Alpha household | Quantity demanded by Beta Household | Total Market Demand |
| 120
100 90 80 |
1 kg
3 kg 5 kg 7 kg |
2 kg
4 kg 6 kg 8 kg |
?
? ? ? |
(a) 2,3,5,7
(b) 3,5,9,13
(c) 3,5,7,13
(d) 3,7,11,13
Answer
Answer: (d) 3,7,11,13
57. Which of the following are the reasons for an upward sloping demand curve
a) Giffen goods
b) Emergencies
c) Quality-price relationship
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
58. A fall in the price results in
a) Expansion of demand
b) Contraction in demand
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Expansion of demand
59. A rise in price results in
a) Expansion of demand
b)Contraction in demand
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b)Contraction in demand
Economics Class 12 ISC MCQs – Term 1
- Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12
- Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ
- Elasticity of Demand
- Supply – Law of Supply and Price Elasticity of Supply
- Market Mechanism
- Law of Returns
- Cost and Revenue Analysis
- Forms of Market
- Producer’s Equilibrium
- Determination of Equilibrium Price and Output under Perfect Competition