What is Journal in accounting – Basic Concept of Journal
What is Journal in accounting ? A Journal is a record of financial transactions in chronological (date-wise, starting from the earliest to the latest date) order. Journal is also known as Book of Original Entry. Journal Entries for Class 11
Given that there are various types of transactions, like purchases, sales etc, depending on the number of transactions, a business can maintain either one single journal record all the transactions, or where the number of transactions are higher, they can maintain one separate journal for each category of such transaction.
When, all the business transactions , are entered in one single journal, we call it a Simple journal.
However, business entities can also maintained separate journals for recording different type of business transactions like Purchases Journal, Sales Journal, Sales Return Journal etc.
Journal is also known as books of original entry because a financial transaction is first time recorded in the journal . Thereafter , such transaction can be posted to the Ledger.
Format of a Journal:
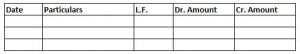
Recording of Transactions in Journal : –
The documents which evidence, the occurrence of a transaction are known as Source Documents. For example, in case of purchase of goods, the business would receive an invoice from the seller. Such an invoice would be the source document, which would be used by the company to create the voucher. All the transactions in a Journal are recorded , on the basis of source documents, i.e. Vouchers, by applying the rules of debit and credit.
Meaning of Voucher:
A voucher is a document , which is used to gather all the supporting documents, which are required to approve the payment of a liability.
It ensures that every payment is properly authorized and that the goods or services purchased are actually received.
To know more about Vouchers , read this Post
Totalling and Carry Forward in Journal :
There are large number of transactions in every business on a day to day basis. It is not possible to record all search transactions in a single page of journal. In view of this, once all possible transactions are recorded in a journal, the debit and credit column of the relevant page of the journal are totalled , and carried forward to the next page Of the journal.
In the particulars column, the word “Total c/f” is written which indicates the total amount carried forward to the next page.
In a similar manner, on the next page, in particulars column, the words “Total b/f” is written which indicates the amount which is brought forward from the previous page.
This process is followed till the recording of the last transaction.
Types of Journal Entries :
Types of Journal Entries Can be divided into the following two categories : –
(i) Simple Journal Entry : A Journal entry in which only two accounts are affected, i.e. one account is debited and the other account is credited , is known as simple entry.
For e.g. Raj started a business with cash of Rs. 50,000. In this transaction, the journal entry would be:
Cash A/c Dr 50,000
To Raj’s Capital A/c 50,000
In this journal entry only two accounts are affected, i.e. Cash A/c is debited and Raj’s Capital A/c is credited
(ii) Compound Journal Entry: Comp
For e.g. ” Paid Rs. 7,000 to Suraj in full settlement of his account of Rs. 10,000″ . The journal entry for the transaction would be:
Suraj’s A/c Dr 10,000
To Cash A/c 7,000
To Discount Received A/c 3,000
In this journal entry Suraj’s A/c is debited while two accounts i.e. Cash A/c and discount received A/c are credited
Some examples of journal entries are as given below:
Journal Entries for Class 11 – Carriage Inward Journal Entry – Accounts
Meaning of Carriage Inwards
Where goods, or any other item is purchased by the company, it we have to increase certain freight charges, to bring the goods from the warehouse of the seller, to the place of the purchaser. The freight or other carriage amount paid by the purchaser is known as carriage inwards. The use of the word in words suggest, that the goods are coming to the purchaser.
Question 1:
What would be the Journal Entry for Carriage Inwards paid amounting to Rs. 100 in Cash for purchase of goods ?
Explanation:
Since Cartage is an expense, so, Carriage Inwards A/c would be debited, because according to the Rules of Debit and Credit, an expense A/c is debited .
Further , on Payment of Carriage Inwards in Cash , Cash, whcih is an Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited, because according to the Rules of Debit and Credit, a reduction in an Asset account is credited.
Hence the Entry would be :
Carriage Inwards A/c Dr. 100
To Cash A/c 100
Salary Paid
Question 2:
What would be the Journal Entry for Salary paid amounting to Rs. 10,000 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Salary is an expense. So, Salary A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Salary in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Salary A/c Dr. 10,000
To Cash A/c 10,000
Journal Entries for Class 11 – Rent Paid
Question 3:
What would be the Journal Entry for Rent paid amounting to Rs. 12,000 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Rent is an expense. So, Rent A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Rent in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Rent A/c Dr. 12,000
To Cash A/c 12,000
Wages Paid
Question 4:
What would be the Journal Entry for Wages paid amounting to Rs. 1,125 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Wages is an expense. So, Wages A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Wages in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Wages A/c Dr 1,125
To Cash A/c 1,125
To Cash A/c 12,000
Interest on Loan
Question 5:
What would be the Journal Entry for Interest on Loan paid amounting to Rs. 10,000 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Interest on Loan is an expense. So, Interest on Loan A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Interest on Loan in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Interest on Loan A/c Dr 10,000
To Cash A/c 10,000
Office Expenses
Question 6:
What would be the Journal Entry for Office Expenses paid amounting to Rs. 10,500 through Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Office Expenses is an expense. So, Office Expenses A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Office Expenses through Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Office Expenses A/c Dr 10,500
To Cash A/c 10,500
Journal Entries for Class 11 – Carriage Outward
Question 7:
What would be the Journal Entry for Carriage Outward paid amounting to Rs. 12,000 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Carriage Outward is an expense. So, Carriage Outward A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Carriage Outward in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Carriage Outward A/c Dr 12,000
To Cash A/c 12,000
Carriage Inward
Question 8:
What would be the Journal Entry for Carriage Inward paid amounting to Rs. 10,500 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Carriage Inward is an expense. So, Carriage Inward A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Carriage Inward in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Carriage Inward A/c Dr 10,500
To Cash A/c 10,500
Sundry Expenses
Question 9:
What would be the Journal Entry for Sundry Expenses paid amounting to Rs. 10,500 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Sundry Expenses is an expense. So, Sundry Expenses A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Sundry Expenses in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Sundry Expenses A/c Dr 10,500
To Cash A/c 10,500
Taxes
Question 10:
What would be the Journal Entry for Municipal taxes paid amounting to Rs. 10,000 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Municipal taxes is an expense. So, Municipal taxes A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Municipal taxes in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Municipal taxes A/c Dr 10,000
To Cash A/c 10,000
Postage Expenses
Question 11:
What would be the Journal Entry for Postage Expenses paid amounting to Rs. 10,000 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Postage Expenses is an expense. So, Postage Expenses A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Postage Expenses in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Postage Expenses A/c Dr 10,000
To Cash A/c 10,000
Travelling Expense
Question 12:
What would be the Journal Entry for Travelling Expenses paid amounting to Rs. 10,800 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Travelling Expenses is an expense. So, Travelling Expenses A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Travelling Expenses in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Travelling Expenses A/c Dr 10,800
To Cash A/c 10,800
Stationery
Question 13:
What would be the Journal Entry for Stationery paid amounting to Rs. 11,250 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Since Stationery is an expense. So, Stationery A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Stationery in Cash , Asset is reduced , so Cash A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Stationery A/c Dr 11,250
To Cash A/c 11,250
Advertisement Expense
Question 14:
What would be the Journal Entry for Advertisement Expense paid amounting to Rs. 10,800 through Cheque ?
Explanation:
Since Advertisement Expense is an expense. So, Advertisement Expense A/c would be debited because expense A/c is debited .
And on Payment of Advertisement Expense through Cheque , Asset is reduced , so Bank A/c is credited.
Hence the correct entry is:
Advertisement Expense A/c Dr 10,800
To Bank A/c 10,800
Journal Entries for Class 11 – Cash Purchases
Question 15:
What would be the Journal Entry for Purchase of goods amounting to Rs. 10,000 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Purchase Account is debited because the firm has purchased goods for the purposes of sale.
And Cash Account is credited because the firm has paid Cash for purchase of goods.
Hence the correct entry is:
Purchases A/c Dr. 10,000
To Cash A/c 10,000
Asset Purchased in Cash
Question 16:
What would be the Journal Entry for Furniture purchased amounting to Rs. 10,000 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Furniture Account is debited because the firm has purchased goods for the purposes of sale.
And Cash Account is credited because the firm has paid Cash for purchase of goods.
Hence the correct entry is:
Furniture A/c Dr. 10,000
To Cash A/c 10,000
Credit Purchases
Question 17:
What would be the Journal Entry for Purchase of goods amounting to Rs. 10,000 from ABC Co. on credit.
Explanation:
Purchase Account is debited because the firm has purchased goods for the purposes of sale.
And ABC Co. Account is credited because the firm has purchased from ABC Co. on credit basis.
Hence the correct entry is:
Purchase A/c Dr. 10,000
To ABC Co. A/c 10,000
Credit Purchase of Asset-I
Question 18:
What would be the Journal Entry for Furniture purchased amounting to Rs. 10,000 from Nived ?
Explanation:
Furniture Account is debited because the firm has purchased goods for the purposes of sale.
And Nived Account is credited because the firm has purchased from Nived on credit basis.
Hence the correct entry is:
Furniture A/c Dr. 10,000
To Nived A/c 10,000
Payment to Creditors
Question 19:
What would be the Journal Entry for payment made to Creditors Rs. 1,200 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Creditors Account is debited because the firm has purchased goods for the purposes of sale.
And Cash Account is credited because the firm has paid to creditors in Cash.
Hence the correct entry is:
Creditors A/c Dr. 1,200
To Cash A/c 1,200
Journal Entries for Class 11 – Drawings
Question 20:
What would be the Journal Entry for Drawings made amounting to Rs. 10,200 for private expenses in Cash ?
Explanation:
Drawings Account is debited because amount is withdrawn for personal use.
And Cash Account is credited because cash has been taken out from the business in the form of drawings.
Hence the correct entry is:
Drawings A/c Dr. 10,200
To Cash A/c 10,200
Sales
Question 21:
What would be the Journal Entry for Sales of goods amounting to Rs. 10,000 in Cash ?
Explanation:
Cash Account is debited because amount is received against goods sold.
And Sales Account is credited because goods are sold on cash basis.
Hence the correct entry is:
Cash A/c Dr. 10,000
To Sales A/c 10,000
Payment of Asset made through cheque
Question 22:
What would be the Journal Entry for Building purchased for Rs. 10,000 through cheque ?
Explanation:
Building Account is debited because the firm has purchased building and it has resulted in increase of an asset.
And Bank Account is credited because the firm has purchased Building by making payment through cheque.
Hence the correct entry is:
Building A/c Dr. 10,000
To Bank A/c 10,000
Sale of Asset and Receipt through Cheque
Question 23:
What would be the Journal Entry for Building sold for Rs. 1,02,000 and payment received through cheque ?
Explanation:
Bank Account is debited because the firm has sold building and received payment through cheque.
And Building Account is credited because the firm has sold Building and it has resulted in decrease of an asset.
Hence the correct entry is:
Building A/c Dr. 1,02,000
To cheque A/c 1,02,000
Journal Entries for Class 11 – Installation of Asset
Question 24:
What would be the Journal Entry for Machinery installed by paying Rs. 10,000 in cheque ?
Explanation:
Machinery Account is debited because the firm has paid for installation of machinery.
And cheque Account is credited because the firm has paid for installation of Machinery in cash.
Hence the correct entry is:
Machinery A/c Dr. 10,000
To cheque A/c 10,000
To cheque A/c 1,02,000
Depreciation
Question 25:
What would be the Journal Entry for Depreciation on Furniture amounting to Rs. 10,000 at the rate of 10% ?
Explanation:
Depreciation Account is debited because the firm has paid for installation of machinery.
And Furniture Account is credited because the firm has paid for installation of Depreciation in cash.
Hence the correct entry is:
Depreciation A/c Dr. 10,000
To Furniture A/c 10,000
To cheque A/c 1,02,000
Unpaid Salary
Question 26:
What would be the Journal Entry for Salaries unpaid for the month of February amounting to Rs. 10,000 ?
Explanation:
Salaries Account is debited because it is an expense to the company and all expenses are debited.
And Salaries Outstanding Account is credited because it is unpaid hence it is a liability to the company.
Hence the correct entry is:
Salaries A/c Dr. 10,000
To Salaries Outstanding A/c 10,000
Chapter 3 – Recording of Transactions
- Business Transactions and Source Document
- Accounting Equation
- Using Debit and Credit
- Books of Original Entry – Click for Journal in Accounts
- The Ledger
- Posting from Journal