Maslow’s Need Hierarchy theory Class 12 explains the hierarchical order of the needs of the employees of an organization. It states how a satisfied need motivates a person to do better. All the points and a brief description of the theory is given below.
Maslow’s need hierarchy theory of motivation Class 12
The motivation process is not very easy. It becomes complex at times because of its human element. There are various theories published on this topic which include Maslow’s need hierarchy theory, Herzberg’s two-factor theory, Locke’s goal-setting theory, Alderfer’s ERG theory- existence needs, relatedness needs and growth needs etc. Maslow’s need hierarchy theory is an important theory to understand the hierarchy of needs of a human being thus it is fundamental to learn about motivation.
This theory was given by an American psychologist named Abraham Maslow in the year 1943. He outlined various needs of an individual which are in a hierarchical form and it motivates a person till the time it is satisfied.
Assumptions of Maslow’s need hierarchy theory Class 12
- An individual always wants to fulfil their unsatisfied need and these unsatisfied needs impact an individual’s behaviour. After fulfilment of their needs, they get satisfied and they act differently.
- The needs of an individual are in a hierarchical order which starts from the basic needs and then it levels up towards esteem needs and self-actualisation needs.
- A person will only be motivated till the time a particular need is unsatisfied and when it is fulfilled and satisfied then the person wants to fulfil/satisfy the next need in that order.
- An individual will move in a systematic and chronological order of the needs, he or she will move toward the fulfilment of the next need only when the lower need is satisfied.
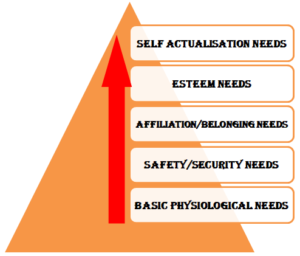
Five needs given by Maslow
Basic physiological needs
As per Maslow’s Need Hierarchy theory Class 12 there are the basic needs of an individual which are at the bottom of the pyramid. These needs are some basic fundamental biological needs of an individual which he or she needs to fulfil so that they can survive. These needs can be food, water, cloth, shelter and sleep. The unsatisfied basic physiological needs will affect an individual’s behaviour to a great extent.
In an organizational context, basic physiological needs will be getting a job, getting a salary, etc.
Safety or security needs
These are the second from the bottom of the pyramid. These needs are related to an individual’s safety and security from any physical, mental or emotional harm. Once the basic physiological needs are satisfied then they are not enough capable of motivating a person. Therefore, security and safety need to come into play. A person works hard to get a secure environment which is free from threats. It is related to personal security, economic security, resources security etc.
In an organizational context: security and safety needs are getting the stability of income, job security, pension after retirement etc.
Social / affiliation/belonging needs
Man can be called a social animal that is always in search of a good company so that he feels connected and socially acceptable. These needs are also related to the same aspect. Maslow’s Need Hierarchy theory Class 12 mentions that A man will work hard to get his connections stronger. These needs are on an emotional frontier. These are related to affection, love, intimacy and friendship.
In an organizational context: social/affection/belonging needs are related to the social groups in an organization, recognition by peers, cordial relationships with colleagues etc.
Esteem needs
When the lower levels’ needs are fulfilled then the esteem needs play a role of a motivator. These needs are related to the self-esteem and self-respect of an individual where the person is looking for achievement, confidence, knowledge, competence and freedom.
In an organizational context: esteem needs are fulfilled in an organization when an employee gets freedom, recognition, self-respect and some importance and status.
Self-actualisation needs
It is at the top of the need hierarchy pyramid. It is a need or drive which motivates a person to become something is capable of i.e. to reach his maximum potential. While working and achieving the lower levels of the need hierarchy sometimes a person is not able to reach this level. But this level is very motivating because there is always something or the other thing that a person can become and achieve.
In an organizational context: the self-actualisation need of an employee will be to reach the top level in an organization i.e. be a part of the board of directors or become a CEO or will seek other growth opportunities. They may also wish to start their own business and become a successful entrepreneur.
According to Maslow there are some qualities of the self-actualising people under Maslow’s Need Hierarchy theory
When a person has reached the top of the pyramid then he or she will become aware of the surroundings and will be thoroughly aware of right and wrong and would have taken learning from past mistakes. There are some other qualities of these people which are described by Maslow, they are:
- Truth and honesty
- Goodness, rightness and benevolence
- Quality of detachment and spending time in privacy
- Unity, integration and sense of community
- Dichotomy and transcendence
- Aliveness
- Uniqueness and individuality
- Perfection, nothing superfluous or lacking.
- Necessity
- Completion
- Justice, fairness, order and lawfulness
- Bluntness and simplicity
- Richness and totality
- Effortlessness and ease in doing things
- Playful and joyful
- Self sufficiency and autonomy
- Appreciation and gratitude for things
- Acceptance of reality
- Problem centred approach
- Seeking deeper and real connections
Maslow’s Need Hierarchy theory Class 12 clearly states that a person is motivated by an unsatisfied need only till the time it gets satisfied. These needs will not motivate a person after he or she reaches the next level. Exceptions are always there and this theory does not take into account that every employee will have different kinds of needs. But still, this theory is one of the most correctly stated theories of motivation.
Chapter 7 – Directing
- Directing – Introduction, Meaning, Importance & Principles
- Motivation – Element of Directing
- Incentives – Types of Incentives
- Maslow’s need hierarchy theory of motivation
- Leadership
- Communication