Financing Decision Class 12 deals with various financing decisions that an organization needs to make for the working of an organization. A detailed explanation of all the decisions is given below.
Financial Decisions Class 12 in Financial Management
Decision-making is a very crucial and non – negotiable part of any business. Several decisions are taken in a firm. The main decision is to start the company and then acquire resources like money. This decision related to business finance mobilization, utilization, and distribution is called financial decisions in financial management.
Financial decisions are usually made by the financial manager either single-handedly or with other managers having expertise in financial management. Financial decisions are required for proper usage of the finances available and avoidance of shortage of funds along with lowering the risk and cost involved so that returns can be higher. It brings coordination in the firm and financial discipline so that the administration works efficiently and effectively.
There are three major decisions in financial decisions of financial management –
- Investment decisions,
- Financial decisions
- Dividend decisions.
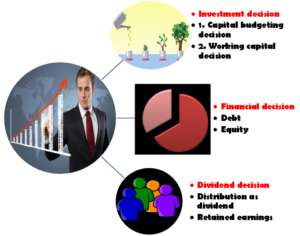
Let us understand these decisions in more detail and knowledge about the factors affecting these decisions.
Investing under Financing Decision Class 12
Investing decisions is a fact that the world has limited resources and our needs are unlimited. Similarly, in businesses too, business finance is limited but the ways it can be put to use are unlimited. Therefore, it becomes important to choose wisely where to invest so that the finance gets the highest return possible. Thus, how and where the firm’s funds are invested is the core of investment decisions.
The investment decision is broadly classified into two categories and they are:
- Long-term investment decision: long-term investment decision is also called a ‘capital budgeting decision’. Capital budgeting decision involves capital expenditure. Capital expenditure itself means a high amount of investment for a long period of time. These decisions are very crucial because they affect the profitability and competitiveness of the firm because of their commitment for a longer period. They are difficult to reverse and cannot be done after putting in a huge cost. They should be taken with utmost care because a bad capital budgeting decision will affect a firm’s financial fortune severely.
Some examples of capital budgeting decisions are: investment in new machinery, opening a new branch of the firm or buying a new fixed asset, etc.
- Short-term investment decision: short-term investment decision is working capital decisions. These decisions are for a short period of time, for daily activities. These decisions affect the working of the business, its liquidity, and profitability. A sound working capital decision includes proper cash management, inventories management, bills receivables management, etc. good working capital management will try to achieve both, higher profitability and higher liquidity.
Factors affecting capital budgeting decisions
There are various factors that affect the capital budgeting decision or long-term investment decision because there is a number of projects where the business can invest and it depends on this decision whether the project will be selected or rejected based on careful analysis.
- Cash flow of the project: despite the availability of cash with the firm, it is important to consider the cash flow of the project. Every project that the firm invests in involves cash flow for the period it is invested for. The cash receivables and cash payments are part of this cash flow. The firm needs to carefully analyze this before taking any decision regarding capital budgeting because of the huge cost involved.
- The rate of return: businesses run for profit. They look for some return from every activity they do. Thus, every investment is made so that some good amount of return is gained with the lowest risk and lowest cost possible. If there are two projects which have the same cost involved then a good financial manager would choose the project with higher returns.
- The investment criteria involved: a capital budgeting decision is a difficult decision because it is made for a long period of time and involves a high amount of cost with a higher degree of risk and is irreversible which can affect the competitive strengths of the business. There are various principles and methods of the company to select a proper capital budgeting area to invest in. these techniques can differ for each business based on the procedure they follow. These are called capital budgeting techniques. For example internal rate of return, accounting rate of return, payback period method, etc.
Financing decisions Class 12
The financing decision Class 12 is regarding the quantum/amount of finance that is to be raised from various sources for a long period of time. The financial decision does not involve the decision regarding funds for a short period of time; it is considered under working capital management. Identification of various sources, careful analysis, and then selection of the source which is considered best for the firm are the main steps under financial decision.
Financial risk is the main element in this decision. It means the risk of default on payment. There can be various reasons for the default including lower or no profit, increased cost, etc. To avoid this, it becomes important to properly analyze the sources of finance.
Funds can be raised from shareholders or debt (borrowed funds). Both have different kinds of benefits and limitations. Borrowed funds involve a fixed rate of interest and are to be repaid on time. Shareholders, on the other hand, involve committed to the payment and they can even take part in the management thus the control is diluted.
Another important financial management decision is the flotation cost, which is the cost involved in raising funds from a certain source of finance. It must be considered while the evaluation of the various sources available. Different sources involve different kinds of costs. Debt is considered the cheapest in terms of cost because of the tax deductibility.
Still, there are other factors also which are to be considered while taking a financial decision.
Factors affecting the financial decision
- Cost: all finance comes with some cost. No source of funds is free. These costs involved in the sources are to be carefully analyzed and a good financial manager will choose the cheapest source possible. For example source A involves the cost of Rs. 10 lakhs and source B involves the cost of Rs. 12 lakhs, keeping other things constant, source A should be chosen.
- Risk: risk is also inevitable. The risk associated with the owner’s fund is different and the risk associated with debt is different. These sources will be evaluated and then the source with the lowest financial risk will be selected.
- Flotation cost: raising the funds involves certain costs. This cost should be low because the higher the floatation cost, the less attractive the source becomes.
- Cash flow position of the business: cash flow position means the position of the firm where cash inflows and outflows are considered. The amount of cash held by the firm helps in determining the source of the fund.
- Level of fixed operating costs: if the company has higher fixed operating costs such as salaries, rent of the building, etc, then it must opt for lower debt financing because it will add up to the cost. In the same way, lower fixed operating costs will mean that the firm can take up funds from debt finance.
- Control considerations: taking up funds from the equity source means that the firm is allowing the shareholders to get involved in the management. This will dilute the control of the owners. If the company is afraid of takeovers then it must go for more debt than equity.
- State of capital markets: there are two states in a capital market. One is a bull period when the prices of stocks are rising and in that period more and more people are ready to invest and second, is a bear period, in which pessimism takes over and prices go down and thus becomes difficult for the firm to issue the shares.
Dividend decisions
The third important financial management decision is the dividend decision. It is a decision regarding the distribution of the profit. A financial manager decides how much amount is to be distributed to the shareholders and how much is to be retained back in the business. Retained earnings are very important for a business’s financial position. It affects financial decisions because a firm raises a fund from the available funds in the business. On the other hand, maximizing the shareholder’s wealth is equally important as it is the main aim of financial management.
There are various factors that affect the dividend decision of the firm.
Factors affecting the dividend decisions
- Earnings: when the company has a good amount of earnings including the current and past earnings then the dividend can be distributed easily because the dividend is mainly distributed from the earnings of the company.
- Stability of earnings: when a company has stable earnings, then it is in a position to declare the same amount of dividends as the past year or a higher amount of dividend if the earnings are higher. But, when the company has unstable earnings i.e. the company has earned a good amount of profit in one year and lower or no profit the next year, then it is not in a position to declare higher amounts of dividends.
- Stability of dividends: a company likes to stabilize its dividends. When the earnings are regularly going up then the company is in the position to declare more dividends but, when the company has higher earnings but they are temporary in nature and the earnings can go down the next year or in a few years then higher dividends cannot be declared as it would create a bad impression on the shareholders.
- Growth opportunities: when a company sees growth opportunities, then they tend to retain more and distribute fewer dividends as they would take up the opportunity with the help of retained earnings. Growth companies tend to save or retain more than non-growth companies.
- Shareholder preference: there are different kinds of shareholders. Some depend on dividends for their regular earnings and some would like a higher amount of dividends even if there are no dividends in some years. The company should keep in mind, the preference of the shareholders so that they remain satisfied.
- Cash flow position: when the company wants more cash in the company then it would choose to retain more and distribute less because distributing dividends involves a high amount of outflow of the cash.
- Taxation policy: dividend is free from tax for the shareholders but the tax is levied on the company. This may affect the choice of retaining and distribution of profit. When the tax levied is higher, then the company may choose to retain more. Similarly, when the tax rate is lower on dividends then the company would choose to distribute the dividends more.
- Stock market reaction: investors react positively or negatively based on the dividend offered to them. When they get higher dividends then they act positively and share prices may rise accordingly. Similarly, when the dividends declared are less, then the shareholders act negatively.
- Legal constraints: there are certain constraints put by the companies act for the benefit of shareholders and companies as well and these must be followed to avoid any legal chaos.
- Access to capital market: access to the capital market is a critical factor to consider. Some companies may have more access to the capital market for their growth and thus they would have less need to retain the profit. They can distribute more as dividends and on the other hand, smaller companies or the companies that have less access would retain more.
- Contractual constraints: there are some terms and conditions of different contracts which must be adhered to before distributing the dividend so that it does not violate any condition.
Financial management Class 12 is thus the process of managing the finance of the firm and it involves various decisions such as investment decisions, financial decisions, and dividend decisions, which are interrelated and must be taken carefully so that they do not affect the financial health of the company negatively. A company takes these decisions in the normal course of the business but may not always take these decisions in a sequence.
BST Chapter 9 – Financial Management
- Business Finance
- Objectives of Financial Management
- Financial Planning
- Financial decisions in Financial Management
- Capital Structure in Financial Management