Cash book: It is a book in which ONLY cash transactions of an organization are recorded hence credit-based transactions will not be recorded in cash book. Transactions are recorded in chronological order i.e. date wise. Cash Book is treated as both an Account and Ledger. Debit side or Left side of cash book records cash receipts and Credit side or right side of cash book records cash payments. Opening balance of the cash is written on the debit side of the cash book.
Types of Cash Book
There are three types of Cash Book
- Single Column Cash Book (Normal Cash Book)
- Double Column Cash Book
- Triple Column Cash Book
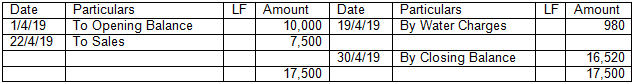
1. Single Cash Book:
It is a normal Cash Book / Account in which there is only one column of amount on each debit and credit side. Format is as below.
In the Books of ABC & Co.
Cash Account
2. Double Column Cash Book:
Double column cash book has two amount columns on each side.
Two column cash book has one column for cash amount but second column can be either bank column or discount amount column.
Double column Cash book with Bank Column
In the Books of ABC & Co.
Cash Account (Double Column)
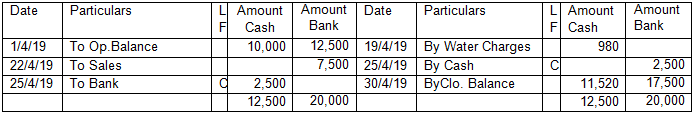
In this type of cash book, bank account is also maintained with cash book. Today lot of transactions are done with internet banking and money comes in directly in bank and goes directly from bank as well. Double column cash book along with bank column helps to keep the track of bank transactions. Entries in bank column are done in similar way i.e. when money is received in bank, it is recorded on debit side of cash book- bank column and when money is paid from the bank, it is recorded on credit side of the cash book- bank column.
See the illustration above. We can see that company did cash sales on 22/04/2019 and money was received in bank (internet banking/cheque/ direct deposit). So, it is entered on the debit side of the cash book but in bank column.
Similarly, cash was withdrawn from bank on 25/4/2019. Balance in the bank is reduced and balance of cash has increased. Here please note that money has not been paid to an outsider. These types of transactions are called Contra transaction.
Double column Cash book with Discount Column:
In the Books of ABC & Co.
Cash Account (Double Column)
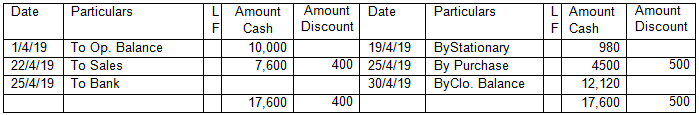
See carefully above cash book with discount column. This type of double column cash book is maintained when company is mainly dealing in cash. When company deals in cash, it can get cash discount from suppliers as well as it has to give cash discounts to its customers. When the discount column is placed next to the cash column, it becomes easy for an Accountant to track the discount received or given.
For e.g. on 22/4/2019, cash sales were made of Rs. 8,000 @ 5 % cash discount. Hence actual cash received for this sale is Rs. 7600 which is recorded on the debit side of the cash book in cash column and discount allowed of Rs. 400 to the customer is recorded next to the corresponding sale.
On 25/04/2019, cash purchases of Rs. 5,000 were made and availed discount of 10%. So, actual amount paid to the supplier was Rs. 4500 is recorded in the cash column on the credit side of the cash book and discount of Rs. 500 received on the purchase is recorded in the discount column.
In this type of cash book, it is not compulsory that discount column should be balanced. Discount column is there only for the sake of convenience to track the discount pertaining to a particular cash sale or cash purchase.
Triple Column Cash Book:
It is a combination of double column cash book with bank column and discount column. Hence, we can say that it gives benefit of referring all the transactions simultaneously i.e. cash, bank and discount received or allowed at the same time. Format of triple column cash book is as below:
In the Books of ABC & Co.
Cash Account (Triple Column)
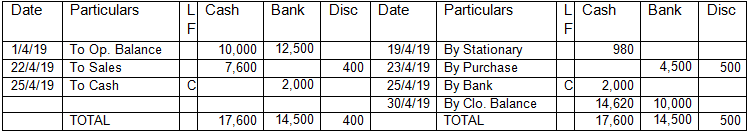
See in above example, all the three columns are appearing in the same account. It becomes easy to track the receipt and payments and contra transactions of the organization.
Petty Cash Book
Petty means small. In any office there are small expenses everyday like postage, staff expenses etc. Small amount of cash kept to cover small expenses. It is called Petty Cash. An accountant may keep come cash in his drawer and money will be given to other employees against receipt. Means if any employee spends his money for some office work, he/she must produce the receipt to get the reimbursement of the amount spend. For e.g. if a marketing person spends Rs. 100 on petrol which is used for office work, he must submit the petrol receipt to the accountant to get his Rs. 100 back.
Petty cash is recorded comes under current asset. Every month an accountant puts some fix amount in the petty cash box. That time below journal entry will be posted by him
Petty cash A/c Dr.
To Cash A/c Cr.
And when money is spent below journal entry is passed.
<Particular Expense A/c> Dr.
To Petty cash A/c Cr.
See the format of the Petty Cash A/c
In the books of Ravi & Sons
Petty Cash A/c
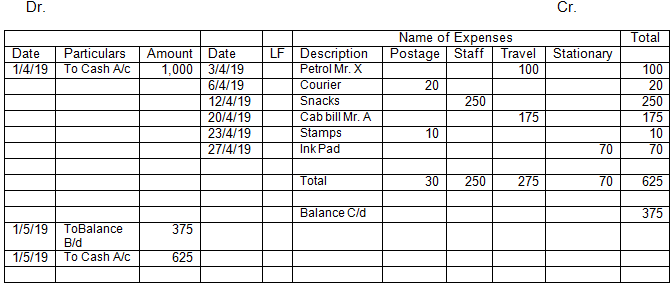
In above format, we can see that there are columns of the expenses on right side i.e. credit side of the Petty Cash A/c, which may change company to company depends what are their petty cash expenses. Throughout the month these expenses are recorded and at the end of the month petty cash is reconciled. On the 1st day of the next month, petty cash box is topped up with the amount in such a way that total amount does not exceed the maximum amount in the petty cash box which is agreed by the company. In above case it is Rs. 1,000.
This system is also called Imprest system of Petty cash.
Chapter 4 – Recording of Transactions Accountancy Class 11